正在加载图片...
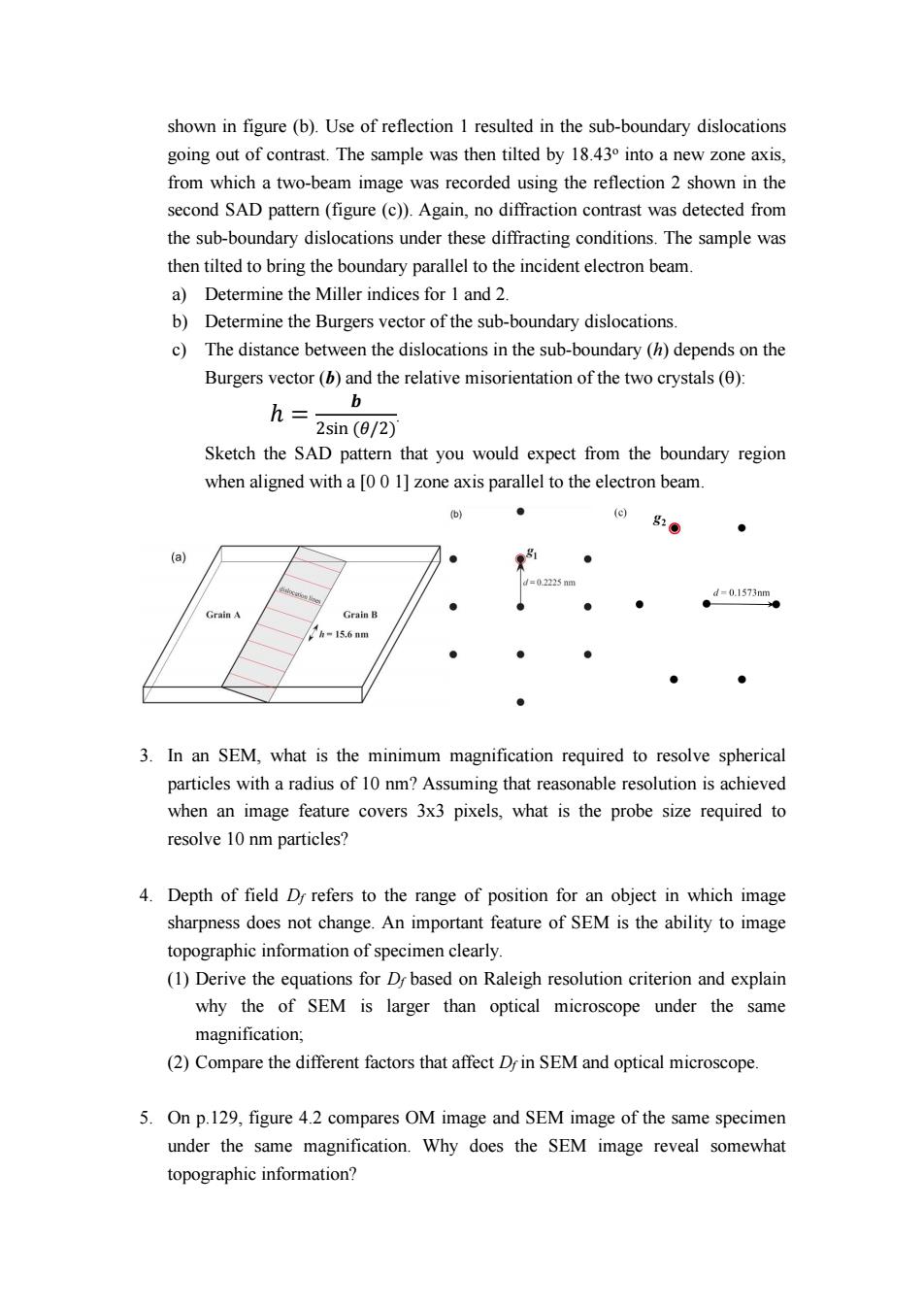
shown in figure(b).Use of reflection 1 resulted in the sub-boundary dislocations going out of contrast.The sample was then tilted by 18.430 into a new zone axis, from which a two-beam image was recorded using the reflection 2 shown in the second SAD pattern(figure(c)).Again,no diffraction contrast was detected from the sub-boundary dislocations under these diffracting conditions.The sample was then tilted to bring the boundary parallel to the incident electron beam. a)Determine the Miller indices for 1 and 2. b)Determine the Burgers vector of the sub-boundary dislocations. c)The distance between the dislocations in the sub-boundary (h)depends on the Burgers vector(b)and the relative misorientation of the two crystals(0): h= b 2sin(0/2) Sketch the SAD pattern that you would expect from the boundary region when aligned with a [00 1]zone axis parallel to the electron beam. (b) ● ⊙g20 ● (a) =02225nm d=0.1573nm Grain A Grain B 1h-15.6nm ● 3.In an SEM,what is the minimum magnification required to resolve spherical particles with a radius of 10 nm?Assuming that reasonable resolution is achieved when an image feature covers 3x3 pixels,what is the probe size required to resolve 10 nm particles? 4.Depth of field D refers to the range of position for an object in which image sharpness does not change.An important feature of SEM is the ability to image topographic information of specimen clearly. (1)Derive the equations for Dy based on Raleigh resolution criterion and explain why the of SEM is larger than optical microscope under the same magnification; (2)Compare the different factors that affect D in SEM and optical microscope. 5.On p.129,figure 4.2 compares OM image and SEM image of the same specimen under the same magnification.Why does the SEM image reveal somewhat topographic information?shown in figure (b). Use of reflection 1 resulted in the sub-boundary dislocations going out of contrast. The sample was then tilted by 18.43 o into a new zone axis, from which a two-beam image was recorded using the reflection 2 shown in the second SAD pattern (figure (c)). Again, no diffraction contrast was detected from the sub-boundary dislocations under these diffracting conditions. The sample was then tilted to bring the boundary parallel to the incident electron beam. a) Determine the Miller indices for 1 and 2. b) Determine the Burgers vector of the sub-boundary dislocations. c) The distance between the dislocations in the sub-boundary (h) depends on the Burgers vector (b) and the relative misorientation of the two crystals (): = sin h . Sketch the SAD pattern that you would expect from the boundary region when aligned with a [0 0 1] zone axis parallel to the electron beam. 3. In an SEM, what is the minimum magnification required to resolve spherical particles with a radius of 10 nm? Assuming that reasonable resolution is achieved when an image feature covers 3x3 pixels, what is the probe size required to resolve 10 nm particles? 4. Depth of field Df refers to the range of position for an object in which image sharpness does not change. An important feature of SEM is the ability to image topographic information of specimen clearly. (1) Derive the equations for Df based on Raleigh resolution criterion and explain why the of SEM is larger than optical microscope under the same magnification; (2) Compare the different factors that affect Df in SEM and optical microscope. 5. On p.129, figure 4.2 compares OM image and SEM image of the same specimen under the same magnification. Why does the SEM image reveal somewhat topographic information?