正在加载图片...
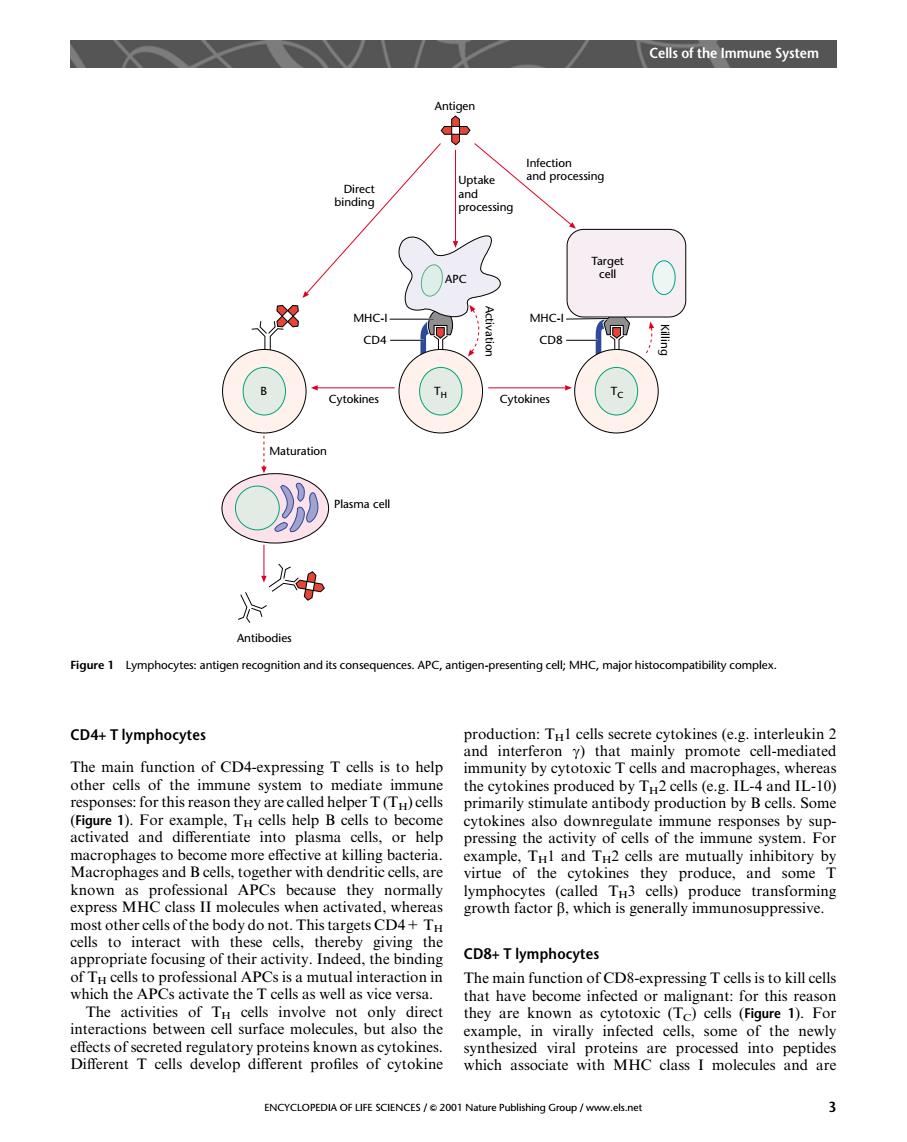
Cells of the Immune System Uptake processin MHC-I. CD8- ytokines ma cel Antibodies Figure 1 Lymphocytes:antigen recognition and its consequences.APC,antigen-presenting cell:MHC,major histocompatibility complex. CD4+T lymphocytes The main function of CD4-expressing T cells is to help other cells of the immune system to mediate immune oduced by Tu2 cells (e.g.IL-4 and IL-10) responses:for this reason they are called helper T(TH)cells primarily stimulate antibody production by B cells.Some elp B cells to become cytokines also downregul e immune responses by sup- press nha at killins.or Macrand Betterthendir own as professional APCs because they normally lymphocytes (called TH3 cells)produce transforming ules when activat growth factor B.which is generally immunosuppressive. her cell act with t appropriate focusing of their activity.Indeedthe bnding CD&+T lymphocytes The main function of CD8-expressing T cells is to kill cells vers cted effects of secreted regulatory proteins known as cytokines. somed into Different T cells develop different profiles of cytokine which associate with MHC classI molccules and are ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LFE CENCES/001 Nature Publishing Group/www.esnetCD4+ T lymphocytes The main function of CD4-expressing T cells is to help other cells of the immune system to mediate immune responses: for this reason they are called helper T (TH) cells (Figure 1). For example, TH cells help B cells to become activated and differentiate into plasma cells, or help macrophages to become more effective at killing bacteria. Macrophages and B cells, together with dendritic cells, are known as professional APCs because they normally express MHC class II molecules when activated, whereas most other cells of the body do not. This targets CD4+ TH cells to interact with these cells, thereby giving the appropriate focusing of their activity. Indeed, the binding of TH cells to professional APCs is a mutual interaction in which the APCs activate the T cells as well as vice versa. The activities of TH cells involve not only direct interactions between cell surface molecules, but also the effects of secreted regulatory proteins known as cytokines. Different T cells develop different profiles of cytokine production: TH1 cells secrete cytokines (e.g. interleukin 2 and interferon g) that mainly promote cell-mediated immunity by cytotoxic T cells and macrophages, whereas the cytokines produced by TH2 cells (e.g. IL-4 and IL-10) primarily stimulate antibody production by B cells. Some cytokines also downregulate immune responses by suppressing the activity of cells of the immune system. For example, TH1 and TH2 cells are mutually inhibitory by virtue of the cytokines they produce, and some T lymphocytes (called TH3 cells) produce transforming growth factor b, which is generally immunosuppressive. CD8+ T lymphocytes The main function of CD8-expressing T cells is to kill cells that have become infected or malignant: for this reason they are known as cytotoxic (TC) cells (Figure 1). For example, in virally infected cells, some of the newly synthesized viral proteins are processed into peptides which associate with MHC class I molecules and are Killing B Cytokines Maturation Plasma cell Antibodies TH MHC-I CD4 APC Activation Cytokines TC MHC-I CD8 Target cell Uptake and processing Infection and processing Antigen Direct binding Figure 1 Lymphocytes: antigen recognition and its consequences. APC, antigen-presenting cell; MHC, major histocompatibility complex. Cells of the Immune System ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 3