正在加载图片...
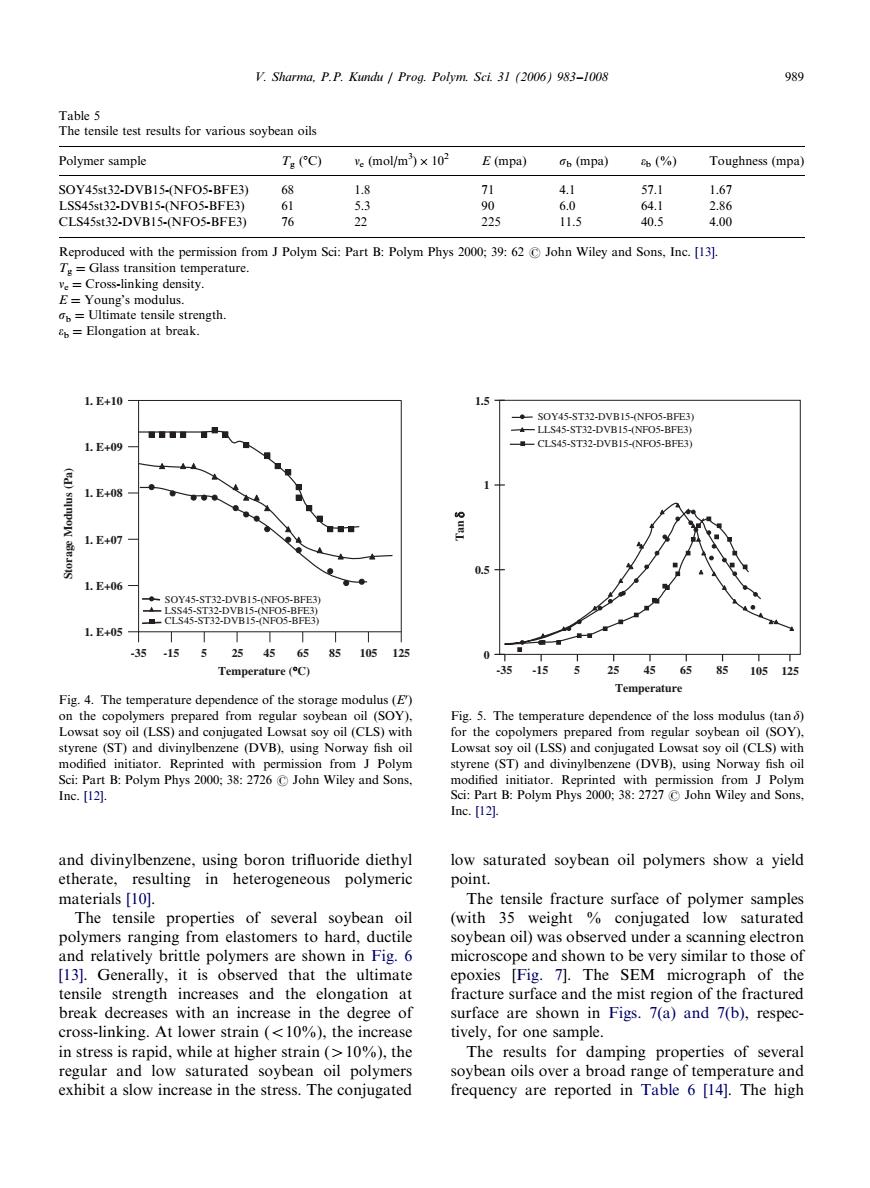
V.Sharma.P.P.Kundu Prog.Polym.Scl.31(2006)983-100 989 Polymer sample 7(g(molm×102 E(mpa)(mpa)(%)Toughness (mpa) 53 CLS45st32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 225 40.5 Reproduced with the permision from Polym Sci:Part B:Polym 62John Wiley and Sons,Ine.[ 1.E+10- SOY45-ST32-DVBIS-(NFO5-BFE 1.E+09 CLS45-ST32-DVBIS-(NFOS-BFES 1E+08 1 L.E40 05 1.E+06 土然電 1.E+05 1 125 are (C) 35155254565510s125 Temperature Fig.4.The temperature dependence of the storage modulus (E) regular soybean oil (SOY) enzene (DVB).using vay fis () Inc.[12. and divinylbenzene,using boron trifluoride diethyl low saturated soybean oil polymers show a yield etherate,resulting in heterogeneous polymeric point. materials [10]. The tensile fracture surface of polymer samples The tensile properties of several soybean oil (with 35 weight conjugated low saturated stomers har soybean oil)was observe d under a se polymers ope and n very similar SEM r the tensile strength fracture surface nd the mist fracture hreak decreases with an increase in the degree of surface are shown in Figs.7(a)and 7(b),respec cross-linking.At lower strain(<10%),the increase tively.for one sample. in stress is rapid,while at higher strain(0%),the The results for damping properties of several regular and low saturated soybean oil polymers soybean oils over a broad range of temperature and exhibit a slow increase in the stress.The conjugated frequency are reported in Table 6 [14].The high and divinylbenzene, using boron trifluoride diethyl etherate, resulting in heterogeneous polymeric materials [10]. The tensile properties of several soybean oil polymers ranging from elastomers to hard, ductile and relatively brittle polymers are shown in Fig. 6 [13]. Generally, it is observed that the ultimate tensile strength increases and the elongation at break decreases with an increase in the degree of cross-linking. At lower strain (o10%), the increase in stress is rapid, while at higher strain (410%), the regular and low saturated soybean oil polymers exhibit a slow increase in the stress. The conjugated low saturated soybean oil polymers show a yield point. The tensile fracture surface of polymer samples (with 35 weight % conjugated low saturated soybean oil) was observed under a scanning electron microscope and shown to be very similar to those of epoxies [Fig. 7]. The SEM micrograph of the fracture surface and the mist region of the fractured surface are shown in Figs. 7(a) and 7(b), respectively, for one sample. The results for damping properties of several soybean oils over a broad range of temperature and frequency are reported in Table 6 [14]. The high ARTICLE IN PRESS Table 5 The tensile test results for various soybean oils Polymer sample Tg (1C) ne (mol/m3 ) 102 E (mpa) sb (mpa) eb (%) Toughness (mpa) SOY45st32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 68 1.8 71 4.1 57.1 1.67 LSS45st32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 61 5.3 90 6.0 64.1 2.86 CLS45st32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 76 22 225 11.5 40.5 4.00 Reproduced with the permission from J Polym Sci: Part B: Polym Phys 2000; 39: 62 r John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [13]. Tg ¼ Glass transition temperature. ne ¼ Cross-linking density. E ¼ Young’s modulus. sb ¼ Ultimate tensile strength. eb ¼ Elongation at break. SOY45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) LSS45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) CLS45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) Temperature (°C) 1. E+10 1. E+09 1. E+08 1. E+07 1. E+06 1. E+05 Storage Modulus (Pa) -35 -15 5 25 45 85 105 12 65 5 Fig. 4. The temperature dependence of the storage modulus (E0 ) on the copolymers prepared from regular soybean oil (SOY), Lowsat soy oil (LSS) and conjugated Lowsat soy oil (CLS) with styrene (ST) and divinylbenzene (DVB), using Norway fish oil modified initiator. Reprinted with permission from J Polym Sci: Part B: Polym Phys 2000; 38: 2726 r John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [12]. -35 -15 5 25 45 85 105 125 Temperature Tan δ SOY45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 0 0.5 1 1.5 CLS45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) LLS45-ST32-DVB15-(NFO5-BFE3) 65 Fig. 5. The temperature dependence of the loss modulus (tan d) for the copolymers prepared from regular soybean oil (SOY), Lowsat soy oil (LSS) and conjugated Lowsat soy oil (CLS) with styrene (ST) and divinylbenzene (DVB), using Norway fish oil modified initiator. Reprinted with permission from J Polym Sci: Part B: Polym Phys 2000; 38: 2727 r John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [12]. V. Sharma, P.P. Kundu / Prog. Polym. Sci. 31 (2006) 983–1008 989�