正在加载图片...
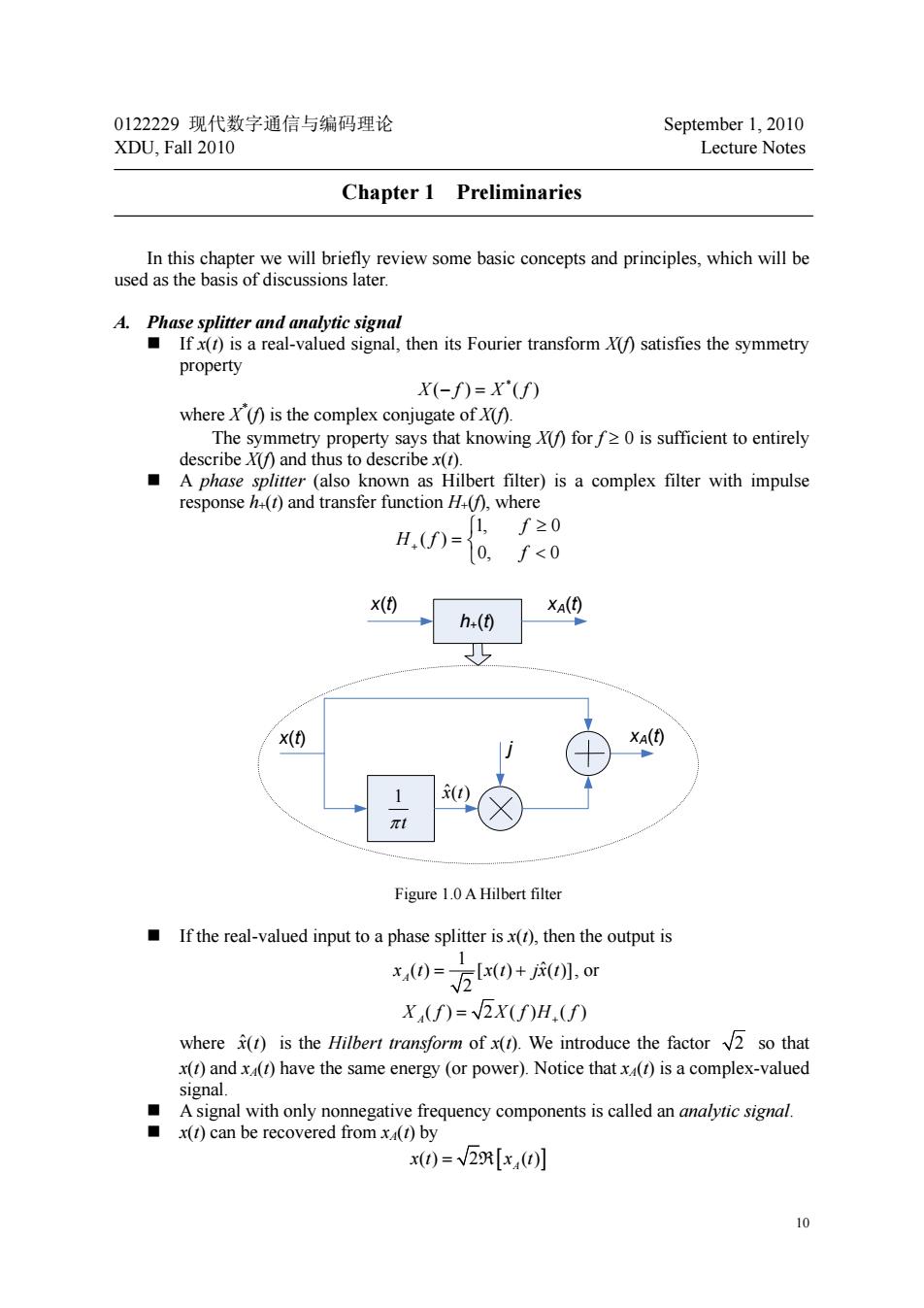
0122229现代数字通信与编码理论 September 1,2010 XDU Fall 2010 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Preliminaries In this chapter we will briefly review some basic concepts and principles,which will be used as the basis of discussions later. A.Phase splitter and analytic signal Ifx(t)is a real-valued signal,then its Fourier transform X()satisfies the symmetry property X(-f)=X'(f) where is the complex conjugate of ) ■A phase] also kno wn as Hilbert filter)is a complex filter with impulse response()and transfer function.where f≥0 10,f<0 h-(0 XA() x(t) 40 Figure 1.0A Hilbert filter If the real-valued input to a phase splitter isx(),then the output is x,0=方0+0.or X,(f)=2x(f)H.(f) where()is the Hilbert transform of x(t).We introduce the factor 2 so that x(t)andx(r)have the same energy (or power).Notice thatx(r)is a complex-valued signal. Asignal with only nonnegative frequency components is called an analytic signal. x(t)can be recovered from x(t)by x()=x] 1010 0122229 现代数字通信与编码理论 September 1, 2010 XDU, Fall 2010 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Preliminaries In this chapter we will briefly review some basic concepts and principles, which will be used as the basis of discussions later. A. Phase splitter and analytic signal If x(t) is a real-valued signal, then its Fourier transform X(f) satisfies the symmetry property * X ( ) () − = f Xf where X* (f) is the complex conjugate of X(f). The symmetry property says that knowing X(f) for f ≥ 0 is sufficient to entirely describe X(f) and thus to describe x(t). A phase splitter (also known as Hilbert filter) is a complex filter with impulse response h+(t) and transfer function H+(f), where ⎩ ⎨ ⎧ < ≥ + = 0, 0 1, 0 ( ) f f H f h+(t) x(t) xA(t) x(t) xA(t) 1 πt j xˆ( )t Figure 1.0 A Hilbert filter If the real-valued input to a phase splitter is x(t), then the output is 1 ( ) [ ( ) ( )] ˆ 2 A x t x t jx t = + , or () 2 () () X A f XfH f = + where xˆ( )t is the Hilbert transform of x(t). We introduce the factor 2 so that x(t) and xA(t) have the same energy (or power). Notice that xA(t) is a complex-valued signal. A signal with only nonnegative frequency components is called an analytic signal. x(t) can be recovered from xA(t) by x() 2 () t xt = R[ A ]