正在加载图片...
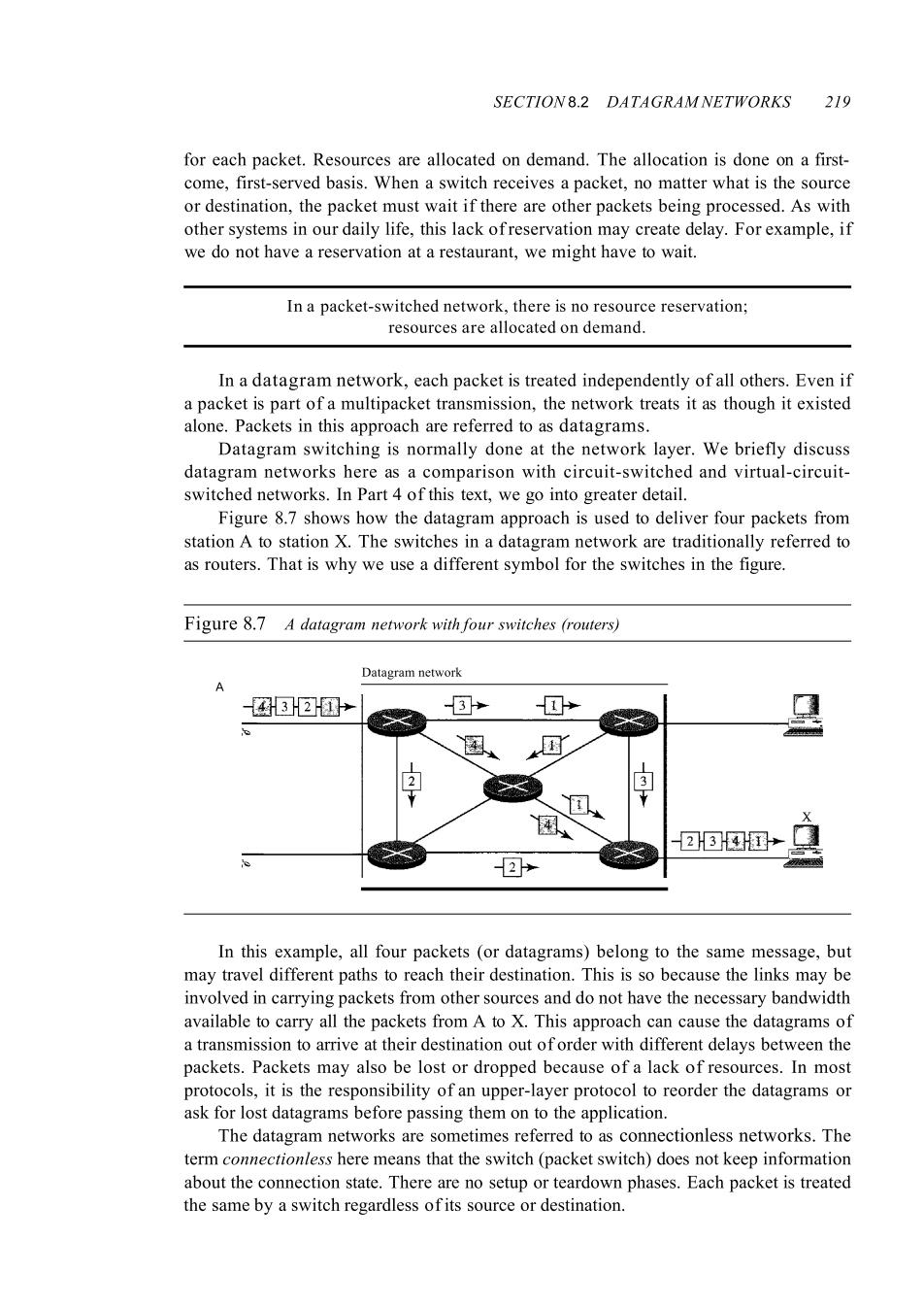
SECTION8.2 DATAGRAMNETWORKS 219 for each packet.Resources are allocated on demand.The allocation is done on a first- come,first-served basis.When a switch receives a packet,no matter what is the source or destination,the packet must wait if there are other packets being processed.As with other systems in our daily life,this lack ofreservation may create delay.For example,if we do not have a reservation at a restaurant,we might have to wait. In a packet-switched network,there is no resource reservation; resources are allocated on demand. In a datagram network,each packet is treated independently of all others.Even if a packet is part of a multipacket transmission,the network treats it as though it existed alone.Packets in this approach are referred to as datagrams. Datagram switching is normally done at the network layer.We briefly discuss datagram networks here as a comparison with circuit-switched and virtual-circuit- switched networks.In Part 4 of this text,we go into greater detail. Figure 8.7 shows how the datagram approach is used to deliver four packets from station A to station X.The switches in a datagram network are traditionally referred to as routers.That is why we use a different symbol for the switches in the figure. Figure 8.7 A datagram network with four switches (routers) Datagram network 32团 3 2 2341 2 In this example,all four packets (or datagrams)belong to the same message,but may travel different paths to reach their destination.This is so because the links may be involved in carrying packets from other sources and do not have the necessary bandwidth available to carry all the packets from A to X.This approach can cause the datagrams of a transmission to arrive at their destination out oforder with different delays between the packets.Packets may also be lost or dropped because of a lack of resources.In most protocols,it is the responsibility of an upper-layer protocol to reorder the datagrams or ask for lost datagrams before passing them on to the application. The datagram networks are sometimes referred to as connectionless networks.The term connectionless here means that the switch (packet switch)does not keep information about the connection state.There are no setup or teardown phases.Each packet is treated the same by a switch regardless ofits source or destination.
!"!##
$%$&%$ '##
(%(!$%%(!
) &*(!
)!+$,!(! -%!.(
(+!
*%&
.
(!
!" $!
(%
(%*
&"!
.(
(
!,(%/
!!$ 0!.(
!1!
&!(%"$(#1#(*
(!#
!+
(%&1
$#1 23&
#*( .$%
+!+
(%
!
"%
*.&(/
+
.(
4%
)!.(
$%
.
*
(!%!"!+
(%5 !"!##
$%$&%$ 4%$
/&%
.
*
(!
$(%$
%$%
#1##
! 6+%(
(!
&"#
(
%!&(!!(%*
%
.
!(
!
"/(
3(!
$ #% 7
!(%
(!
$
!$
/&! 8
/&!.(
(%/(!%&##1$%
%
.
#1 -,(#1$(!"!! $
/&%
.
!!&
(!%.(
("(
)!.(
$%$+(
"#)("(
) !.(
$%
.
! 4%7
9
(!
3
*./(%
/
$
(# 2(/": ;!.!.
$
/&
(!"!$
$#(+"
!& !
(%0
!
(%< '!.(
!(%$
/&%
.
$(
(%##1$
!"
! '
(!.1."!$(%
!1&,#
!.(
!(%
(/" 2(/": ;
=>?>@A>BCD?EFAGEH?IJFKALEH?MIDLNAFK?DALO 8
/&%
.
P 4%
(!3&
#*##"
!Q$
/&!R,#%/
!&&!!/*,"
&1
+#$(%
!
($!
(%
(% '(!(!!,"!
#(%
!&1, (%+#+$(%1(%/
!&
!"!%$$%
+
%!!1,%$.($
+(#,#
1##
!&0
< '(!
%"!
$
/&!
%!&(!!(%
(+
($!
(%
(%"
$.(
$(%
$#1!,
.%
! 7
!&1#!,#!
$
$,"!#
!"! 4%&!
#!*(
(!
!
%!(,(#(
1%"
)#1
#
$
$
/&! !
#!
$
/&!,
!!(%/
&%
#(
(% '$
/&%
.
!!&
(&!$
!%%
(%#!!%
.
! '
&MFCCDM?HFCSDLL&%!
!.(
Q
!.(
R$!%
(%&
(% ,"
%%
(%!
'%!
"
$.%
!! 6
(!
$
!&,1!.(
/$#!!(
!!"$!
(%
(% ���