正在加载图片...
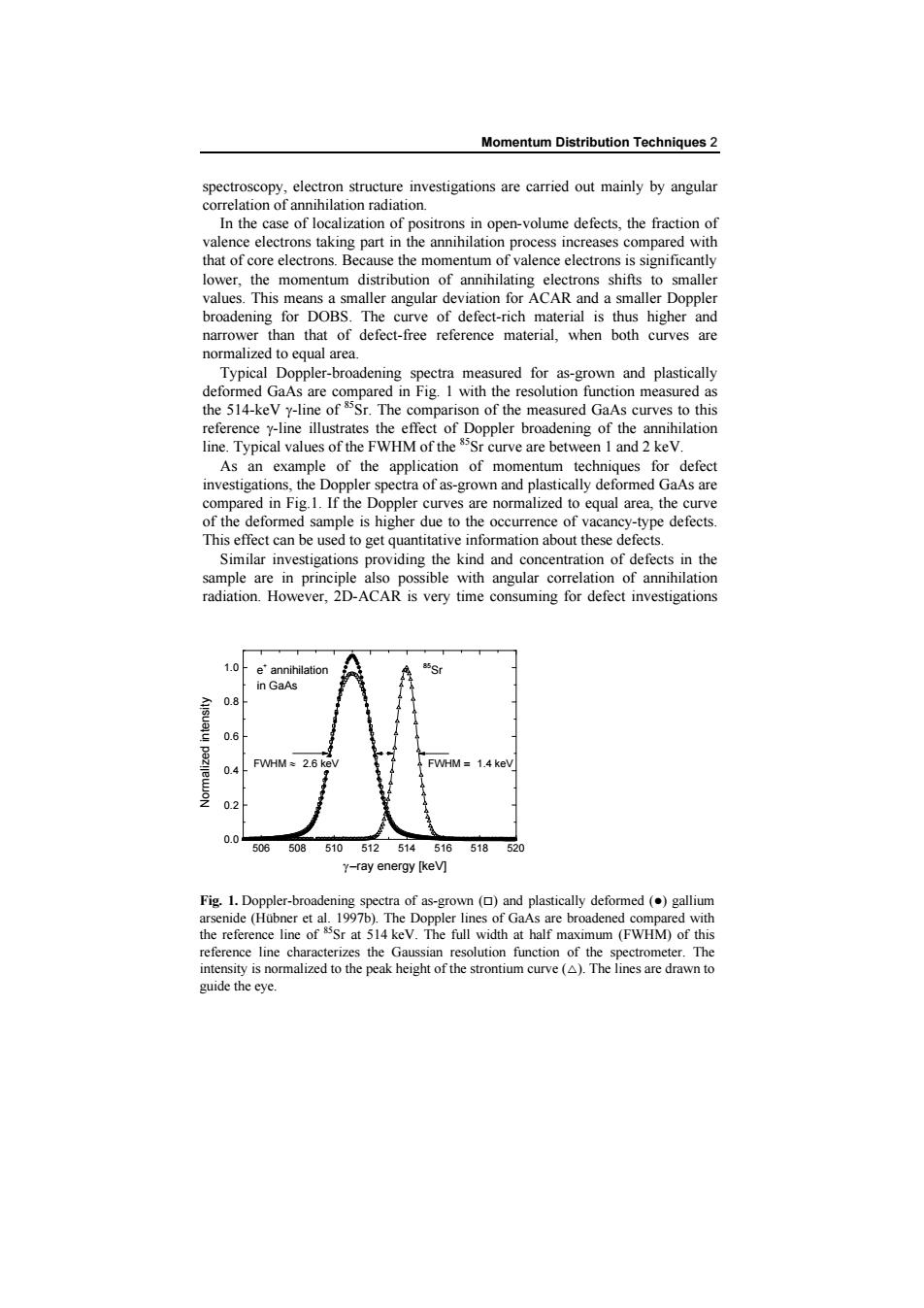
Momentum Distribution Techniques 2 spectroscopy,electron structure investigations are carried out mainly by angular correlation of annihilation radiation In the case of localization of positrons in open-volume defects,the fraction of valence electrons taking part in the annihilation process increases compared with that of core electrons.Because the momentum of valence electrons is significantly lower,the momentum distribution of annihilating electrons shifts to smaller values.This means a smaller angular deviation for ACAR and a smaller Doppler broadening for DOBS.The curve of defect-rich material is thus higher and narrower than that of defect-free reference material,when both curves are normalized to equal area. Typical Doppler-broadening spectra measured for as-grown and plastically deformed GaAs are compared in Fig.I with the resolution function measured as the 514-keV y-line of &Sr.The comparison of the measured GaAs curves to this reference y-line illustrates the effect of Doppler broadening of the annihilation line.Typical values of the FWHM of the $5Sr curve are between 1 and 2 keV. As an example of the application of momentum techniques for defect investigations,the Doppler spectra of as-grown and plastically deformed GaAs are compared in Fig.1.If the Doppler curves are normalized to equal area,the curve of the deformed sample is higher due to the occurrence of vacancy-type defects. This effect can be used to get quantitative information about these defects. Similar investigations providing the kind and concentration of defects in the sample are in principle also possible with angular correlation of annihilation radiation.However,2D-ACAR is very time consuming for defect investigations 1.0 e annihilation 85S in GaAs 0.8 0.6 FWHM=2.6 keV FWHM=14 kev 0.4 0.2 0.0 506 508 510 512514 516 518 520 y-ray energy [kev] Fig.1.Doppler-broadening spectra of as-grown (and plastically deformed ()gallium arsenide (Hubner et al.1997b).The Doppler lines of GaAs are broadened compared with the reference line of Sr at 514 keV.The full width at half maximum (FWHM)of this reference line characterizes the Gaussian resolution function of the spectrometer.The intensity is normalized to the peak height of the strontium curve (A).The lines are drawn to guide the eye.Momentum Distribution Techniques 2 spectroscopy, electron structure investigations are carried out mainly by angular correlation of annihilation radiation. In the case of localization of positrons in open-volume defects, the fraction of valence electrons taking part in the annihilation process increases compared with that of core electrons. Because the momentum of valence electrons is significantly lower, the momentum distribution of annihilating electrons shifts to smaller values. This means a smaller angular deviation for ACAR and a smaller Doppler broadening for DOBS. The curve of defect-rich material is thus higher and narrower than that of defect-free reference material, when both curves are normalized to equal area. Typical Doppler-broadening spectra measured for as-grown and plastically deformed GaAs are compared in Fig. 1 with the resolution function measured as the 514-keV g-line of 85Sr. The comparison of the measured GaAs curves to this reference g-line illustrates the effect of Doppler broadening of the annihilation line. Typical values of the FWHM of the 85Sr curve are between 1 and 2 keV. As an example of the application of momentum techniques for defect investigations, the Doppler spectra of as-grown and plastically deformed GaAs are compared in Fig.1. If the Doppler curves are normalized to equal area, the curve of the deformed sample is higher due to the occurrence of vacancy-type defects. This effect can be used to get quantitative information about these defects. Similar investigations providing the kind and concentration of defects in the sample are in principle also possible with angular correlation of annihilation radiation. However, 2D-ACAR is very time consuming for defect investigations 506 508 510 512 514 516 518 520 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 e + annihilation in GaAs FWHM » 2.6 keV 85Sr FWHM = 1.4 keV Normalized intensity g–ray energy [keV] Fig. 1. Doppler-broadening spectra of as-grown (®) and plastically deformed (l) gallium arsenide (Hübner et al. 1997b). The Doppler lines of GaAs are broadened compared with the reference line of 85Sr at 514 keV. The full width at half maximum (FWHM) of this reference line characterizes the Gaussian resolution function of the spectrometer. The intensity is normalized to the peak height of the strontium curve (r). The lines are drawn to guide the eye