正在加载图片...
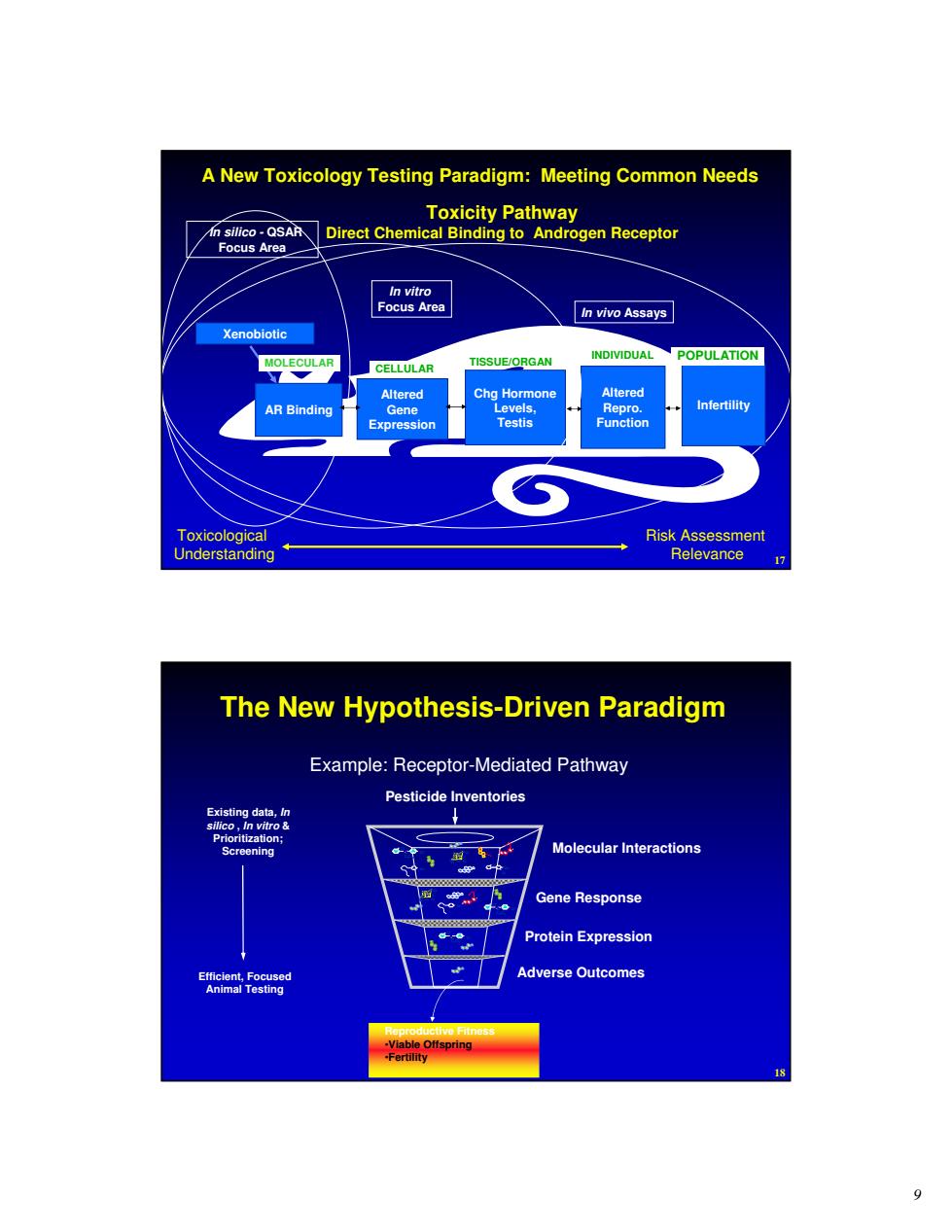
A New Toxicology Testing Paradigm:Meeting Common Needs Toxicity Pathway silco-QSAR Direct Chemical Bir ng to An gen Receptor Js Area In vivo Assays (enobiotic CELLULAR TISSUE/ORGAN POPULATION AR Binding xpression Risk Assessment Relevance The New Hypothesis-Driven Paradigm Example:Receptor-Mediated Pathway Pesticide Inventories Molecular Interactions Gene Response Protein Expression Adverse Outcomes9 17 In silico - QSAR Focus Area Xenobiotic AR Binding Altered Gene Expression Chg Hormone Levels, Testis Altered Repro. Function Toxicological Understanding Risk Assessment Relevance In vivo Assays In vitro Focus Area MOLECULAR CELLULAR TISSUE/ORGAN INDIVIDUAL Infertility POPULATION Toxicity Pathway Direct Chemical Binding to Androgen Receptor A New Toxicology Testing Paradigm: Meeting Common Needs 18 Reproductive Fitness •Viable Offspring •Fertility Molecular Interactions Gene Response Protein Expression Pesticide Inventories C2Cl3 Cl C Cl C2Cl3 Cl C Cl C2Cl3 Cl C Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl C l Cl Cl C l Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl C l Cl Cl C l Cl Cl OH OH OH The New Hypothesis-Driven Paradigm Existing data, In silico , In vitro & Prioritization; Screening Example: Receptor-Mediated Pathway Efficient, Focused Adverse Outcomes Animal Testing