正在加载图片...
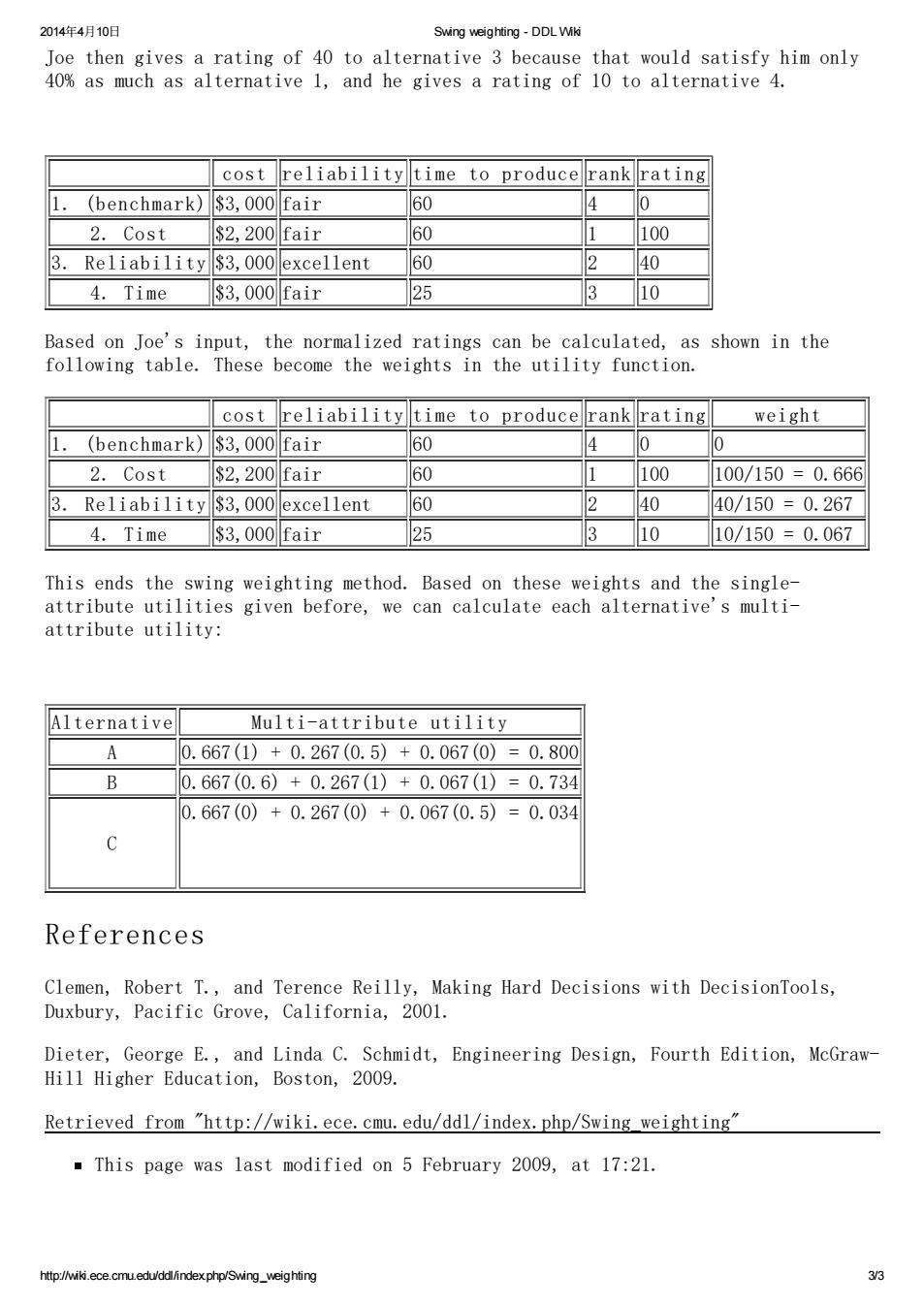
2014年4月10日 Swing weighting-DDL Wiki Joe then gives a rating of 40 to alternative 3 because that would satisfy him only 40%as much as alternative 1,and he gives a rating of 10 to alternative 4. cost reliability time to producel rankrating (benchmark) $3,000fair 60 4 0 2.Cost $2,200fair 60 1 100 3. Reliability $3,000excellent 60 2 40 4.Time $3,000fair 25 3 10 Based on Joe's input,the normalized ratings can be calculated,as shown in the following table.These become the weights in the utility function. cost reliability time to producerankrating weight (benchmark) $3,000fair 60 4 0 2.Cost $2,200fair 60 1 100 100/150=0.666 3.Reliability $3,000excellent 60 2 40 40/150=0.267 4.Time $3,000fair 25 3 10 10/150=0.067 This ends the swing weighting method.Based on these weights and the single- attribute utilities given before,we can calculate each alternative's multi- attribute utility: Iternative Multi-attribute utility A 0.667(1)+0.267(0.5)+0.067(0)=0.800 B 0.667(0.6)+0.267(1)+0.067(1)=0.734 0.667(0)+0.267(0)+0.067(0.5)=0.034 References Clemen,Robert T.,and Terence Reilly,Making Hard Decisions with DecisionTools, Duxbury,Pacific Grove,California,2001. Dieter,George E.,and Linda C.Schmidt,Engineering Design,Fourth Edition,McGraw- Hill Higher Education,Boston,2009. Retrieved from "http://wiki.ece.cmu.edu/ddl/index.php/Swing weighting" This page was last modified on 5 February 2009,at 17:21. http://wiki.ece.cmu.edu/ddl/indexphp/Swing_weighting 332014年4月10日 Swing weighting - DDL Wiki http://wiki.ece.cmu.edu/ddl/index.php/Swing_weighting 3/3 Joe then gives a rating of 40 to alternative 3 because that would satisfy him only 40% as much as alternative 1, and he gives a rating of 10 to alternative 4. cost reliability time to produce rank rating 1. (benchmark) $3,000 fair 60 4 0 2. Cost $2,200 fair 60 1 100 3. Reliability $3,000 excellent 60 2 40 4. Time $3,000 fair 25 3 10 Based on Joe's input, the normalized ratings can be calculated, as shown in the following table. These become the weights in the utility function. cost reliability time to produce rank rating weight 1. (benchmark) $3,000 fair 60 4 0 0 2. Cost $2,200 fair 60 1 100 100/150 = 0.666 3. Reliability $3,000 excellent 60 2 40 40/150 = 0.267 4. Time $3,000 fair 25 3 10 10/150 = 0.067 This ends the swing weighting method. Based on these weights and the singleattribute utilities given before, we can calculate each alternative's multiattribute utility: Alternative Multi-attribute utility A 0.667(1) + 0.267(0.5) + 0.067(0) = 0.800 B 0.667(0.6) + 0.267(1) + 0.067(1) = 0.734 C 0.667(0) + 0.267(0) + 0.067(0.5) = 0.034 References Clemen, Robert T., and Terence Reilly, Making Hard Decisions with DecisionTools, Duxbury, Pacific Grove, California, 2001. Dieter, George E., and Linda C. Schmidt, Engineering Design, Fourth Edition, McGrawHill Higher Education, Boston, 2009. Retrieved from "http://wiki.ece.cmu.edu/ddl/index.php/Swing_weighting" This page was last modified on 5 February 2009, at 17:21