正在加载图片...
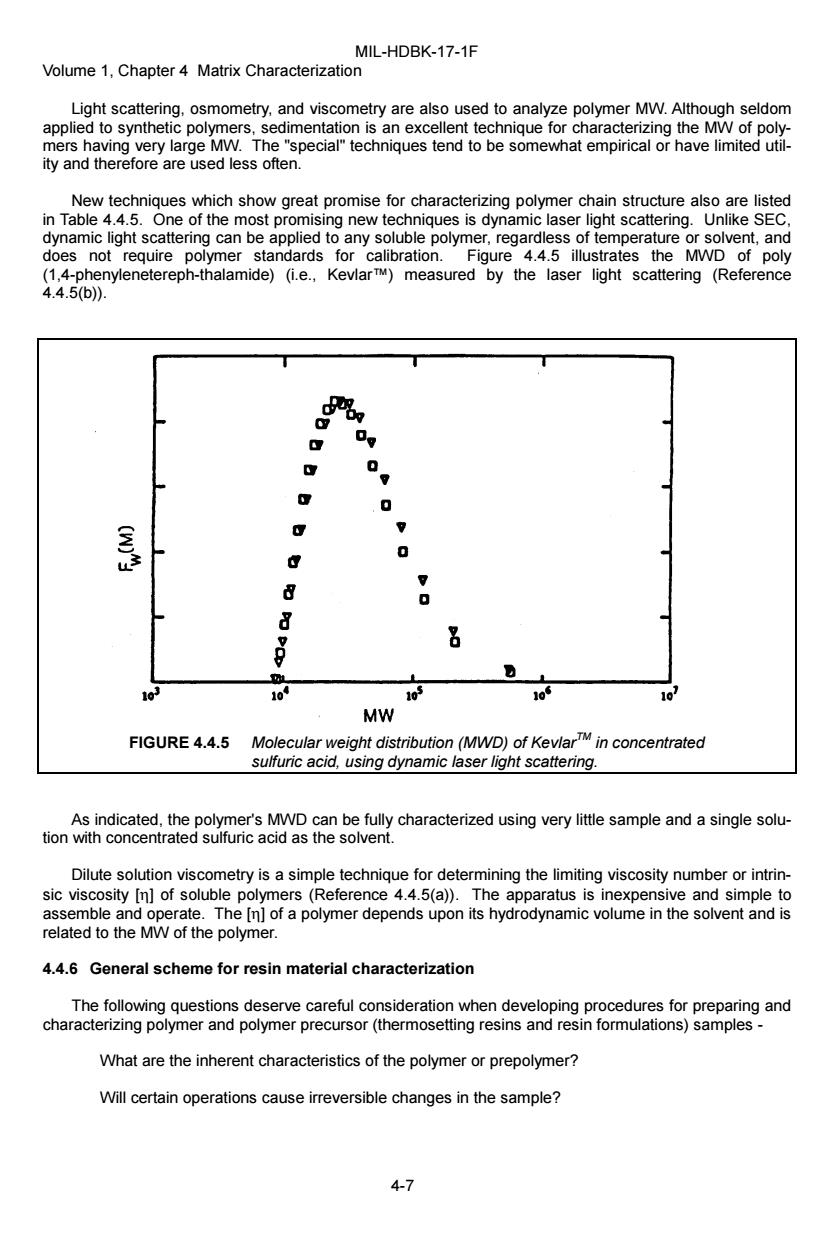
MIL-HDBK-17-1F Volume 1,Chapter 4 Matrix Characterization Light scattering,osmometry,and viscometry are also used to analyze polymer MW.Although seldom applied to synthetic polymers,sedimentation is an excellent technique for characterizing the MW of poly- mers having very large MW.The "special"techniques tend to be somewhat empirical or have limited util- ity and therefore are used less often. New techniques which show great promise for characterizing polymer chain structure also are listed in Table 4.4.5.One of the most promising new techniques is dynamic laser light scattering.Unlike SEC. dynamic light scattering can be applied to any soluble polymer,regardless of temperature or solvent,and does not require polymer standards for calibration.Figure 4.4.5 illustrates the MWD of poly (1,4-phenylenetereph-thalamide)(i.e.,KevlarTM)measured by the laser light scattering (Reference 4.4.5(b). 0 g , g 0 盖 0 ⊙ 7 8 0 8 g 0 10 10 MW FIGURE 4.4.5 Molecular weight distribution(MWD)of KevlarTM in concentrated sulfuric acid,using dynamic laser light scattering. As indicated,the polymer's MWD can be fully characterized using very little sample and a single solu- tion with concentrated sulfuric acid as the solvent. Dilute solution viscometry is a simple technique for determining the limiting viscosity number or intrin- sic viscosity [n]of soluble polymers (Reference 4.4.5(a)).The apparatus is inexpensive and simple to assemble and operate.The [n]of a polymer depends upon its hydrodynamic volume in the solvent and is related to the MW of the polymer. 4.4.6 General scheme for resin material characterization The following questions deserve careful consideration when developing procedures for preparing and characterizing polymer and polymer precursor(thermosetting resins and resin formulations)samples- What are the inherent characteristics of the polymer or prepolymer? Will certain operations cause irreversible changes in the sample? 4-7MIL-HDBK-17-1F Volume 1, Chapter 4 Matrix Characterization 4-7 Light scattering, osmometry, and viscometry are also used to analyze polymer MW. Although seldom applied to synthetic polymers, sedimentation is an excellent technique for characterizing the MW of polymers having very large MW. The "special" techniques tend to be somewhat empirical or have limited utility and therefore are used less often. New techniques which show great promise for characterizing polymer chain structure also are listed in Table 4.4.5. One of the most promising new techniques is dynamic laser light scattering. Unlike SEC, dynamic light scattering can be applied to any soluble polymer, regardless of temperature or solvent, and does not require polymer standards for calibration. Figure 4.4.5 illustrates the MWD of poly (1,4-phenylenetereph-thalamide) (i.e., Kevlar™) measured by the laser light scattering (Reference 4.4.5(b)). FIGURE 4.4.5 Molecular weight distribution (MWD) of KevlarTM in concentrated sulfuric acid, using dynamic laser light scattering. As indicated, the polymer's MWD can be fully characterized using very little sample and a single solution with concentrated sulfuric acid as the solvent. Dilute solution viscometry is a simple technique for determining the limiting viscosity number or intrinsic viscosity [η] of soluble polymers (Reference 4.4.5(a)). The apparatus is inexpensive and simple to assemble and operate. The [η] of a polymer depends upon its hydrodynamic volume in the solvent and is related to the MW of the polymer. 4.4.6 General scheme for resin material characterization The following questions deserve careful consideration when developing procedures for preparing and characterizing polymer and polymer precursor (thermosetting resins and resin formulations) samples - What are the inherent characteristics of the polymer or prepolymer? Will certain operations cause irreversible changes in the sample?