正在加载图片...
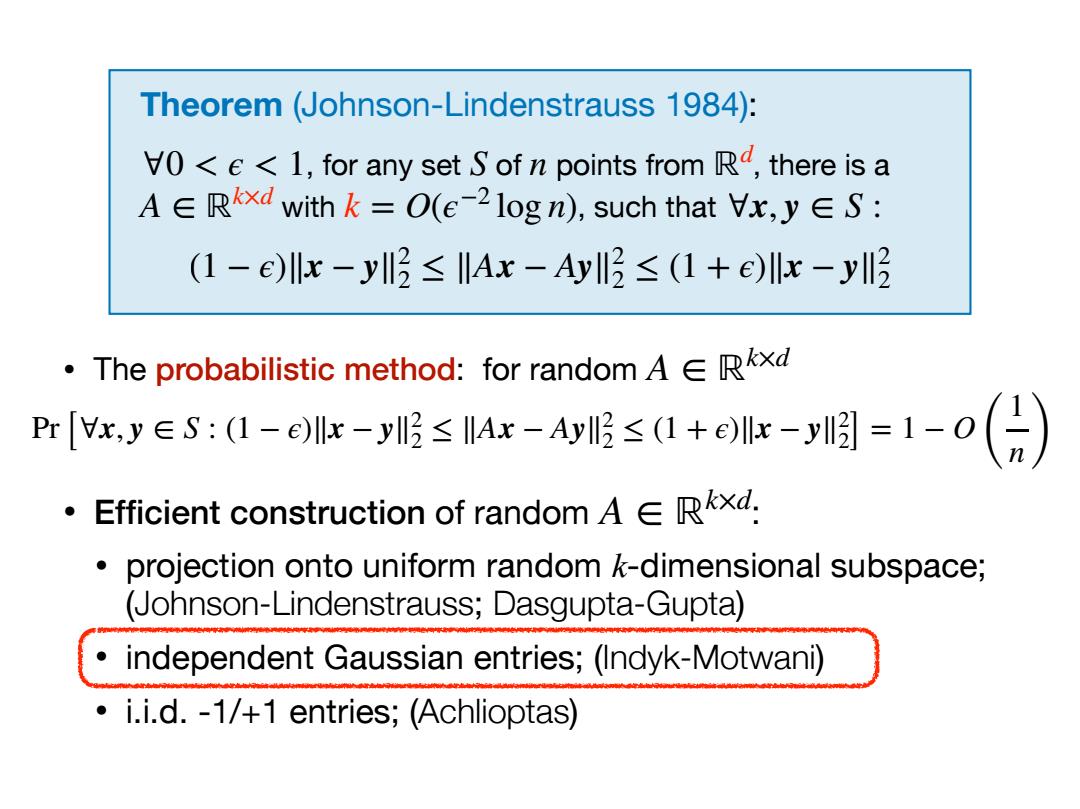
Theorem (Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984): VO<e<1,for any set S of n points from Rd,there is a A∈Rxd with k=O(e-2logn),such that Vx,y∈S: (1-e)lx-y3≤Ax-Ay3≤(1+elx-y3 ·The probabilistic method:for random A∈Rkxd Pr[xy∈s:-ok-脂≤Ar-a服≤+or-明=1-o(日) o Efficient construction of random A Rxd. 。 projection onto uniform random k-dimensional subspace; (Johnson-Lindenstrauss;Dasgupta-Gupta) independent Gaussian entries;(Indyk-Motwani) i.i.d.-1/+1 entries;(Achlioptas)Theorem (Johnson-Lindenstrauss 1984): , for any set of points from , there is a with , such that ∀0 < ϵ < 1 S n ℝd A ∈ ℝk×d k = O(ϵ−2 log n) ∀x, y ∈ S : (1 − ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2 ≤ ∥Ax − Ay∥2 2 ≤ (1 + ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2 • The probabilistic method: for random A ∈ ℝk×d Pr[∀x, y ∈ S : (1 − ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2 ≤ ∥Ax − Ay∥2 2 ≤ (1 + ϵ)∥x − y∥2 2] = 1 − O ( 1 n) • Efficient construction of random : • projection onto uniform random k-dimensional subspace; (Johnson-Lindenstrauss; Dasgupta-Gupta) • independent Gaussian entries; (Indyk-Motwani) • i.i.d. -1/+1 entries; (Achlioptas) A ∈ ℝk×d