正在加载图片...
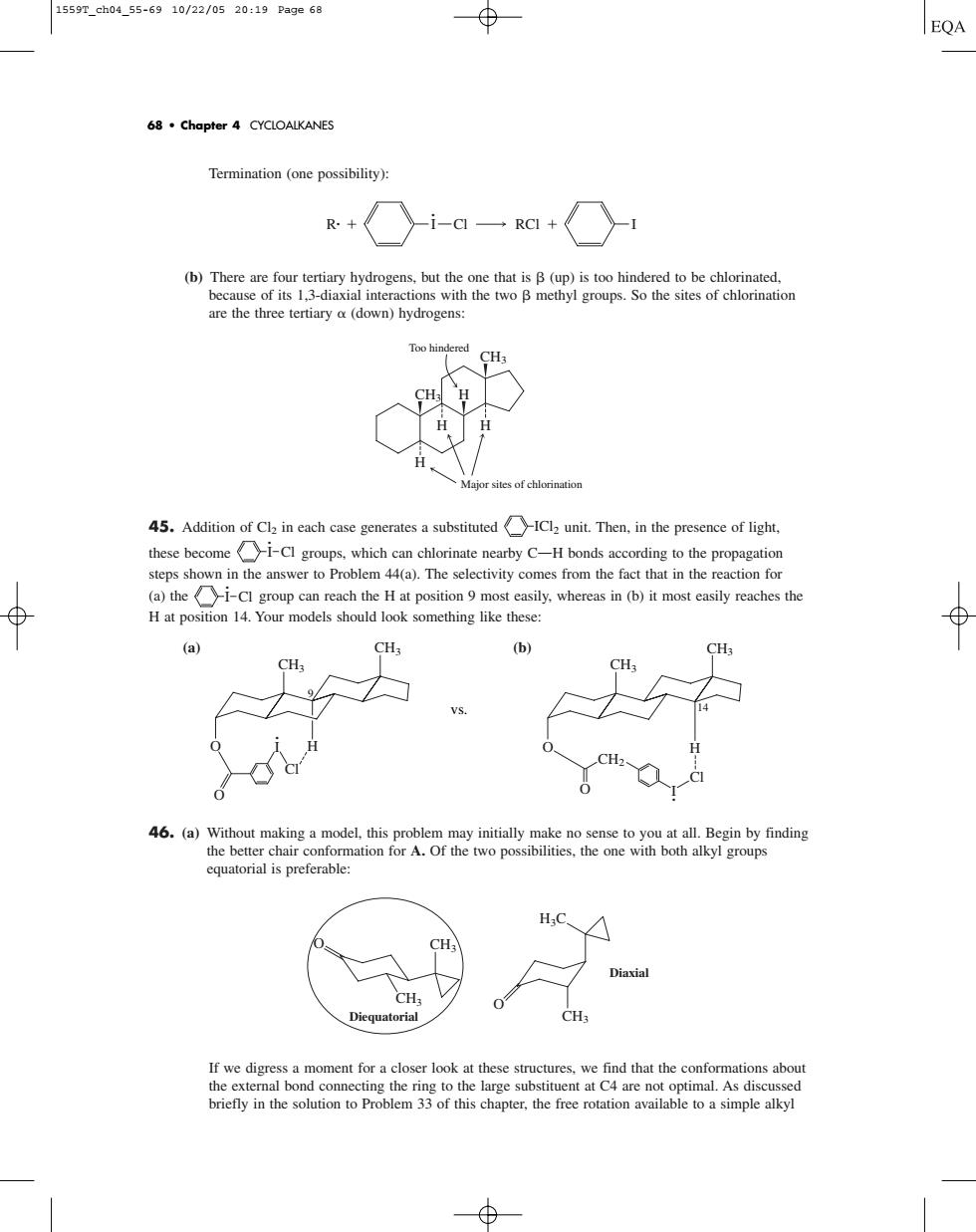
1559Tch0455-6910/22/0520:19Page6a 68.Chapter 4 CYCLOALKANES Termination(one possibility): R.+ i-一RC+ are the three tertiary a(down)hydrogens: Too h 45.Addition case generates a,in the presence of light. these become1-Cl groups,which can chlorinate nearby C-H bonds according to the propagation steps shown in the answer to Problem 44(a).The selectivity comes from the fact that in the reaction for (a)the-Cl group can reach the H at position 9 most easily,whereas in (b)it most easily reaches the ⊕ H at position 14.Your models should look something like these (a) auatorial is preferable If we digress a moment for a closer look at these structures,we find that the conformations abou connecting the ring to the large substituent at C4are not optimal.As discussed tion to Problem 33 of this chapter,the free rotation available to a simple alkylTermination (one possibility): (b) There are four tertiary hydrogens, but the one that is (up) is too hindered to be chlorinated, because of its 1,3-diaxial interactions with the two methyl groups. So the sites of chlorination are the three tertiary (down) hydrogens: 45. Addition of Cl2 in each case generates a substituted unit. Then, in the presence of light, these become groups, which can chlorinate nearby COH bonds according to the propagation steps shown in the answer to Problem 44(a). The selectivity comes from the fact that in the reaction for (a) the group can reach the H at position 9 most easily, whereas in (b) it most easily reaches the H at position 14. Your models should look something like these: (a) (b) 46. (a) Without making a model, this problem may initially make no sense to you at all. Begin by finding the better chair conformation for A. Of the two possibilities, the one with both alkyl groups equatorial is preferable: If we digress a moment for a closer look at these structures, we find that the conformations about the external bond connecting the ring to the large substituent at C4 are not optimal. As discussed briefly in the solution to Problem 33 of this chapter, the free rotation available to a simple alkyl CH3 O O CH3 CH3 H3C Diequatorial Diaxial CH2 I O O H Cl · 14 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 O I O H Cl · 9 I Cl · I Cl · ICl2 CH3 CH3 H H H H Major sites of chlorination Too hindered R· I Cl RCl I · 68 • Chapter 4 CYCLOALKANES vs. 1559T_ch04_55-69 10/22/05 20:19 Page 68��