正在加载图片...
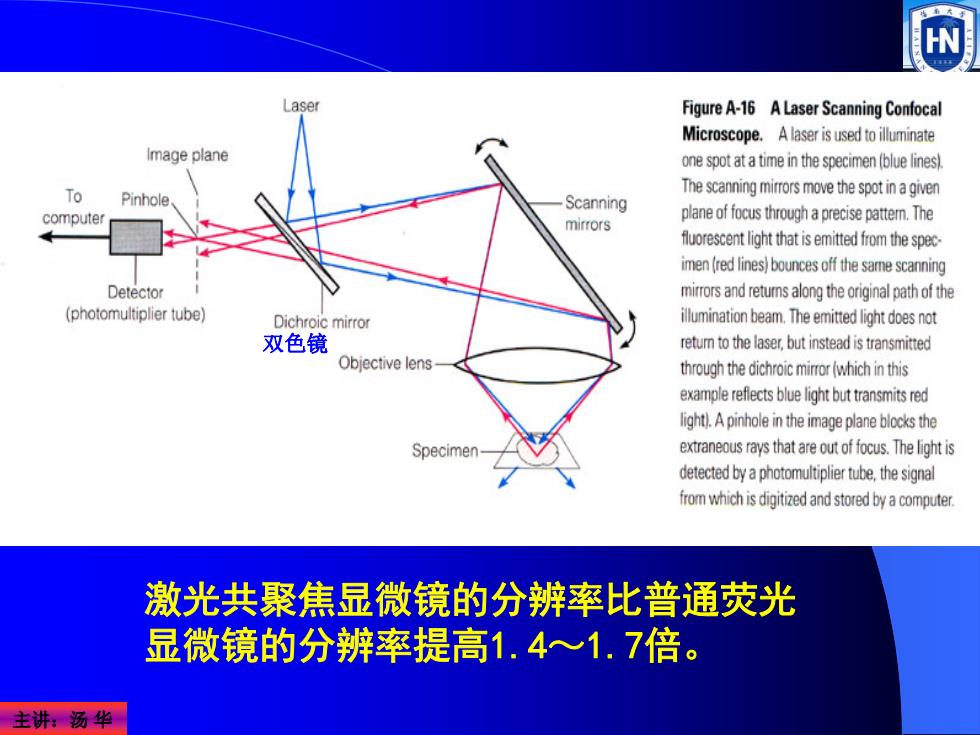
Figure A-16 A Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope.A laser is used to illuminate Image plane one spot at a time in the specimen(blue lines) To The scanning mirrors move the spot in agiven Pinhole Scanning computer mirrors plane of focus through a precise pattem.The fluoresn light that is emitted from the spec- imen (red lines)bounces off the same scanning Detector mirrors and returns along the original path of the (photomultiplier tube) Dichroic mirror illumination beam.The emitted light doesnot 双色镜 retum to the laser,but instead is transmitted Objective lens through the dichroic mirror (which in this example reflects blue light but transmitsred light).A pinhole in the image plane bocks the Specimen extraneous rays that are outof focus.The light is detected by a photomultiplier tube.the signal omwhichisigtidndstored byacmuter. 激光共聚焦显微镜的分辨率比普通荧光 显微镜的分辨率提高1.4心1.7倍。 主讲:汤华 主讲:汤 华 双色镜 激光共聚焦显微镜的分辨率比普通荧光 显微镜的分辨率提高1.4~1.7倍