正在加载图片...
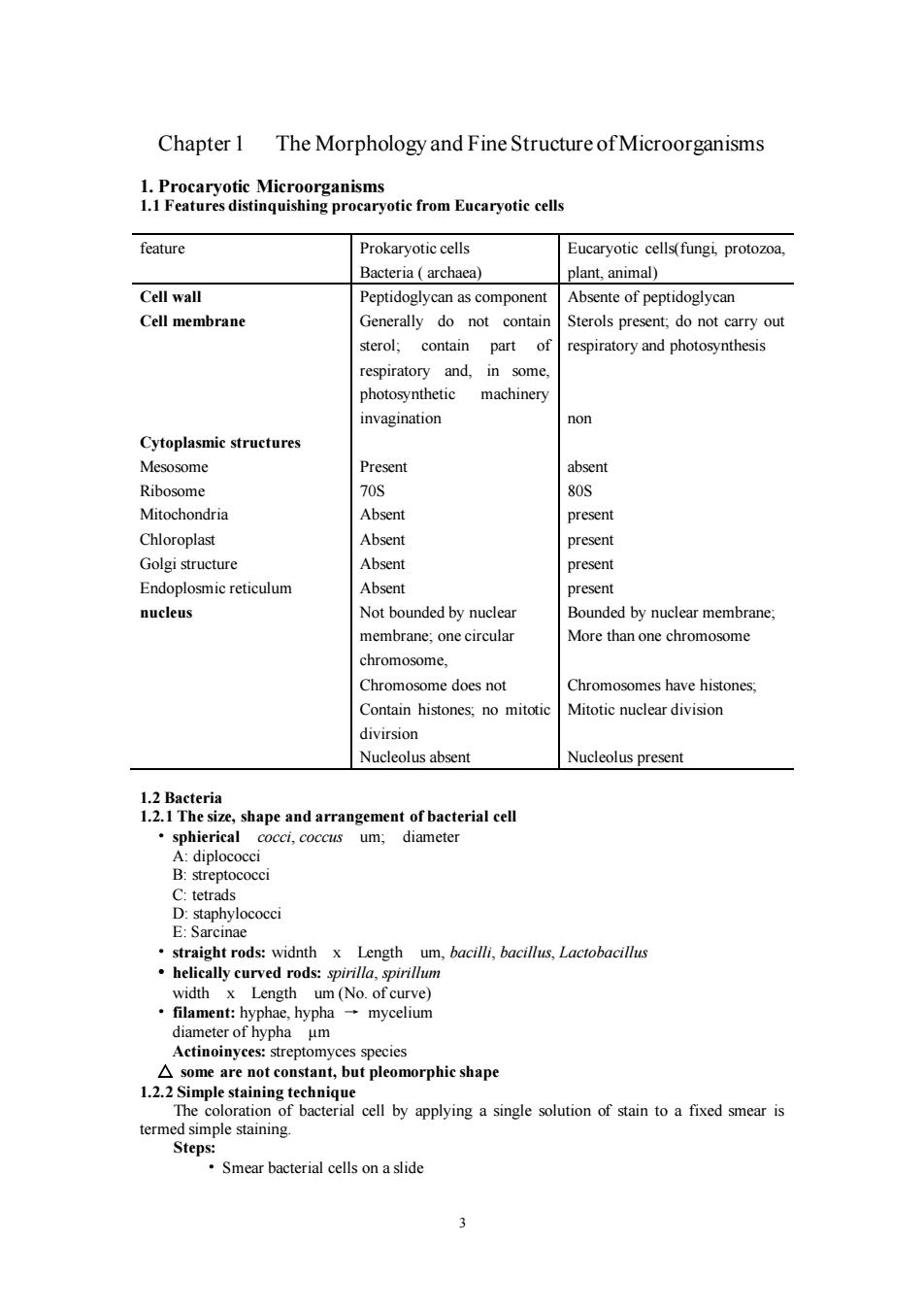
3 Chapter 1 The Morphology and Fine Structure of Microorganisms 1. Procaryotic Microorganisms 1.1 Features distinquishing procaryotic from Eucaryotic cells feature Prokaryotic cells Bacteria ( archaea) Eucaryotic cells(fungi, protozoa, plant, animal) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasmic structures Mesosome Ribosome Mitochondria Chloroplast Golgi structure Endoplosmic reticulum nucleus Peptidoglycan as component Generally do not contain sterol; contain part of respiratory and, in some, photosynthetic machinery invagination Present 70S Absent Absent Absent Absent Not bounded by nuclear membrane; one circular chromosome, Chromosome does not Contain histones; no mitotic divirsion Nucleolus absent Absente of peptidoglycan Sterols present; do not carry out respiratory and photosynthesis non absent 80S present present present present Bounded by nuclear membrane; More than one chromosome Chromosomes have histones; Mitotic nuclear division Nucleolus present 1.2 Bacteria 1.2.1 The size, shape and arrangement of bacterial cell • sphierical cocci, coccus um; diameter A: diplococci B: streptococci C: tetrads D: staphylococci E: Sarcinae • straight rods: widnth x Length um, bacilli, bacillus, Lactobacillus • helically curved rods: spirilla, spirillum width x Length um (No. of curve) • filament: hyphae, hypha → mycelium diameter of hypha μm Actinoinyces: streptomyces species △ some are not constant, but pleomorphic shape 1.2.2 Simple staining technique The coloration of bacterial cell by applying a single solution of stain to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. Steps: • Smear bacterial cells on a slide3 Chapter 1 The Morphology and Fine Structure of Microorganisms 1. Procaryotic Microorganisms 1.1 Features distinquishing procaryotic from Eucaryotic cells feature Prokaryotic cells Bacteria ( archaea) Eucaryotic cells(fungi, protozoa, plant, animal) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasmic structures Mesosome Ribosome Mitochondria Chloroplast Golgi structure Endoplosmic reticulum nucleus Peptidoglycan as component Generally do not contain sterol; contain part of respiratory and, in some, photosynthetic machinery invagination Present 70S Absent Absent Absent Absent Not bounded by nuclear membrane; one circular chromosome, Chromosome does not Contain histones; no mitotic divirsion Nucleolus absent Absente of peptidoglycan Sterols present; do not carry out respiratory and photosynthesis non absent 80S present present present present Bounded by nuclear membrane; More than one chromosome Chromosomes have histones; Mitotic nuclear division Nucleolus present 1.2 Bacteria 1.2.1 The size, shape and arrangement of bacterial cell • sphierical cocci, coccus um; diameter A: diplococci B: streptococci C: tetrads D: staphylococci E: Sarcinae • straight rods: widnth x Length um, bacilli, bacillus, Lactobacillus • helically curved rods: spirilla, spirillum width x Length um (No. of curve) • filament: hyphae, hypha → mycelium diameter of hypha μm Actinoinyces: streptomyces species △ some are not constant, but pleomorphic shape 1.2.2 Simple staining technique The coloration of bacterial cell by applying a single solution of stain to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. Steps: • Smear bacterial cells on a slide