正在加载图片...
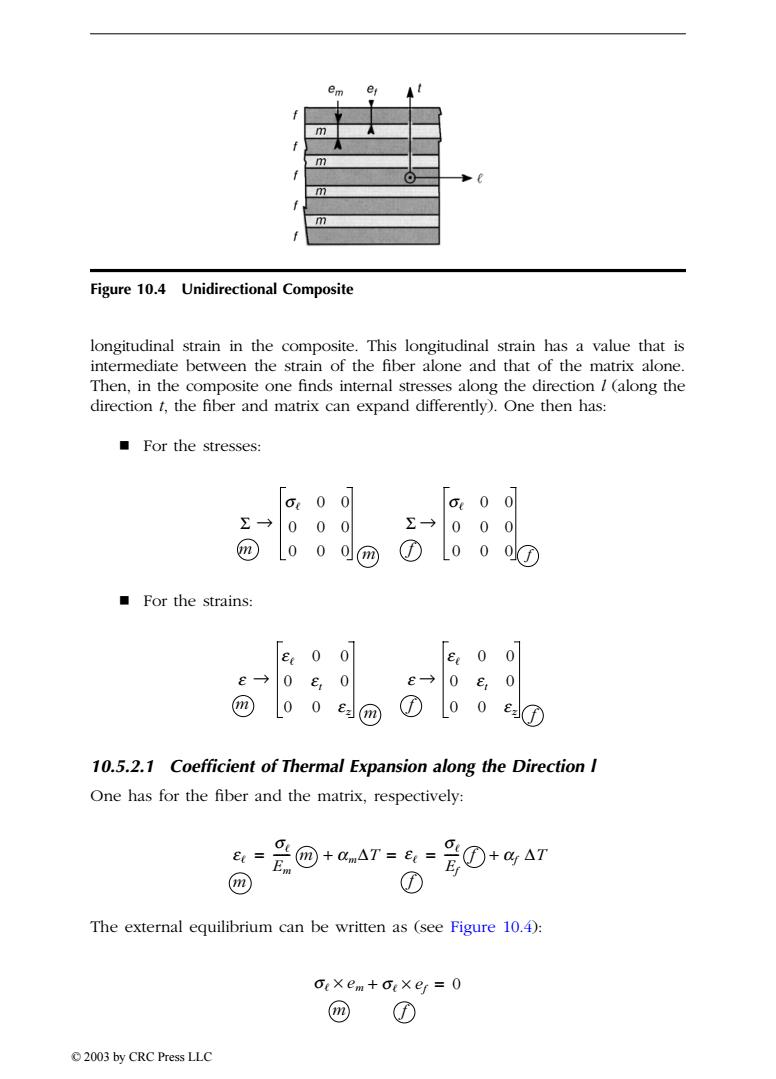
em m m Figure 10.4 Unidirectional Composite longitudinal strain in the composite.This longitudinal strain has a value that is intermediate between the strain of the fiber alone and that of the matrix alone. Then,in the composite one finds internal stresses along the direction /(along the direction t,the fiber and matrix can expand differently).One then has: ■For the stresses: Or 00 6 0 0 E 0 00 Σ→ 0 0 m 00 m ① 0 0 ■For the strains: 0 0入 [e0 0入 £→ 0 0 e→ 0 E 0 @ 0 0 m 00 10.5.2.1 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion along the Direction I One has for the fiber and the matrix,respectively: Ot Et= m ① The external equilibrium can be written as (see Figure 10.4): Gexem+oixef=0 ① 2003 by CRC Press LLClongitudinal strain in the composite. This longitudinal strain has a value that is intermediate between the strain of the fiber alone and that of the matrix alone. Then, in the composite one finds internal stresses along the direction l (along the direction t, the fiber and matrix can expand differently). One then has: For the stresses: For the strains: 10.5.2.1 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion along the Direction l One has for the fiber and the matrix, respectively: The external equilibrium can be written as (see Figure 10.4): Figure 10.4 Unidirectional Composite S m s 0 0 0 00 0 00 m S f s 0 0 0 00 0 00 f Æ Æ e m e 0 0 0 et 0 0 0 e z m e f e 0 0 0 et 0 0 0 e z f Æ Æ e m s Em ------ m + amDT e f s Ef = == ----- f + af DT s ¥ em m s ¥ ef f + = 0 TX846_Frame_C10 Page 220 Monday, November 18, 2002 12:25 PM © 2003 by CRC Press LLC