正在加载图片...
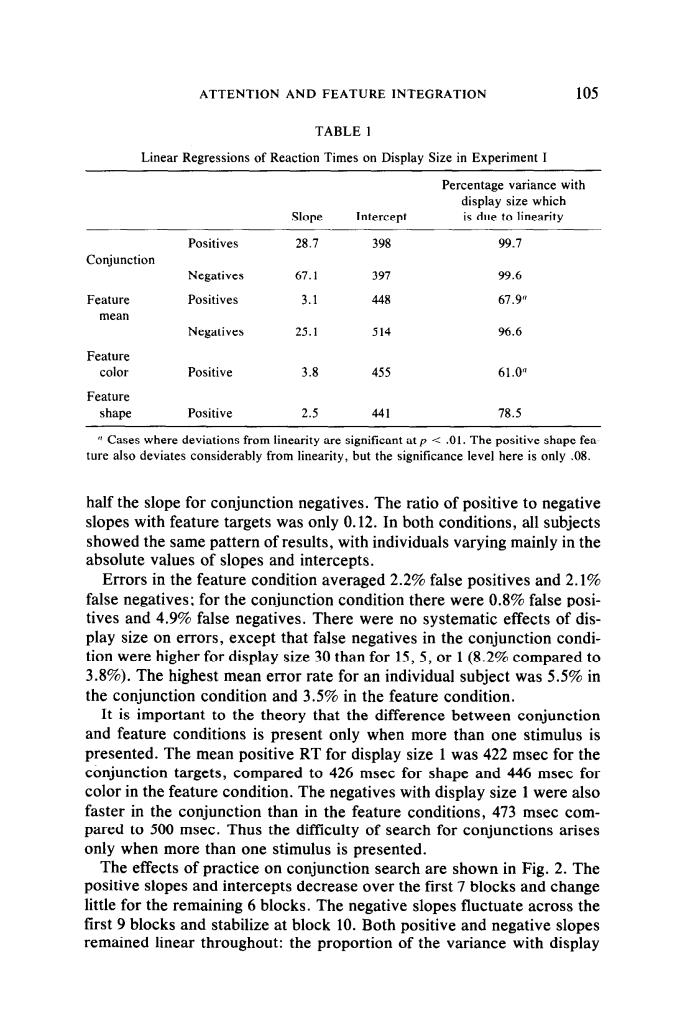
ATTENTION AND FEATURE INTEGRATION 105 TABLE 1 Linear Regressions of Reaction Times on Display Size in Experiment I Slope Positives 28.7 398 997 Conjunction Negatives 67.1 397 99.6 Feature Positives 3.1 448 67.9m mear Negatives 25.1 514 96.6 Feature color Positive 3.8 455 61.09 Feature shape Positive 441 78.5 half the slope for conjunction negatives.The ratio of positive to negative slopes with feature targets was only 0.12.In both conditions,all subjects showed the same pattern of results,with individuals varying mainly in the absolute values of slopes and intercepts. Errors in the feature condition averaged 2.2%false positives and 2.1% false negatives:for the conjunction condition there were 0.8%false posi- tives and 4.9%false negatives.There were no systematic effects of dis- play size on errors,except that false negatives in the conjunction condi- tion were higher for display size 30 than for 15,5,or 1(8.2%com 3.8%).The highest ear erro e conjunction condition and 3.5%in the feature condition. It is important to the theory that the difference between conjunction and feature conditions is present only when more than one stimulus is presented.The mean positive RT for display size 1 was 422 msec for the ed to 426 for and 446 tion.The negatives with display size 1were as faster in the conjunction than in the feature conditions,473 msec com- pared to 500 msec.Thus the difficulty of search for conjunctions arises only when more than one stimulus is presented. The effects of practice on conjunction search are shown in Fig.2.The positive slopes and intercepts decrease over the first 7 blocks and change little for the remaining 6 hlocks The ative slopes flu ctuate acros first 9 block <s and stab ize at ock 10.Both pos tive and negative remained linear throughout:the proportion of the variance with display ATTENTION AND FEATURE INTEGRATION 105 TABLE 1 Linear Regressions of Reaction Times on Display Size in Experiment I Slope Intercept Percentage variance with display size which is due to linearity Positives 28.7 398 99.7 Conjunction Negatives 67.1 397 99.6 Feature Positives 3.1 448 67.9” mean Negatives 25.1 514 96.6 Feature color Positive 3.8 455 61.0” Feature shape Positive 2.5 441 78.5 ” Cases where deviations from linearity are significant at p < .Ol. The positive shape feature also deviates considerably from linearity, but the significance level here is only .08. half the slope for conjunction negatives. The ratio of positive to negative slopes with feature targets was only 0.12. In both conditions, all subjects showed the same pattern of results, with individuals varying mainly in the absolute values of slopes and intercepts. Errors in the feature condition averaged 2.2% false positives and 2.1% false negatives; for the conjunction condition there were 0.8% false positives and 4.9% false negatives. There were no systematic effects of display size on errors, except that false negatives in the conjunction condition were higher for display size 30 than for 15,5, or 1 (8.2% compared to 3.8%). The highest mean error rate for an individual subject was 5.5% in the conjunction condition and 3.5% in the feature condition. It is important to the theory that the difference between conjunction and feature conditions is present only when more than one stimulus is presented. The mean positive RT for display size 1 was 422 msec for the conjunction targets, compared to 426 msec for shape and 446 msec for color in the feature condition. The negatives with display size 1 were also faster in the conjunction than in the feature conditions, 473 msec compared to 500 msec. Thus the difficulty of search for conjunctions arises only when more than one stimulus is presented. The effects of practice on conjunction search are shown in Fig. 2. The positive slopes and intercepts decrease over the first 7 blocks and change little for the remaining 6 blocks. The negative slopes fluctuate across the first 9 blocks and stabilize at block 10. Both positive and negative slopes remained linear throughout: the proportion of the variance with display