正在加载图片...
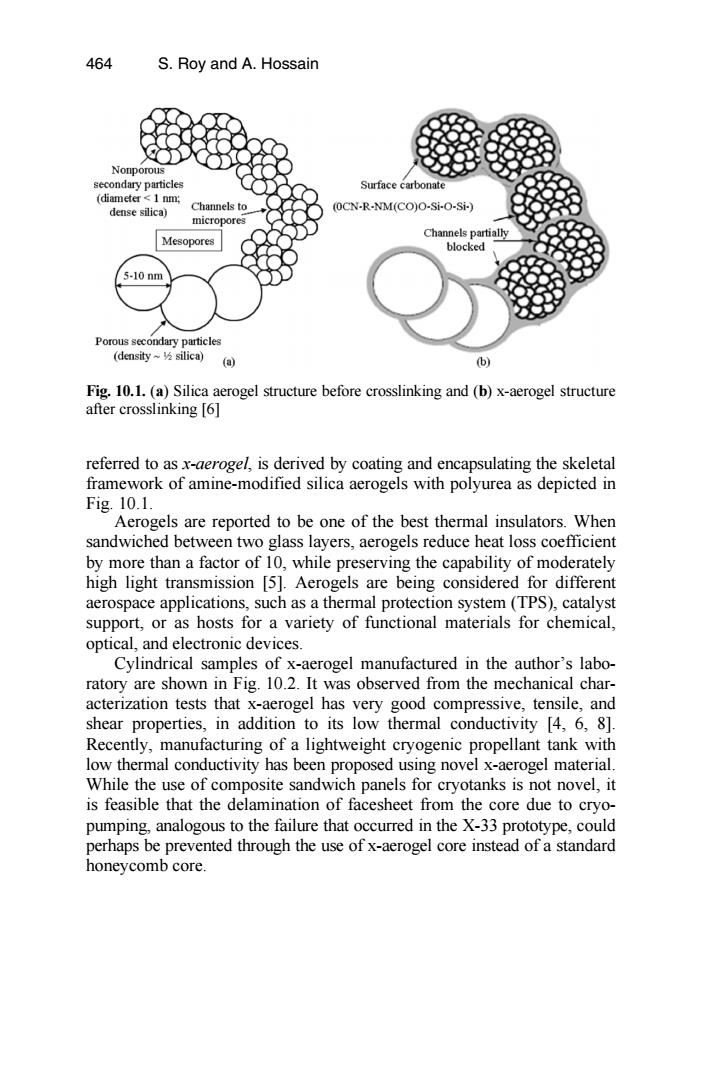
464 S.Roy and A.Hossain Nonporous secondary particles Surface carbonate (diamete灯<1nm dense silica) Channels to (OCN-R-NM(CO)O-Si-O-Si-) micropores Channels partially Mesopores blocked 5-10nm Porous secondary particles (density~2 silica0)(间 (b) Fig.10.1.(a)Silica aerogel structure before crosslinking and (b)x-aerogel structure after crosslinking [6] referred to as x-aerogel,is derived by coating and encapsulating the skeletal framework of amine-modified silica aerogels with polyurea as depicted in Fig.10.1 Aerogels are reported to be one of the best thermal insulators.When sandwiched between two glass layers,aerogels reduce heat loss coefficient by more than a factor of 10,while preserving the capability of moderately high light transmission [5].Aerogels are being considered for different aerospace applications,such as a thermal protection system (TPS),catalyst support,or as hosts for a variety of functional materials for chemical, optical,and electronic devices. Cylindrical samples of x-aerogel manufactured in the author's labo- ratory are shown in Fig.10.2.It was observed from the mechanical char- acterization tests that x-aerogel has very good compressive,tensile,and shear properties,in addition to its low thermal conductivity [4,6,8]. Recently,manufacturing of a lightweight cryogenic propellant tank with low thermal conductivity has been proposed using novel x-aerogel material. While the use of composite sandwich panels for cryotanks is not novel,it is feasible that the delamination of facesheet from the core due to cryo- pumping,analogous to the failure that occurred in the X-33 prototype,could perhaps be prevented through the use of x-aerogel core instead of a standard honeycomb core.referred to as x-aerogel, is derived by coating and encapsulating the skeletal framework of amine-modified silica aerogels with polyurea as depicted in Fig. 10.1. Fig. 10.1. (a) Silica aerogel structure before crosslinking and (b) x-aerogel structure after crosslinking [6] Aerogels are reported to be one of the best thermal insulators. When sandwiched between two glass layers, aerogels reduce heat loss coefficient by more than a factor of 10, while preserving the capability of moderately high light transmission [5]. Aerogels are being considered for different aerospace applications, such as a thermal protection system (TPS), catalyst support, or as hosts for a variety of functional materials for chemical, optical, and electronic devices. Cylindrical samples of x-aerogel manufactured in the author’s laboratory are shown in Fig. 10.2. It was observed from the mechanical characterization tests that x-aerogel has very good compressive, tensile, and shear properties, in addition to its low thermal conductivity [4, 6, 8]. Recently, manufacturing of a lightweight cryogenic propellant tank with low thermal conductivity has been proposed using novel x-aerogel material. While the use of composite sandwich panels for cryotanks is not novel, it is feasible that the delamination of facesheet from the core due to cryopumping, analogous to the failure that occurred in the X-33 prototype, could perhaps be prevented through the use of x-aerogel core instead of a standard honeycomb core. 464 S. Roy and A. Hossain