正在加载图片...
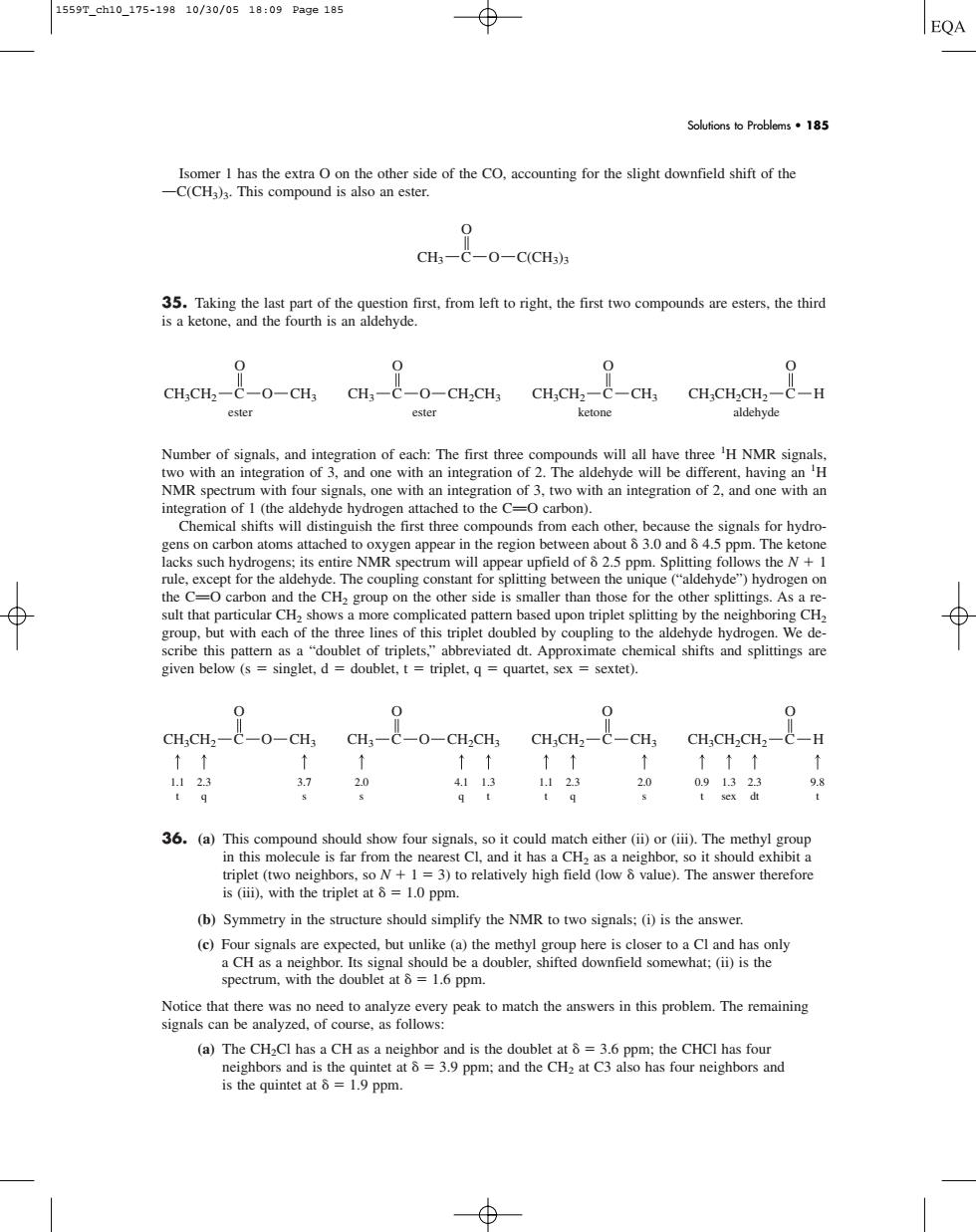
1559T_ch10_175-19810/30/0518:09Pa9e185 EQA Solutions to Problems.185 the other side of the CO.accounting for the slight downfield shift of the 0 CH;-C-0-C(CHa) nnn s a ketone,and 0 0 0 CH;CH2-C-0-CH;CH;-C-0-CH2CH CH;CH2-C- CH; CH;CH.CH2-C-H ester ester ketone Number of signals.and integration of each:The first three c ounds will all have three 'H NMR signal hnoneron ofThe aldelyde ben H with an integration of 2,and one with an Chemical shifts will distinguish the first three compounds from each other.because the signals for hydro gens on carbon atoms attached to oxygen appear in the region between about3.0 and45 pm.The keton the C O carbon and the CH2 group on the other side is smaller than those for the other splittings.As a re ult tha given below (s singlet,d doublet.t triplet,q quartet,sex sextet). CH.CHz C-0-CH,CH-C-0-CH.CH,CHCH-c inthismcrneishoit hould shibit in this molecule is tar from (b)Symmetry in the structure should simplify the NMR to two signals:(i)is the answer. (c)Four signals are expected.but unlike (a)the methyl group here is closer to a Cl and has only geaaceagtomhtcmh邮mincee (a)The CH-Cl has a CH as a neighbor and is the doublet at 8 =3.6 ppm;the CHCI has four he pp:and the CHa at C3 also has four neighbors and Isomer 1 has the extra O on the other side of the CO, accounting for the slight downfield shift of the OC(CH3)3. This compound is also an ester. 35. Taking the last part of the question first, from left to right, the first two compounds are esters, the third is a ketone, and the fourth is an aldehyde. Number of signals, and integration of each: The first three compounds will all have three 1 H NMR signals, two with an integration of 3, and one with an integration of 2. The aldehyde will be different, having an 1 H NMR spectrum with four signals, one with an integration of 3, two with an integration of 2, and one with an integration of 1 (the aldehyde hydrogen attached to the CPO carbon). Chemical shifts will distinguish the first three compounds from each other, because the signals for hydrogens on carbon atoms attached to oxygen appear in the region between about 3.0 and 4.5 ppm. The ketone lacks such hydrogens; its entire NMR spectrum will appear upfield of 2.5 ppm. Splitting follows the N 1 rule, except for the aldehyde. The coupling constant for splitting between the unique (“aldehyde”) hydrogen on the CPO carbon and the CH2 group on the other side is smaller than those for the other splittings. As a result that particular CH2 shows a more complicated pattern based upon triplet splitting by the neighboring CH2 group, but with each of the three lines of this triplet doubled by coupling to the aldehyde hydrogen. We describe this pattern as a “doublet of triplets,” abbreviated dt. Approximate chemical shifts and splittings are given below (s singlet, d doublet, t triplet, q quartet, sex sextet). 36. (a) This compound should show four signals, so it could match either (ii) or (iii). The methyl group in this molecule is far from the nearest Cl, and it has a CH2 as a neighbor, so it should exhibit a triplet (two neighbors, so N 1 3) to relatively high field (low value). The answer therefore is (iii), with the triplet at 1.0 ppm. (b) Symmetry in the structure should simplify the NMR to two signals; (i) is the answer. (c) Four signals are expected, but unlike (a) the methyl group here is closer to a Cl and has only a CH as a neighbor. Its signal should be a doubler, shifted downfield somewhat; (ii) is the spectrum, with the doublet at 1.6 ppm. Notice that there was no need to analyze every peak to match the answers in this problem. The remaining signals can be analyzed, of course, as follows: (a) The CH2Cl has a CH as a neighbor and is the doublet at 3.6 ppm; the CHCl has four neighbors and is the quintet at 3.9 ppm; and the CH2 at C3 also has four neighbors and is the quintet at 1.9 ppm. CH3 O CH2CH3 O O CH3 C O CH3CH2 C CH3CH2 C CH3 O CH3CH2CH2 C H O 1.1 t 2.3 q 3.7 s 2.0 s 4.1 q 1.3 t 1.1 t 2.3 q 0.9 t 1.3 sex 2.3 dt 9.8 t 2.0 s CH3 O CH2CH3 O O CH3 C O CH3CH2 C CH3CH2 C CH3 O CH3CH2CH2 C H O ester ester ketone aldehyde CH3 O C O C(CH3)3 Solutions to Problems • 185 1559T_ch10_175-198 10/30/05 18:09 Page 185���������