正在加载图片...
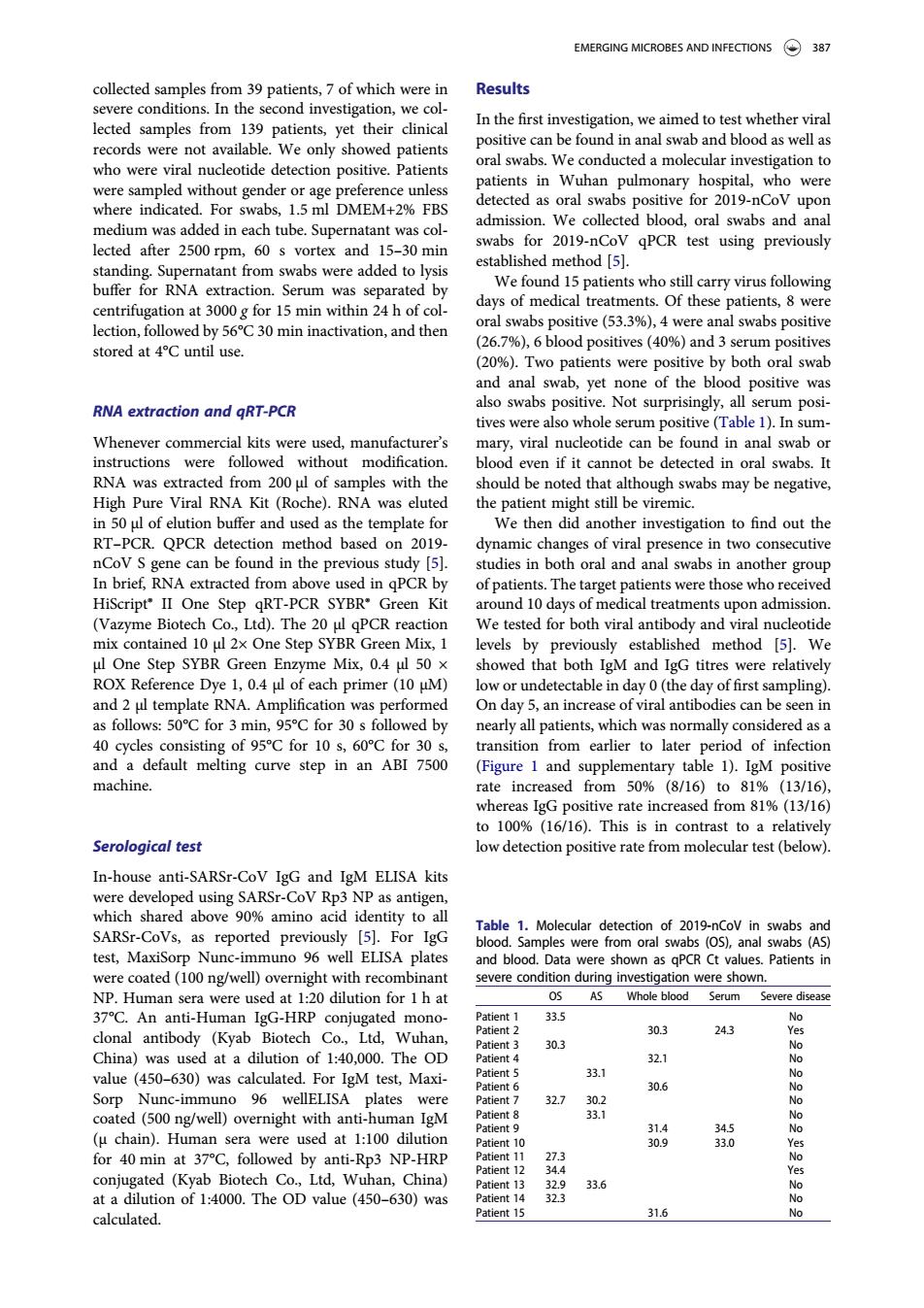
EMERGING MICROBES AND INFECTIONS 387 collected samples from 39 patients,7 of which were in Results severe condit ions.In the second investigation,we co lected sample In the first ir in ana s wen a who were viral nucleotide detection positive Patients nts in Wuhan pulmonary hospital.who wer detected as oral swabs positive for 2019-nCoV upor medium wasadd d in tube admission.We collected blood,oral swabs and ana 2019-n qPCR test using previously vortex ar buffer for rna extraction serum was separated by s who still ca centrifugation at 000g for 15 min within 24h of co days of medical treatments.Of these patients,8 were lection,followed by 56C30 min inactivation,and then oral swabs positive(53.%),4 were anal swabs positive stored at 4C until use (%),6 blood positives(%and3s h oral swa RNA extraction and qRT-PCR also swabs positive.Not surp y all serum posi tives were also whole serum positive(Table 1).In sum mary,viral nucleotide can be found in anal swab o ruction wer out 、2 oral swab Hih Pure Viral RNA Kit (Roche).RNA was eluted wabs may be negativ in 50 ul of elution buffer and used as the template for We then did another investigation to find out the RT-PCR.QPCR detection method based on 2019 dynamic changes of viral presence in two consecutive nd ir the previo s st RT-PCR e Biotech Co Itd)The 20 PCR reaction We tested for both viral an cleotide mix contained 10 ul 2x One Step SYBR Green Mix,1 levels by previously established method [5].We showed that both IgM and IgG titres were relativel each prim undetectable in day 0(th day of first mpling 50C for 3 min 95℃for30s all pa hich 40 cycles consisting of 95C for 10 s.60C for 30 transition from earlier to later neriod of infectio and a default melting curve step in an ABI 7500 (Figure 1 and supplementary table 1).IgM positive machine. rate incre om509 (8/16)to81% 1316 his ow dete In-house anti-SARSr-CoV IgG and IgM ELISA kits were dey eloped SARS-CoVp detection of 2019-nCov ir test Maxiso om oral nal aPC were coated(100 ng/well)overnight with recombinant AS Whole bloo Serum iseas An IgG-HR 303 4好 of140.000.The 303 32.1 value (450-630)was calculated.For IgM test,Maxi- 30.6 No Sorp Nunc-immuno 96 wellELISA were coate d(500 ng/well)overnight with anti-huma n IgM 30g ted (Kyab Biotech Co Ltd,Wuh at a dilution of 1:4000.The OD value(450-630)was 323 6 calculated.collected samples from 39 patients, 7 of which were in severe conditions. In the second investigation, we collected samples from 139 patients, yet their clinical records were not available. We only showed patients who were viral nucleotide detection positive. Patients were sampled without gender or age preference unless where indicated. For swabs, 1.5 ml DMEM+2% FBS medium was added in each tube. Supernatant was collected after 2500 rpm, 60 s vortex and 15–30 min standing. Supernatant from swabs were added to lysis buffer for RNA extraction. Serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000 g for 15 min within 24 h of collection, followed by 56°C 30 min inactivation, and then stored at 4°C until use. RNA extraction and qRT-PCR Whenever commercial kits were used, manufacturer’s instructions were followed without modification. RNA was extracted from 200 μl of samples with the High Pure Viral RNA Kit (Roche). RNA was eluted in 50 μl of elution buffer and used as the template for RT–PCR. QPCR detection method based on 2019- nCoV S gene can be found in the previous study [5]. In brief, RNA extracted from above used in qPCR by HiScript® II One Step qRT-PCR SYBR® Green Kit (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd). The 20 μl qPCR reaction mix contained 10 μl 2× One Step SYBR Green Mix, 1 μl One Step SYBR Green Enzyme Mix, 0.4 μl 50 × ROX Reference Dye 1, 0.4 μl of each primer (10 μM) and 2 μl template RNA. Amplification was performed as follows: 50°C for 3 min, 95°C for 30 s followed by 40 cycles consisting of 95°C for 10 s, 60°C for 30 s, and a default melting curve step in an ABI 7500 machine. Serological test In-house anti-SARSr-CoV IgG and IgM ELISA kits were developed using SARSr-CoV Rp3 NP as antigen, which shared above 90% amino acid identity to all SARSr-CoVs, as reported previously [5]. For IgG test, MaxiSorp Nunc-immuno 96 well ELISA plates were coated (100 ng/well) overnight with recombinant NP. Human sera were used at 1:20 dilution for 1 h at 37°C. An anti-Human IgG-HRP conjugated monoclonal antibody (Kyab Biotech Co., Ltd, Wuhan, China) was used at a dilution of 1:40,000. The OD value (450–630) was calculated. For IgM test, MaxiSorp Nunc-immuno 96 wellELISA plates were coated (500 ng/well) overnight with anti-human IgM (µ chain). Human sera were used at 1:100 dilution for 40 min at 37°C, followed by anti-Rp3 NP-HRP conjugated (Kyab Biotech Co., Ltd, Wuhan, China) at a dilution of 1:4000. The OD value (450–630) was calculated. Results In the first investigation, we aimed to test whether viral positive can be found in anal swab and blood as well as oral swabs. We conducted a molecular investigation to patients in Wuhan pulmonary hospital, who were detected as oral swabs positive for 2019-nCoV upon admission. We collected blood, oral swabs and anal swabs for 2019-nCoV qPCR test using previously established method [5]. We found 15 patients who still carry virus following days of medical treatments. Of these patients, 8 were oral swabs positive (53.3%), 4 were anal swabs positive (26.7%), 6 blood positives (40%) and 3 serum positives (20%). Two patients were positive by both oral swab and anal swab, yet none of the blood positive was also swabs positive. Not surprisingly, all serum positives were also whole serum positive (Table 1). In summary, viral nucleotide can be found in anal swab or blood even if it cannot be detected in oral swabs. It should be noted that although swabs may be negative, the patient might still be viremic. We then did another investigation to find out the dynamic changes of viral presence in two consecutive studies in both oral and anal swabs in another group of patients. The target patients were those who received around 10 days of medical treatments upon admission. We tested for both viral antibody and viral nucleotide levels by previously established method [5]. We showed that both IgM and IgG titres were relatively low or undetectable in day 0 (the day of first sampling). On day 5, an increase of viral antibodies can be seen in nearly all patients, which was normally considered as a transition from earlier to later period of infection (Figure 1 and supplementary table 1). IgM positive rate increased from 50% (8/16) to 81% (13/16), whereas IgG positive rate increased from 81% (13/16) to 100% (16/16). This is in contrast to a relatively low detection positive rate from molecular test (below). Table 1. Molecular detection of 2019-nCoV in swabs and blood. Samples were from oral swabs (OS), anal swabs (AS) and blood. Data were shown as qPCR Ct values. Patients in severe condition during investigation were shown. OS AS Whole blood Serum Severe disease Patient 1 33.5 No Patient 2 30.3 24.3 Yes Patient 3 30.3 No Patient 4 32.1 No Patient 5 33.1 No Patient 6 30.6 No Patient 7 32.7 30.2 No Patient 8 33.1 No Patient 9 31.4 34.5 No Patient 10 30.9 33.0 Yes Patient 11 27.3 No Patient 12 34.4 Yes Patient 13 32.9 33.6 No Patient 14 32.3 No Patient 15 31.6 No EMERGING MICROBES AND INFECTIONS 387