正在加载图片...
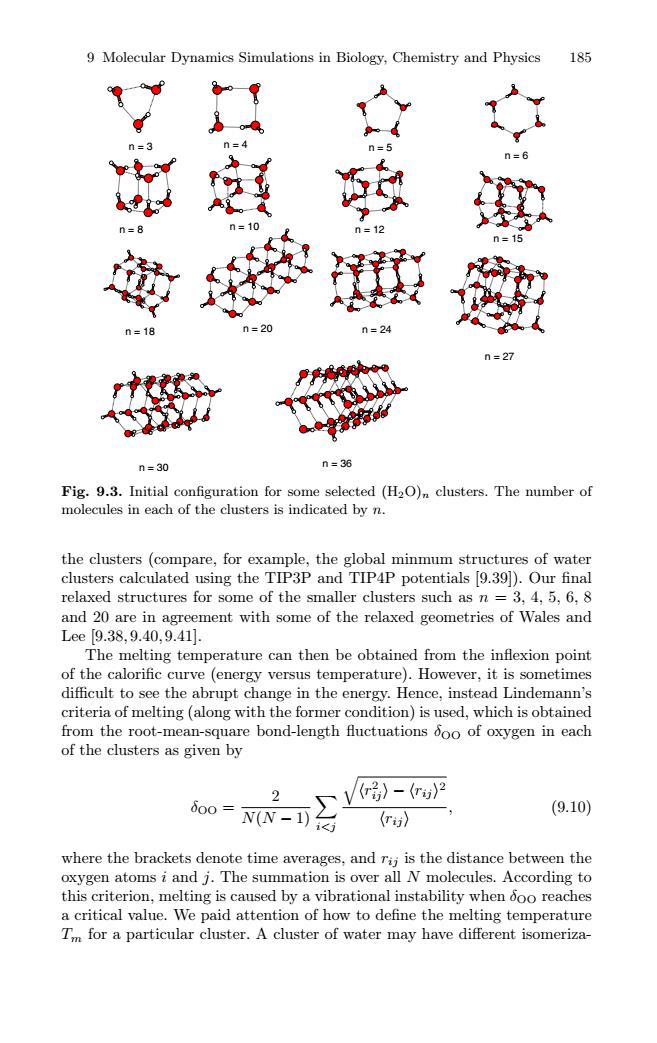
9 Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Biology,Chemistry and Physics 185 n=20 n=27 n=30 n=36 Fig.9.3.Initial configuration for some selected (H2O)n clusters.The number of molecules in each of the clusters is indicated by n. the clusters (compare,for example,the global minmum structures of water clusters calculated using the TIP3P and TIP4P potentials [9.39]).Our final relaxed structures for some of the smaller clusters such as n =3,4,5,6,8 and 20 are in agreement with some of the relaxed geometries of Wales and Lee[9.38,9.40,9.41]. The melting temperature can then be obtained from the inflexion point of the calorific curve (energy versus temperature).However,it is sometimes difficult to see the abrupt change in the energy.Hence,instead Lindemann's criteria of melting (along with the former condition)is used,which is obtained from the root-mean-square bond-length fluctuations ooo of oxygen in each of the clusters as given by 2 (r》-(r》2 800= N(N-1) (9.10) (r》 where the brackets denote time averages,and rij is the distance between the oxygen atoms i and j.The summation is over all N molecules.According to this criterion,melting is caused by a vibrational instability when ooo reaches a critical value.We paid attention of how to define the melting temperature Tm for a particular cluster.A cluster of water may have different isomeriza-9 Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Biology, Chemistry and Physics 185 n = 8 n = 10 n = 15 n = 27 n = 30 n = 18 n = 3 n = 4 n = 5 n = 12 n = 6 n = 20 n = 24 n = 36 Fig. 9.3. Initial configuration for some selected (H2O)n clusters. The number of molecules in each of the clusters is indicated by n. the clusters (compare, for example, the global minmum structures of water clusters calculated using the TIP3P and TIP4P potentials [9.39]). Our final relaxed structures for some of the smaller clusters such as n = 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 and 20 are in agreement with some of the relaxed geometries of Wales and Lee [9.38, 9.40, 9.41]. The melting temperature can then be obtained from the inflexion point of the calorific curve (energy versus temperature). However, it is sometimes difficult to see the abrupt change in the energy. Hence, instead Lindemann’s criteria of melting (along with the former condition) is used, which is obtained from the root-mean-square bond-length fluctuations δOO of oxygen in each of the clusters as given by δOO = 2 N(N − 1) i<j 7 r2 ij −rij 2 rij , (9.10) where the brackets denote time averages, and rij is the distance between the oxygen atoms i and j. The summation is over all N molecules. According to this criterion, melting is caused by a vibrational instability when δOO reaches a critical value. We paid attention of how to define the melting temperature Tm for a particular cluster. A cluster of water may have different isomeriza-���