正在加载图片...
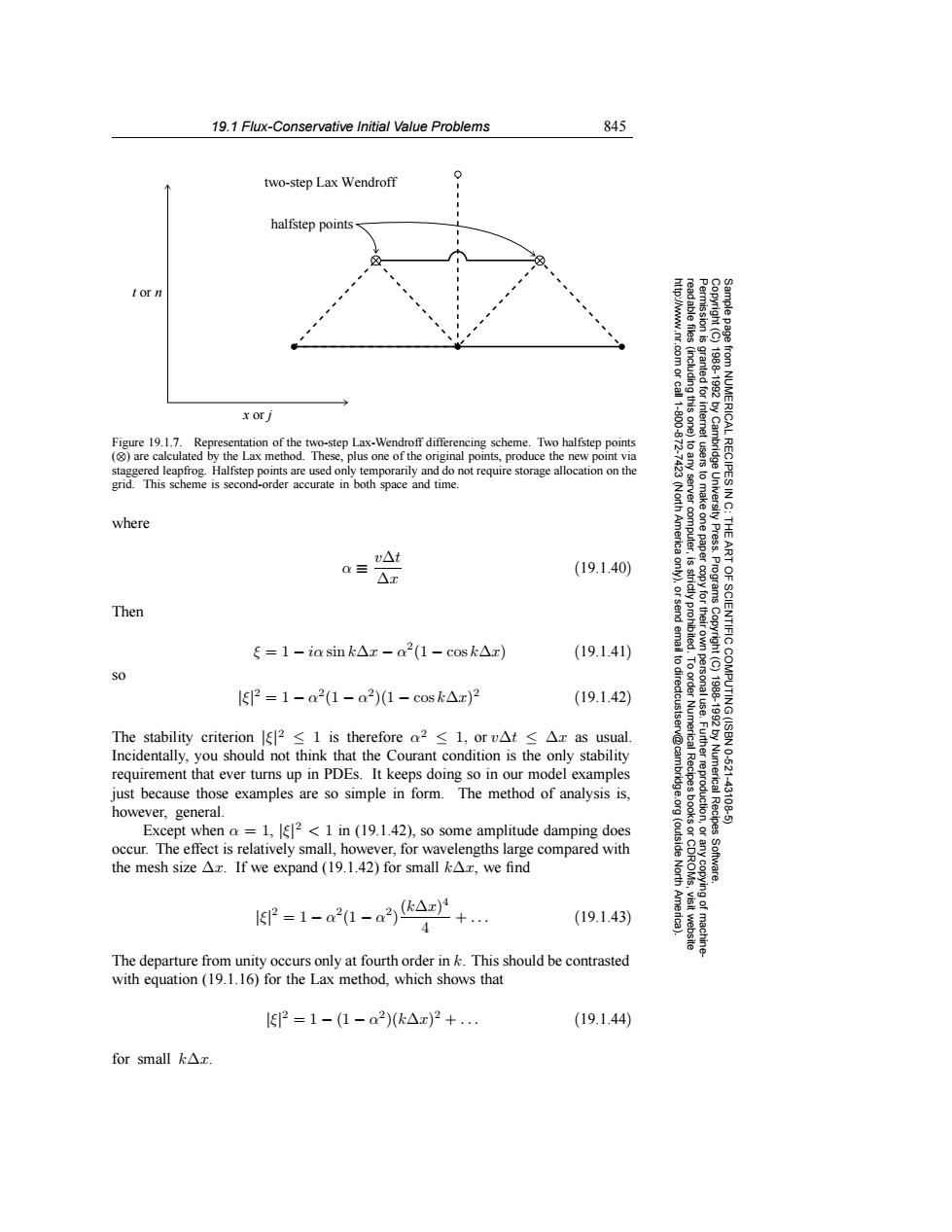
19.1 Flux-Conservative Initial Value Problems 845 two-step Lax Wendroff 0 halfstep points tor n 3 x orj gO7 83g granted for 1.800 Figure 19.1.7.Representation of the two-step Lax-Wendroff differencing scheme.Two halfstep points (are calculated by the Lax method.These,plus one of the original points,produce the new point via staggered leapfrog.Halfstep points are used only temporarily and do not require storage allocation on the grid.This scheme is second-order accurate in both space and time. ⊙ (North where America Press. THE v△t a三 △x (19.1.40) 9 Programs Then SCIENTIFIC ξ=1-ia sin k△x-a2(1-cosk△x) (19.1.41) SO 12=1-a2(1-a2)1-cosk△x)2 (19.1.42) COMPUTING (ISBN The stability criterion|2≤1 is therefore o2≤l,orv△t≤△c as usual. 1920 Incidentally,you should not think that the Courant condition is the only stability requirement that ever turns up in PDEs.It keeps doing so in our model examples Numerical 10-621 just because those examples are so simple in form.The method of analysis is, 43106 however,general. idge.org uctio Except when a =1,2<1 in (19.1.42),so some amplitude damping does occur.The effect is relatively small,however,for wavelengths large compared with (outside Recipes the mesh size Ax.If we expand(19.1.42)for small kAx,we find North Software. 1r=1-a20-a2ka+. 4 (19.1.43) The departure from unity occurs only at fourth order in k.This should be contrasted with equation(19.1.16)for the Lax method,which shows that 2=1-(1-a2)(k△x)2+.. (19.1.44) for small△x.19.1 Flux-Conservative Initial Value Problems 845 Permission is granted for internet users to make one paper copy for their own personal use. Further reproduction, or any copyin Copyright (C) 1988-1992 by Cambridge University Press. Programs Copyright (C) 1988-1992 by Numerical Recipes Software. Sample page from NUMERICAL RECIPES IN C: THE ART OF SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING (ISBN 0-521-43108-5) g of machinereadable files (including this one) to any server computer, is strictly prohibited. To order Numerical Recipes books or CDROMs, visit website http://www.nr.com or call 1-800-872-7423 (North America only), or send email to directcustserv@cambridge.org (outside North America). t or n x or j halfstep points two-step Lax Wendroff Figure 19.1.7. Representation of the two-step Lax-Wendroff differencing scheme. Two halfstep points (⊗) are calculated by the Lax method. These, plus one of the original points, produce the new point via staggered leapfrog. Halfstep points are used only temporarily and do not require storage allocation on the grid. This scheme is second-order accurate in both space and time. where α ≡ v∆t ∆x (19.1.40) Then ξ = 1 − iα sin k∆x − α2(1 − cos k∆x) (19.1.41) so |ξ| 2 = 1 − α2(1 − α2)(1 − cos k∆x) 2 (19.1.42) The stability criterion |ξ| 2 ≤ 1 is therefore α2 ≤ 1, or v∆t ≤ ∆x as usual. Incidentally, you should not think that the Courant condition is the only stability requirement that ever turns up in PDEs. It keeps doing so in our model examples just because those examples are so simple in form. The method of analysis is, however, general. Except when α = 1, |ξ| 2 < 1 in (19.1.42), so some amplitude damping does occur. The effect is relatively small, however, for wavelengths large compared with the mesh size ∆x. If we expand (19.1.42) for small k∆x, we find |ξ| 2 = 1 − α2(1 − α2) (k∆x)4 4 + ... (19.1.43) The departure from unity occurs only at fourth order in k. This should be contrasted with equation (19.1.16) for the Lax method, which shows that |ξ| 2 = 1 − (1 − α2)(k∆x) 2 + ... (19.1.44) for small k∆x