正在加载图片...
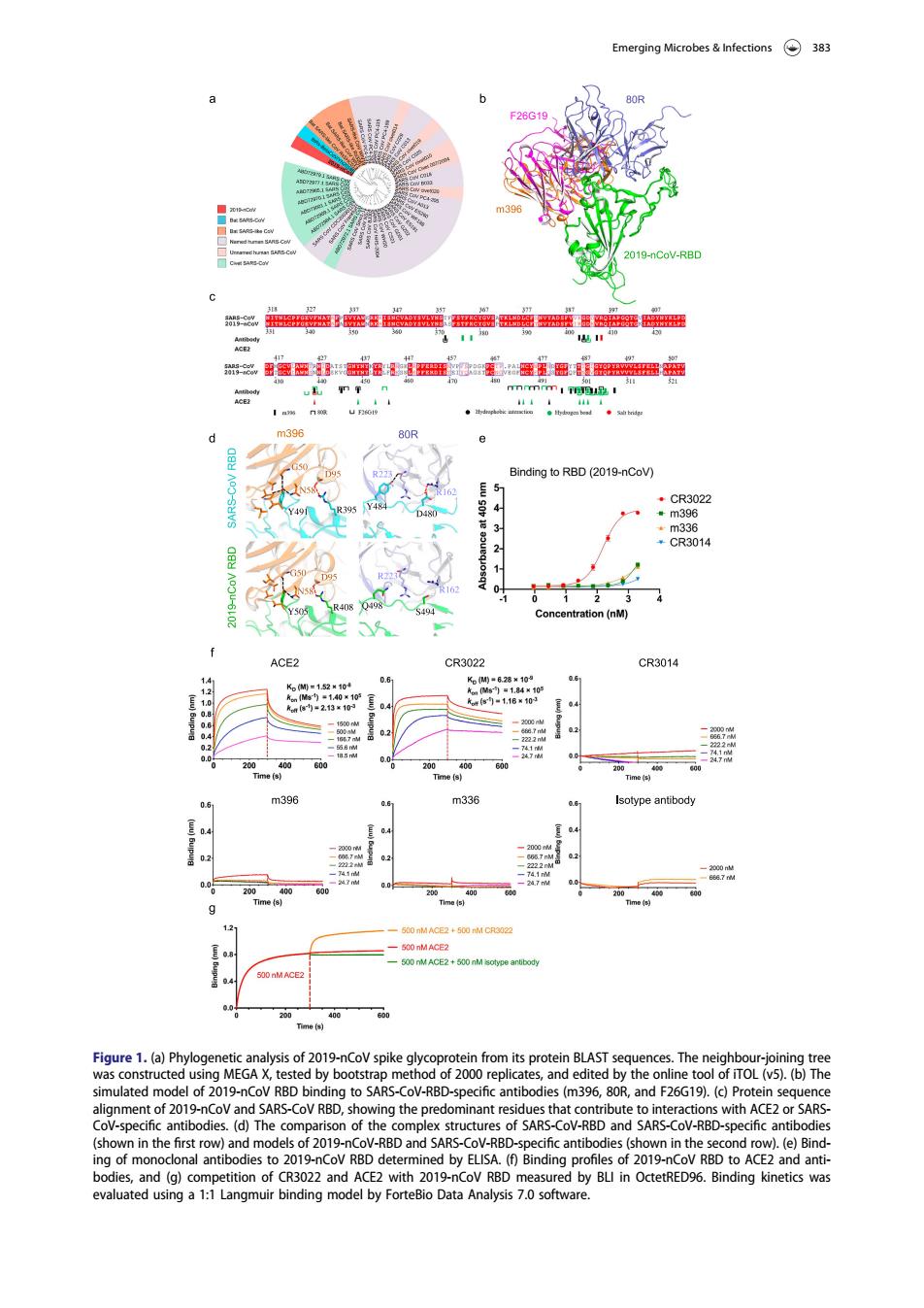
Emerging Microbes Infections 383 019-nCoV-RBI 器之围海臣】器益用器系海金思】严品 Bnding to RBD (2019-nCov CE CR3014 400 Tm330 2+500 Figure1.(a)Phyl sis of 2019-nCoV spike in from its protein BLAST L()Th model of 2019-nCov BBD a by IO SARS-COV-RB mod Dand SARS and (g)co by BU in OctetRED96.Binding kinetics was ated using a 1:1 angmui l by ForteB ata Figure 1. (a) Phylogenetic analysis of 2019-nCoV spike glycoprotein from its protein BLAST sequences. The neighbour-joining tree was constructed using MEGA X, tested by bootstrap method of 2000 replicates, and edited by the online tool of iTOL (v5). (b) The simulated model of 2019-nCoV RBD binding to SARS-CoV-RBD-specific antibodies (m396, 80R, and F26G19). (c) Protein sequence alignment of 2019-nCoV and SARS-CoV RBD, showing the predominant residues that contribute to interactions with ACE2 or SARSCoV-specific antibodies. (d) The comparison of the complex structures of SARS-CoV-RBD and SARS-CoV-RBD-specific antibodies (shown in the first row) and models of 2019-nCoV-RBD and SARS-CoV-RBD-specific antibodies (shown in the second row). (e) Binding of monoclonal antibodies to 2019-nCoV RBD determined by ELISA. (f) Binding profiles of 2019-nCoV RBD to ACE2 and antibodies, and (g) competition of CR3022 and ACE2 with 2019-nCoV RBD measured by BLI in OctetRED96. Binding kinetics was evaluated using a 1:1 Langmuir binding model by ForteBio Data Analysis 7.0 software. Emerging Microbes & Infections 383