正在加载图片...
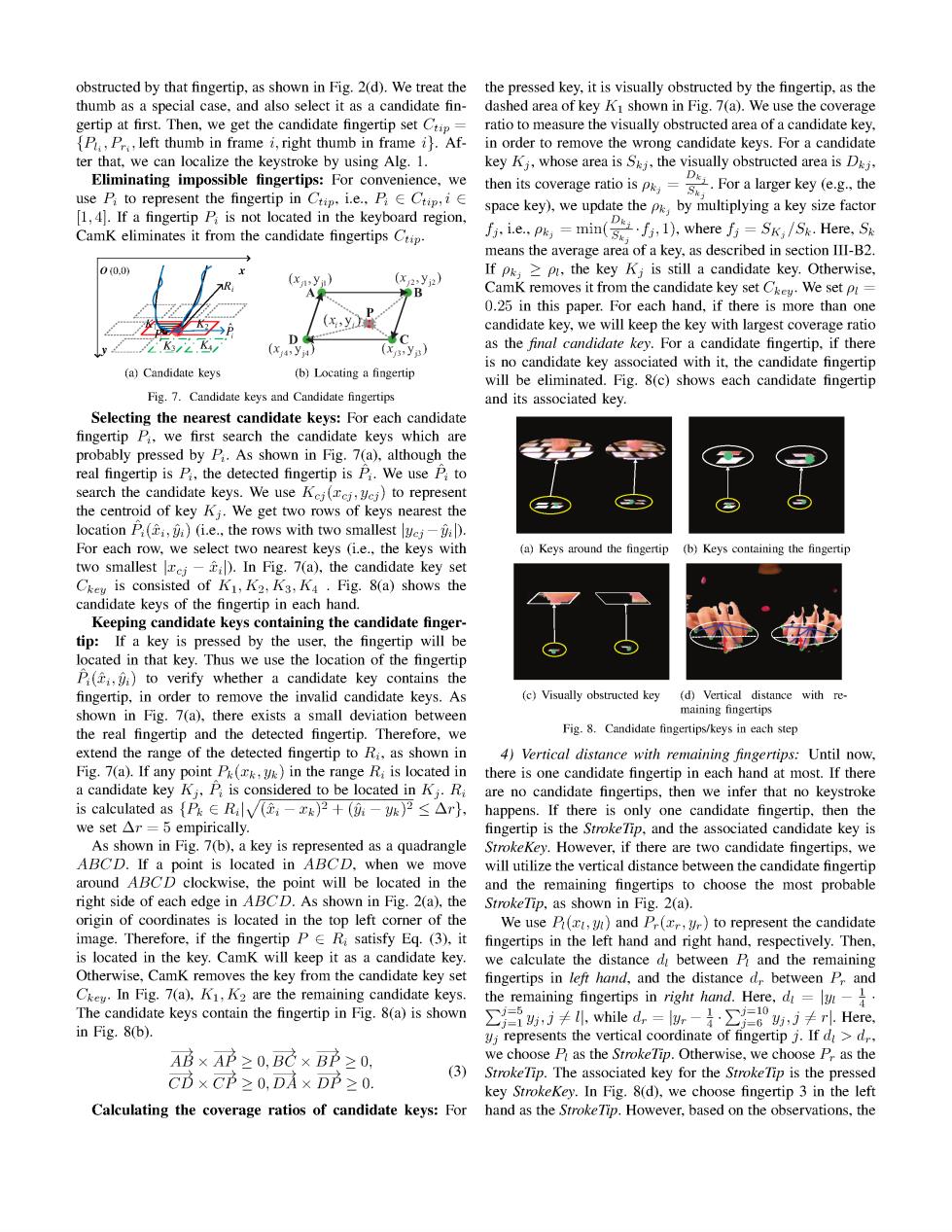
obstructed by that fingertip,as shown in Fig.2(d).We treat the the pressed key,it is visually obstructed by the fingertip,as the thumb as a special case,and also select it as a candidate fin- dashed area of key Ki shown in Fig.7(a).We use the coverage gertip at first.Then,we get the candidate fingertip set Cp= ratio to measure the visually obstructed area of a candidate key, P,Pr left thumb in frame i,right thumb in frame i).Af- in order to remove the wrong candidate keys.For a candidate ter that,we can localize the keystroke by using Alg.1. key Ki,whose area is S,the visually obstructed area is Dj. Eliminating impossible fingertips:For convenience,we use Pi to represent the fingertip in Ctip.i.e..PE Ctip,iE hncoveraisFor larger key (the [1,4].If a fingertip P is not located in the keyboard region, space key),we update the p&,by multiplying a key size factor CamK eliminates it from the candidate fingertips Ctip. fi,i.e..pk =min(se j 1).where fj=SK/Sk.Here,5 means the average area of a key,as described in section III-B2. 00.0) If pk,>p,the key Kj is still a candidate key.Otherwise, (xyn) () A B CamK removes it from the candidate key set Ce We set pi- 0.25 in this paper.For each hand,if there is more than one (x,y2 candidate key,we will keep the key with largest coverage ratio D (y4ya) (x,ya) as the final candidate key.For a candidate fingertip,if there is no candidate key associated with it,the candidate fingertip (a)Candidate keys (b)Locating a fingertip will be eliminated.Fig.8(c)shows each candidate fingertip Fig.7.Candidate keys and Candidate fingertips and its associated key. Selecting the nearest candidate keys:For each candidate fingertip P,we first search the candidate keys which are probably pressed by P.As shown in Fig.7(a),although the real fingertip is P,the detected fingertip is P.We use P to search the candidate keys.We use Kej(rei,yei)to represent the centroid of key Kj.We get two rows of keys nearest the location P()(i.e.,the rows with two smallest ye. For each row,we select two nearest keys (i.e.,the keys with (a)Keys around the fingertip (b)Keys containing the fingertip two smallest ci).In Fig.7(a),the candidate key set Ckey is consisted of K1,K2,K3,K4.Fig.8(a)shows the candidate keys of the fingertip in each hand. Keeping candidate keys containing the candidate finger- tip:If a key is pressed by the user,the fingertip will be located in that key.Thus we use the location of the fingertip P(,)to verify whether a candidate key contains the fingertip,in order to remove the invalid candidate keys.As (c)Visually obstructed key (d)Vertical distance with re shown in Fig.7(a),there exists a small deviation between maining fingertips the real fingertip and the detected fingertip.Therefore,we Fig.8.Candidate fingertips/keys in each step extend the range of the detected fingertip to Ri,as shown in 4)Vertical distance with remaining fingertips:Until now, Fig.7(a).If any point P(k,)in the range Ri is located in there is one candidate fingertip in each hand at most.If there a candidate key Ki,P is considered to be located in Ki.R are no candidate fingertips,then we infer that no keystroke is calculated as {PRilv()2+()2<Ar},happens.If there is only one candidate fingertip,then the we set Ar -5 empirically. fingertip is the StrokeTip,and the associated candidate key is As shown in Fig.7(b),a key is represented as a quadrangle StrokeKey.However,if there are two candidate fingertips,we ABCD.If a point is located in ABCD,when we move will utilize the vertical distance between the candidate fingertip around ABCD clockwise,the point will be located in the and the remaining fingertips to choose the most probable right side of each edge in ABCD.As shown in Fig.2(a).the StrokeTip,as shown in Fig.2(a). origin of coordinates is located in the top left corner of the We use P(x,)and P(xr,r)to represent the candidate image.Therefore,if the fingertip PRi satisfy Eq.(3),it fingertips in the left hand and right hand,respectively.Then is located in the key.CamK will keep it as a candidate key. we calculate the distance d between P and the remaining Otherwise,CamK removes the key from the candidate key set fingertips in left hand,and the distance d between Pr and Ce.In Fig.7(a).K1,K2 are the remaining candidate keys.the remaining fingertips in right hand.Here,d The candidate keys contain the fingertip in Fig.8(a)is shown ∑i5,j≠,while d,,=lr-}·∑0,i≠r小.Here in Fig.8(b). yi represents the vertical coordinate of fingertip j.If d>d, AB×AP≥0,BC×BP≥0, we choose P as the StrokeTip.Otherwise,we choose B.as the Cb×C2≥0,DA×Dp≥0. (3)StrokeTip.The associated key for the StrokeTip is the pressed key StrokeKey.In Fig.8(d),we choose fingertip 3 in the left Calculating the coverage ratios of candidate keys:For hand as the StrokeTip.However,based on the observations,the