正在加载图片...
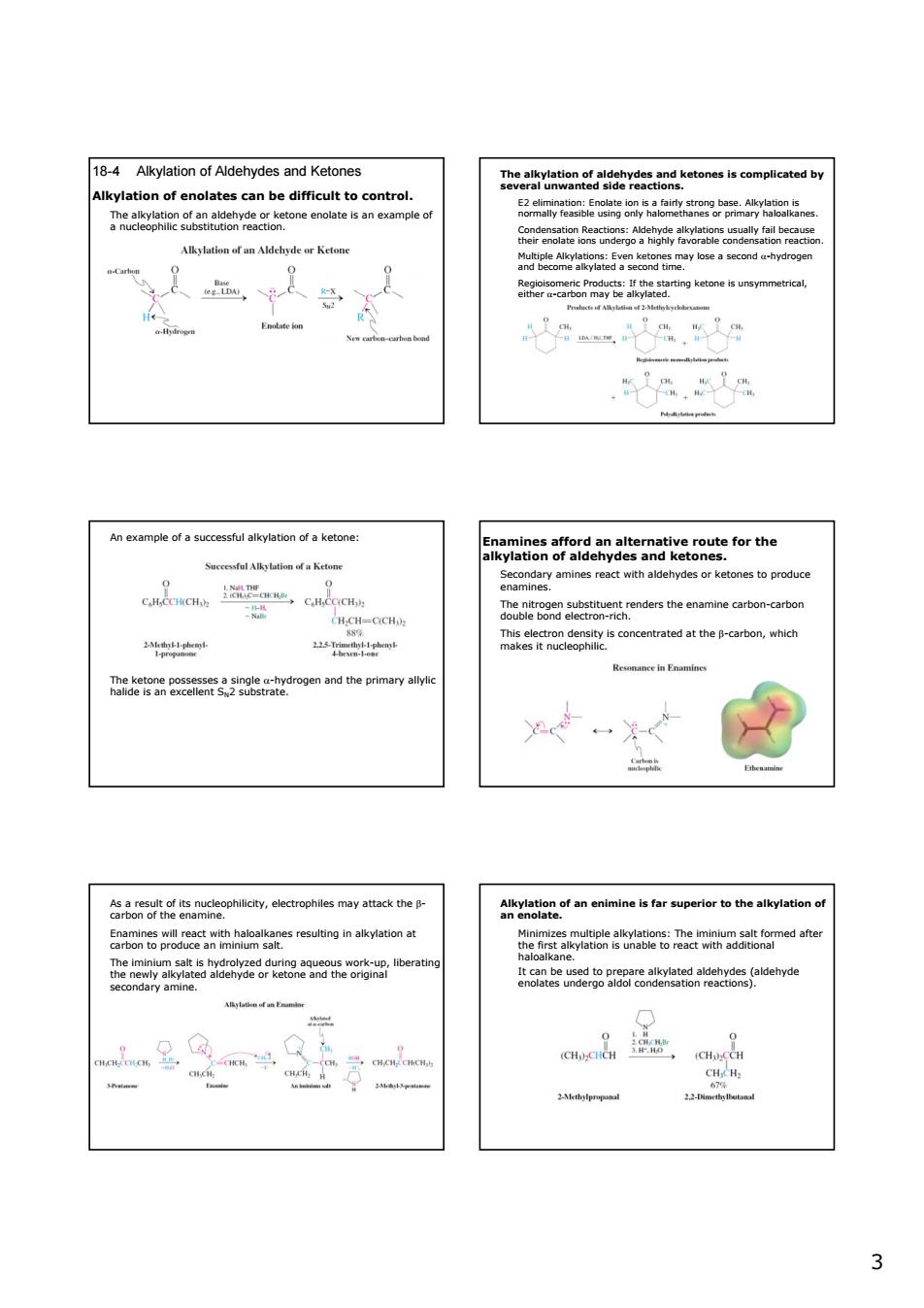
18-4 Alkvlation of Aldehvdes and Ketones control . An example of a successful alkylation of a ketone 5navmeatfeideaateanatikepeteforthe Alkylation of a Ketom CH H.CH-CICH dotble8etiethnenderstheenamnearbonmeartboa 21 d he pimary lve Aheienofanentmineisfarsperiortothealkyiationod eoeeameane saenteseeeeiegi8eeteaee2roesaaerd 3 3 18-4 Alkylation of Aldehydes and Ketones Alkylation of enolates can be difficult to control. The alkylation of an aldehyde or ketone enolate is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The alkylation of aldehydes and ketones is complicated by several unwanted side reactions. E2 elimination: Enolate ion is a fairly strong base. Alkylation is normally feasible using only halomethanes or primary haloalkanes. Condensation Reactions: Aldehyde alkylations usually fail because their enolate ions undergo a highly favorable condensation reaction. Multiple Alkylations: Even ketones may lose a second α-hydrogen and become alkylated a second time. Regioisomeric Products: If the starting ketone is unsymmetrical, either α-carbon may be alkylated. An example of a successful alkylation of a ketone: The ketone possesses a single α-hydrogen and the primary allylic halide is an excellent SN2 substrate. Enamines afford an alternative route for the alkylation of aldehydes and ketones. Secondary amines react with aldehydes or ketones to produce enamines. The nitrogen substituent renders the enamine carbon-carbon double bond electron-rich. This electron density is concentrated at the β-carbon, which makes it nucleophilic. As a result of its nucleophilicity, electrophiles may attack the β- carbon of the enamine. Enamines will react with haloalkanes resulting in alkylation at carbon to produce an iminium salt. The iminium salt is hydrolyzed during aqueous work-up, liberating the newly alkylated aldehyde or ketone and the original secondary amine. Alkylation of an enimine is far superior to the alkylation of an enolate. Minimizes multiple alkylations: The iminium salt formed after the first alkylation is unable to react with additional haloalkane. It can be used to prepare alkylated aldehydes (aldehyde enolates undergo aldol condensation reactions)