正在加载图片...
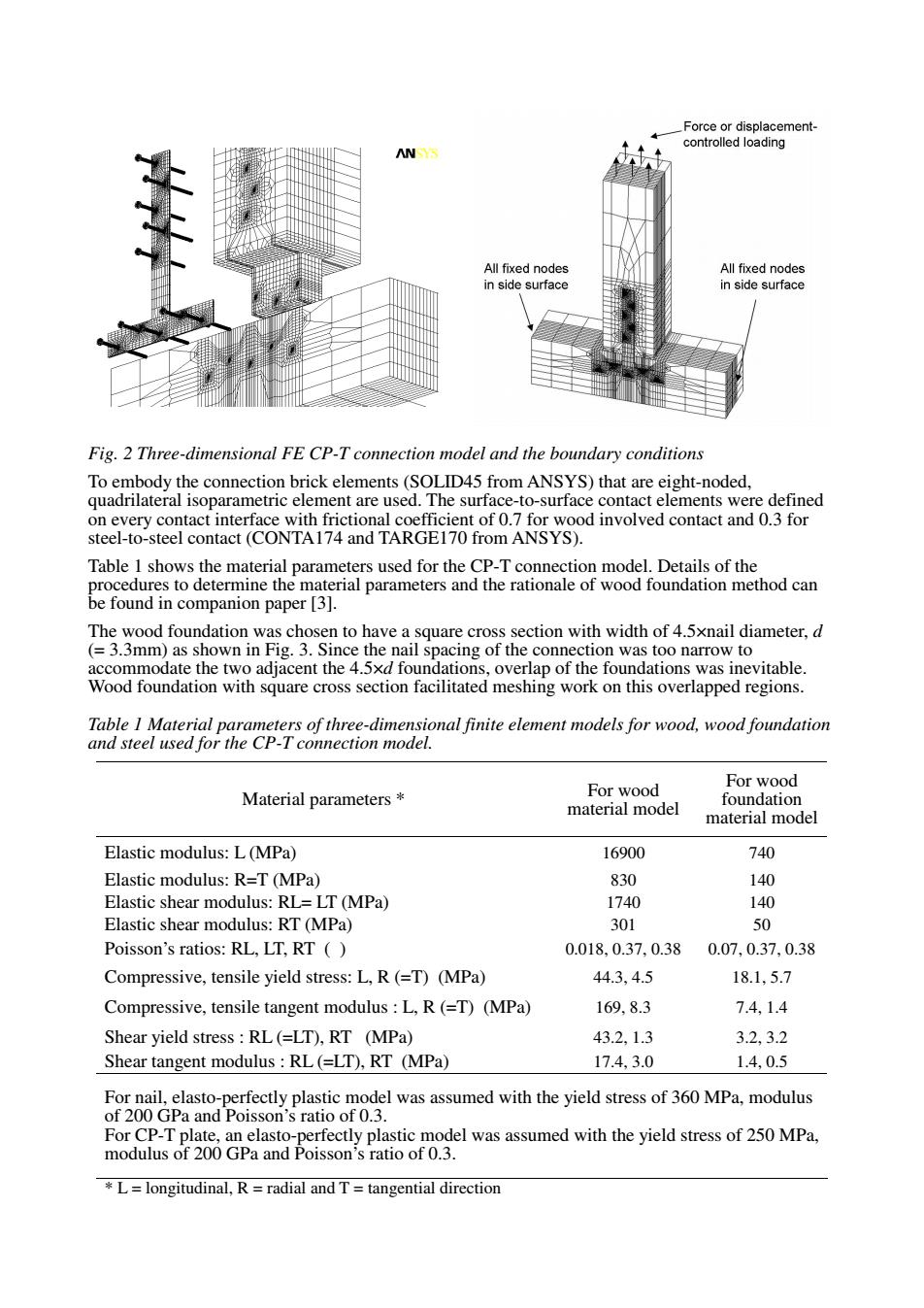
coredeangmen AN Fig.2 Three-dimensional FE CP-T connection model and the boundary conditions Table 1 shows the material parameters used for the CP-T connection model.Details of the ection with width of 4.5xnail diameter,d Wood foundation with square cross section facilitated meshing work on this overlapped regions. Table i mate rs of three dim For For wood Material parameters* material model foundation material mode Elastic modulus:L(MPa) 16900 740 Elastic modulus:R=T (MPa) 830 140 Elastic shear modulus:RL=LT (MPa) 1740 Elastic shear r nodulus:RT(MPa) 201 50 Poisson's ratios:RL,LT,RT() 0.018.0.37,0.38 0.07,0.37,0.38 Compressive,tensile yield stress:L,R(=T)(MPa) 44.3.4.5 18.l,5.7 Compressive,tensile tangent modulus:L.R(=T)(MPa) 169,8.3 7.4,1.4 432,1.3 3.2,3.2 17.4,3.0 1.40.5 the yield e of MPmu For C r 200 GPad Por lastic model was assumed with the yield stress of 250 MPa *L=longitudinal,R=radial and T=tangential directionFig. 2 Three-dimensional FE CP-T connection model and the boundary conditions To embody the connection brick elements (SOLID45 from ANSYS) that are eight-noded, quadrilateral isoparametric element are used. The surface-to-surface contact elements were defined on every contact interface with frictional coefficient of 0.7 for wood involved contact and 0.3 for steel-to-steel contact (CONTA174 and TARGE170 from ANSYS). Table 1 shows the material parameters used for the CP-T connection model. Details of the procedures to determine the material parameters and the rationale of wood foundation method can be found in companion paper [3]. The wood foundation was chosen to have a square cross section with width of 4.5×nail diameter, d (= 3.3mm) as shown in Fig. 3. Since the nail spacing of the connection was too narrow to accommodate the two adjacent the 4.5×d foundations, overlap of the foundations was inevitable. Wood foundation with square cross section facilitated meshing work on this overlapped regions. Table 1 Material parameters of three-dimensional finite element models for wood, wood foundation and steel used for the CP-T connection model. Material parameters * For wood material model For wood foundation material model Elastic modulus: L (MPa) 16900 740 Elastic modulus: R=T (MPa) 830 140 Elastic shear modulus: RL= LT (MPa) 1740 140 Elastic shear modulus: RT (MPa) 301 50 Poisson’s ratios: RL, LT, RT ( ) 0.018, 0.37, 0.38 0.07, 0.37, 0.38 Compressive, tensile yield stress: L, R (=T) (MPa) 44.3, 4.5 18.1, 5.7 Compressive, tensile tangent modulus : L, R (=T) (MPa) 169, 8.3 7.4, 1.4 Shear yield stress : RL (=LT), RT (MPa) 43.2, 1.3 3.2, 3.2 Shear tangent modulus : RL (=LT), RT (MPa) 17.4, 3.0 1.4, 0.5 For nail, elasto-perfectly plastic model was assumed with the yield stress of 360 MPa, modulus of 200 GPa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.3. For CP-T plate, an elasto-perfectly plastic model was assumed with the yield stress of 250 MPa, modulus of 200 GPa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.3. * L = longitudinal, R = radial and T = tangential direction