正在加载图片...
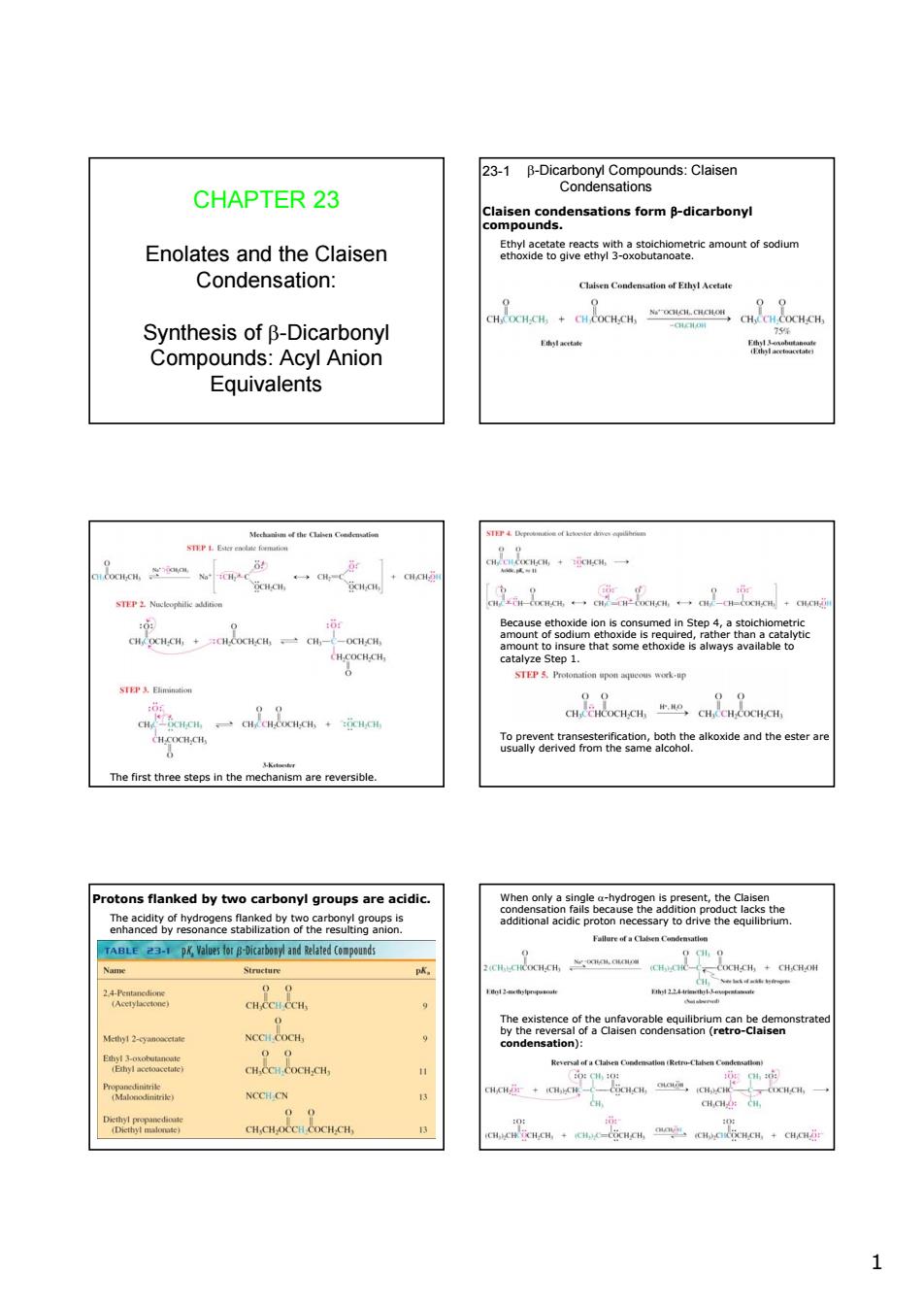
CHAPTER 23 cormdicarbony Enolates and the Claisen etmont odum Condensation: ho:o absioe Synthesis of B-Dicarbonyl Compounds:Acyl Anion Equivalents P&R llde and the The first three st in the mecare reversible. otons flanked by two carbonyl groups are acidic. 3-p NCCH.CN 1 1 CHAPTER 23 Enolates and the Claisen Condensation: Synthesis of β-Dicarbonyl Compounds: Acyl Anion Equivalents β-Dicarbonyl Compounds: Claisen Condensations 23-1 Claisen condensations form β-dicarbonyl compounds. Ethyl acetate reacts with a stoichiometric amount of sodium ethoxide to give ethyl 3-oxobutanoate. The first three steps in the mechanism are reversible. Because ethoxide ion is consumed in Step 4, a stoichiometric amount of sodium ethoxide is required, rather than a catalytic amount to insure that some ethoxide is always available to catalyze Step 1. To prevent transesterification, both the alkoxide and the ester are usually derived from the same alcohol. Protons flanked by two carbonyl groups are acidic. The acidity of hydrogens flanked by two carbonyl groups is enhanced by resonance stabilization of the resulting anion. When only a single α-hydrogen is present, the Claisen condensation fails because the addition product lacks the additional acidic proton necessary to drive the equilibrium. The existence of the unfavorable equilibrium can be demonstrated by the reversal of a Claisen condensation (retro-Claisen condensation):