正在加载图片...
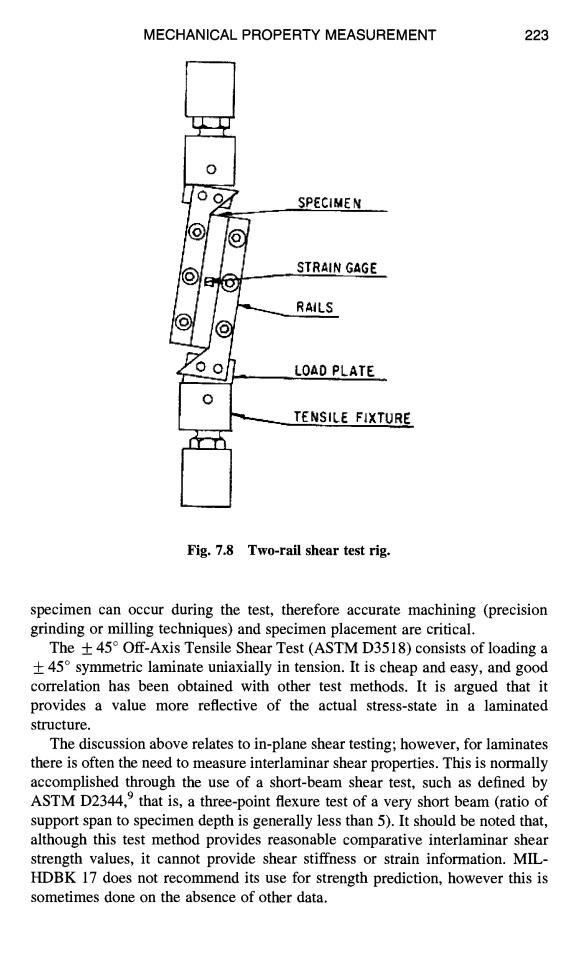
MECHANICAL PROPERTY MEASUREMENT 223 SPECIMEN 0no STRAIN GAGE RAILS LOAD PLATE TENSILE FIXTURE Fig.7.8 Two-rail shear test rig. specimen can occur during the test,therefore accurate machining (precision grinding or milling techniques)and specimen placement are critical. The+45 Off-Axis Tensile Shear Test(ASTM D3518)consists of loading a +45 symmetric laminate uniaxially in tension.It is cheap and easy,and good correlation has been obtained with other test methods.It is argued that it provides a value more reflective of the actual stress-state in a laminated structure. The discussion above relates to in-plane shear testing;however,for laminates there is often the need to measure interlaminar shear properties.This is normally accomplished through the use of a short-beam shear test,such as defined by ASTM D2344,that is,a three-point flexure test of a very short beam (ratio of support span to specimen depth is generally less than 5).It should be noted that, although this test method provides reasonable comparative interlaminar shear strength values,it cannot provide shear stiffness or strain information.MIL- HDBK 17 does not recommend its use for strength prediction,however this is sometimes done on the absence of other data.MECHANICAL PROPERTY MEASUREMENT 223 SPECIMEN STRAIN GAGE RAILS LOAD PLATE TENSILE FjXTURE Fig. 7.8 Two-rail shear test rig. specimen can occur during the test, therefore accurate machining (precision grinding or milling techniques) and specimen placement are critical. The _ 45 ° Off-Axis Tensile Shear Test (ASTM D3518) consists of loading a _ 45 ° symmetric laminate uniaxially in tension. It is cheap and easy, and good correlation has been obtained with other test methods. It is argued that it provides a value more reflective of the actual stress-state in a laminated structure. The discussion above relates to in-plane shear testing; however, for laminates there is often the need to measure interlaminar shear properties. This is normally accomplished through the use of a short-beam shear test, such as defined by ASTM D2344, 9 that is, a three-point flexure test of a very short beam (ratio of support span to specimen depth is generally less than 5). It should be noted that, although this test method provides reasonable comparative interlaminar shear strength values, it cannot provide shear stiffness or strain information. MILHDBK 17 does not recommend its use for strength prediction, however this is sometimes done on the absence of other data