正在加载图片...
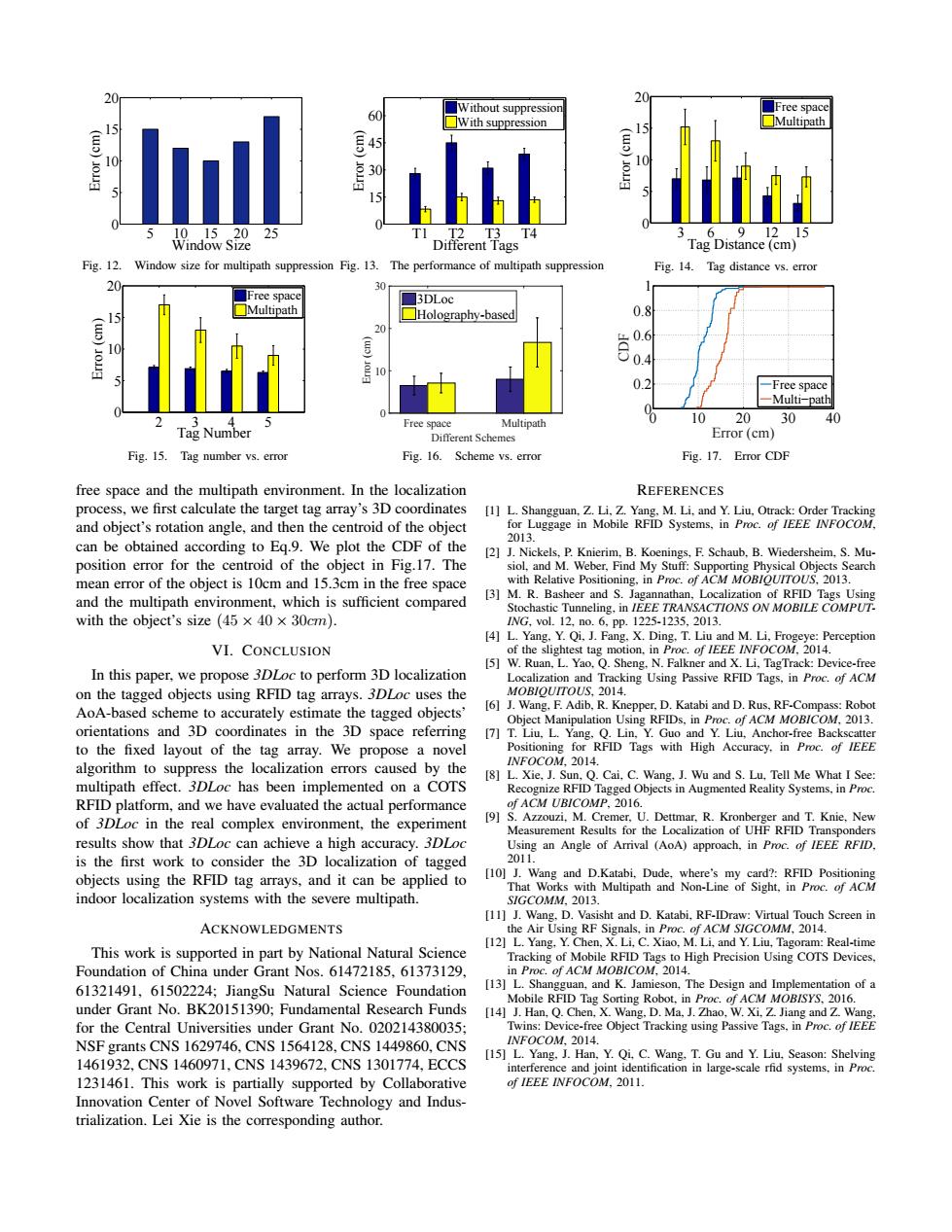
20 ■Without suppression 20 ■Free space 60 ☐Multipath 15 ☐With suppression (w)o 15 15 10 3 l 1015.2025 T4 91215 Window Size Different Tags Tag Distance(cm) Fig.12. Window size for multipath suppression Fig.13. The performance of multipath suppression Fig.14.Tag distance vs.error 30 Free space 3DLoc Multipath ☐Holography-based 0.8 20 0.2 -Free space -Multi-path Free space Multipath 10 20 30 40 Tag Number Different Schemes Error(cm) Fig.15.Tag number vs.error Fig.16.Scheme vs.error Fig.17.Error CDF free space and the multipath environment.In the localization REFERENCES process,we first calculate the target tag array's 3D coordinates [1]L.Shangguan,Z.Li,Z.Yang,M.Li,and Y.Liu,Otrack:Order Tracking and object's rotation angle,and then the centroid of the object for Luggage in Mobile RFID Systems,in Proc.of IEEE INFOCOM. 2013 can be obtained according to Eq.9.We plot the CDF of the [2]J.Nickels,P.Knierim,B.Koenings,F.Schaub,B.Wiedersheim,S.Mu- position error for the centroid of the object in Fig.17.The siol,and M.Weber,Find My Stuff:Supporting Physical Objects Search mean error of the object is 10cm and 15.3cm in the free space with Relative Positioning,in Proc.of ACM MOBIOUITOUS,2013. and the multipath environment,which is sufficient compared [3]M.R.Basheer and S.Jagannathan,Localization of RFID Tags Using Stochastic Tunneling.in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUT. with the object's size(45×40×30cm). NG,ol.12,no.6,Pp.1225-1235,2013. [4]L.Yang.Y.Qi.J.Fang.X.Ding.T.Liu and M.Li,Frogeye:Perception VI.CONCLUSION of the slightest tag motion,in Proc.of IEEE INFOCOM,2014. 5]W.Ruan,L.Yao,Q.Sheng.N.Falkner and X.Li,TagTrack:Device-free In this paper,we propose 3DLoc to perform 3D localization Localization and Tracking Using Passive RFID Tags,in Proc.of ACM on the tagged objects using RFID tag arrays.3DLoc uses the MOBIOUITOUS,2014. AoA-based scheme to accurately estimate the tagged objects' [6]J.Wang.F.Adib,R.Knepper,D.Katabi and D.Rus,RF-Compass:Robot Object Manipulation Using RFIDs,in Proc.of ACM MOB/COM,2013. orientations and 3D coordinates in the 3D space referring [7]T.Liu,L.Yang,Q.Lin,Y.Guo and Y.Liu,Anchor-free Backscatter to the fixed layout of the tag array.We propose a novel Positioning for RFID Tags with High Accuracy.in Proc.of IEEE algorithm to suppress the localization errors caused by the INFOCOM.2014. [8]L.Xie,J.Sun,Q.Cai,C.Wang,J.Wu and S.Lu,Tell Me What I See: multipath effect.3DLoc has been implemented on a COTS Recognize RFID Tagged Objects in Augmented Reality Systems.in Proc. RFID platform,and we have evaluated the actual performance of ACM UBICOMP,2016. of 3DLoc in the real complex environment,the experiment [9]S.Azzouzi,M.Cremer,U.Dettmar.R.Kronberger and T.Knie.New Measurement Results for the Localization of UHF RFID Transponders results show that 3DLoc can achieve a high accuracy.3DLoc Using an Angle of Arrival (AoA)approach.in Proc.of IEEE RFID. is the first work to consider the 3D localization of tagged 2011. objects using the RFID tag arrays,and it can be applied to [10]J.Wang and D.Katabi,Dude.where's my card?:RFID Positioning That Works with Multipath and Non-Line of Sight,in Proc.of ACM indoor localization systems with the severe multipath. SIGCOMM.2013. [11]J.Wang,D.Vasisht and D.Katabi,RF-IDraw:Virtual Touch Screen in ACKNOWLEDGMENTS the Air Using RF Signals,in Proc.of ACM S/GCOMM,2014 [12]L.Yang.Y.Chen,X.Li,C.Xiao,M.Li,and Y.Liu,Tagoram:Real-time This work is supported in part by National Natural Science Tracking of Mobile RFID Tags to High Precision Using COTS Devices. Foundation of China under Grant Nos.61472185.61373129. in Proc.of ACM MOBICOM,2014. 61321491,61502224;JiangSu Natural Science Foundation [13]L.Shangguan,and K.Jamieson,The Design and Implementation of a Mobile RFID Tag Sorting Robot,in Proc.of ACM MOBISYS,2016. under Grant No.BK20151390:Fundamental Research Funds [14]J.Han,Q.Chen,X.Wang,D.Ma,J.Zhao,W.Xi,Z.Jiang and Z.Wang for the Central Universities under Grant No.020214380035: Twins:Device-free Object Tracking using Passive Tags,in Proc.of IEEE NSF grants CNS 1629746,CNS 1564128,CNS 1449860,CNS INFOCOM,2014. [15]L.Yang.J.Han,Y.Qi,C.Wang.T.Gu and Y.Liu,Season:Shelving 1461932.CNS1460971.CNS1439672.CNS1301774.ECCS interference and joint identification in large-scale rfid systems,in Proc. 1231461.This work is partially supported by Collaborative of IEEE INFOCOM,2011. Innovation Center of Novel Software Technology and Indus- trialization.Lei Xie is the corresponding author.5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 20 Window Size Error (cm) Fig. 12. Window size for multipath suppression T1 T2 T3 T4 0 15 30 45 60 Error (cm) Different Tags Without suppression With suppression Fig. 13. The performance of multipath suppression 3 6 9 12 15 0 5 10 15 20 Error (cm) Tag Distance (cm) Free space Multipath Fig. 14. Tag distance vs. error 2 3 4 5 0 5 10 15 20 Error (cm) Tag Number Free space Multipath Fig. 15. Tag number vs. error Different Schemes Free space Multipath Error (cm) 0 10 20 30 3DLoc Holography-based Fig. 16. Scheme vs. error 0 10 20 30 40 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Error (cm) CDF Free space Multi−path Fig. 17. Error CDF free space and the multipath environment. In the localization process, we first calculate the target tag array’s 3D coordinates and object’s rotation angle, and then the centroid of the object can be obtained according to Eq.9. We plot the CDF of the position error for the centroid of the object in Fig.17. The mean error of the object is 10cm and 15.3cm in the free space and the multipath environment, which is sufficient compared with the object’s size (45 × 40 × 30cm). VI. CONCLUSION In this paper, we propose 3DLoc to perform 3D localization on the tagged objects using RFID tag arrays. 3DLoc uses the AoA-based scheme to accurately estimate the tagged objects’ orientations and 3D coordinates in the 3D space referring to the fixed layout of the tag array. We propose a novel algorithm to suppress the localization errors caused by the multipath effect. 3DLoc has been implemented on a COTS RFID platform, and we have evaluated the actual performance of 3DLoc in the real complex environment, the experiment results show that 3DLoc can achieve a high accuracy. 3DLoc is the first work to consider the 3D localization of tagged objects using the RFID tag arrays, and it can be applied to indoor localization systems with the severe multipath. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work is supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61472185, 61373129, 61321491, 61502224; JiangSu Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. BK20151390; Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. 020214380035; NSF grants CNS 1629746, CNS 1564128, CNS 1449860, CNS 1461932, CNS 1460971, CNS 1439672, CNS 1301774, ECCS 1231461. This work is partially supported by Collaborative Innovation Center of Novel Software Technology and Industrialization. Lei Xie is the corresponding author. REFERENCES [1] L. Shangguan, Z. Li, Z. Yang, M. Li, and Y. Liu, Otrack: Order Tracking for Luggage in Mobile RFID Systems, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, 2013. [2] J. Nickels, P. Knierim, B. Koenings, F. Schaub, B. Wiedersheim, S. Musiol, and M. Weber, Find My Stuff: Supporting Physical Objects Search with Relative Positioning, in Proc. of ACM MOBIQUITOUS, 2013. [3] M. R. Basheer and S. Jagannathan, Localization of RFID Tags Using Stochastic Tunneling, in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 1225-1235, 2013. [4] L. Yang, Y. Qi, J. Fang, X. Ding, T. Liu and M. Li, Frogeye: Perception of the slightest tag motion, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, 2014. [5] W. Ruan, L. Yao, Q. Sheng, N. Falkner and X. Li, TagTrack: Device-free Localization and Tracking Using Passive RFID Tags, in Proc. of ACM MOBIQUITOUS, 2014. [6] J. Wang, F. Adib, R. Knepper, D. Katabi and D. Rus, RF-Compass: Robot Object Manipulation Using RFIDs, in Proc. of ACM MOBICOM, 2013. [7] T. Liu, L. Yang, Q. Lin, Y. Guo and Y. Liu, Anchor-free Backscatter Positioning for RFID Tags with High Accuracy, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, 2014. [8] L. Xie, J. Sun, Q. Cai, C. Wang, J. Wu and S. Lu, Tell Me What I See: Recognize RFID Tagged Objects in Augmented Reality Systems, in Proc. of ACM UBICOMP, 2016. [9] S. Azzouzi, M. Cremer, U. Dettmar, R. Kronberger and T. Knie, New Measurement Results for the Localization of UHF RFID Transponders Using an Angle of Arrival (AoA) approach, in Proc. of IEEE RFID, 2011. [10] J. Wang and D.Katabi, Dude, where’s my card?: RFID Positioning That Works with Multipath and Non-Line of Sight, in Proc. of ACM SIGCOMM, 2013. [11] J. Wang, D. Vasisht and D. Katabi, RF-IDraw: Virtual Touch Screen in the Air Using RF Signals, in Proc. of ACM SIGCOMM, 2014. [12] L. Yang, Y. Chen, X. Li, C. Xiao, M. Li, and Y. Liu, Tagoram: Real-time Tracking of Mobile RFID Tags to High Precision Using COTS Devices, in Proc. of ACM MOBICOM, 2014. [13] L. Shangguan, and K. Jamieson, The Design and Implementation of a Mobile RFID Tag Sorting Robot, in Proc. of ACM MOBISYS, 2016. [14] J. Han, Q. Chen, X. Wang, D. Ma, J. Zhao, W. Xi, Z. Jiang and Z. Wang, Twins: Device-free Object Tracking using Passive Tags, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, 2014. [15] L. Yang, J. Han, Y. Qi, C. Wang, T. Gu and Y. Liu, Season: Shelving interference and joint identification in large-scale rfid systems, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM, 2011