正在加载图片...
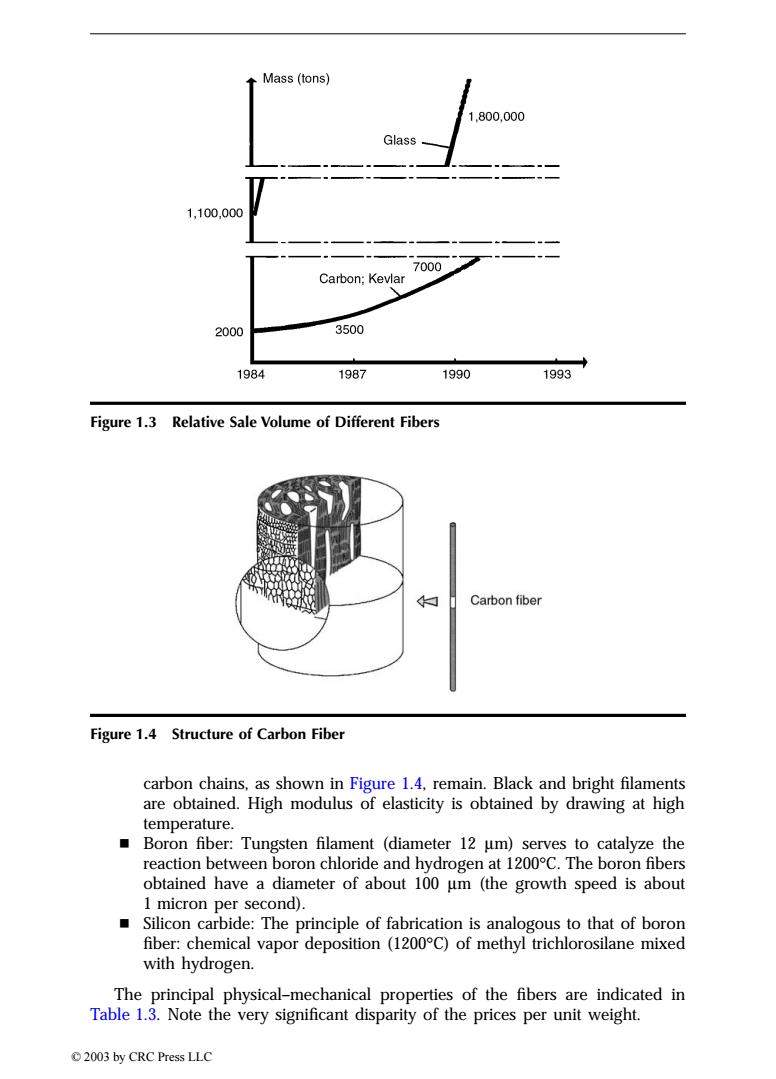
Mass (tons) 1.800,000 Glass 1,100,000 7000 Carbon;Kevlar 2000 3500 1984 1987 1990 1993 Figure 1.3 Relative Sale Volume of Different Fibers Carbon fiber Figure 1.4 Structure of Carbon Fiber carbon chains,as shown in Figure 1.4,remain.Black and bright filaments are obtained.High modulus of elasticity is obtained by drawing at high temperature. ■ Boron fiber:Tungsten filament (diameter 12 um)serves to catalyze the reaction between boron chloride and hydrogen at 1200C.The boron fibers obtained have a diameter of about 100 um (the growth speed is about 1 micron per second). Silicon carbide:The principle of fabrication is analogous to that of boron fiber:chemical vapor deposition (1200C)of methyl trichlorosilane mixed with hydrogen. The principal physical-mechanical properties of the fibers are indicated in Table 1.3.Note the very significant disparity of the prices per unit weight. 2003 by CRC Press LLCcarbon chains, as shown in Figure 1.4, remain. Black and bright filaments are obtained. High modulus of elasticity is obtained by drawing at high temperature. Boron fiber: Tungsten filament (diameter 12 mm) serves to catalyze the reaction between boron chloride and hydrogen at 1200∞C. The boron fibers obtained have a diameter of about 100 mm (the growth speed is about 1 micron per second). Silicon carbide: The principle of fabrication is analogous to that of boron fiber: chemical vapor deposition (1200∞C) of methyl trichlorosilane mixed with hydrogen. The principal physical–mechanical properties of the fibers are indicated in Table 1.3. Note the very significant disparity of the prices per unit weight. Figure 1.3 Relative Sale Volume of Different Fibers Figure 1.4 Structure of Carbon Fiber TX846_Frame_C01 Page 6 Monday, November 18, 2002 10:34 AM © 2003 by CRC Press LLC