正在加载图片...
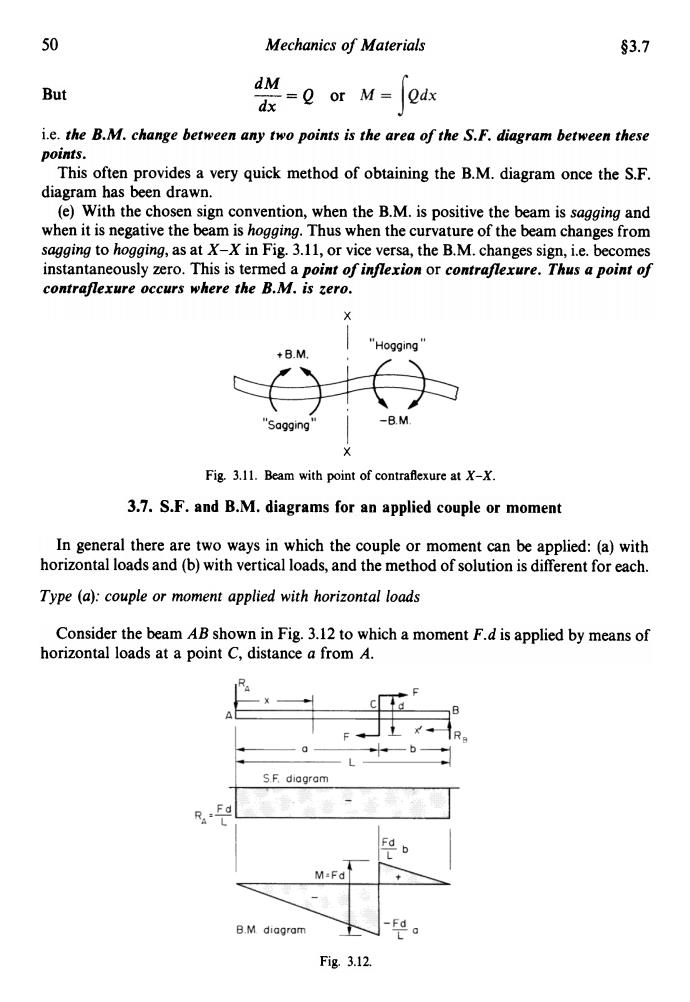
50 Mechanics of Materials §3.7 But or M-ods i.e.the B.M.change between any two points is the area of the S.F.diagram between these points. This often provides a very quick method of obtaining the B.M.diagram once the S.F. diagram has been drawn. (e)With the chosen sign convention,when the B.M.is positive the beam is sagging and when it is negative the beam is hogging.Thus when the curvature of the beam changes from sagging to hogging,as at X-X in Fig.3.11,or vice versa,the B.M.changes sign,i.e.becomes instantaneously zero.This is termed a point of inflexion or contraflexure.Thus a point of contraflexure occurs where the B.M.is zero. X +B.M. "Hogging' "Sagging -B.M Fig.3.11.Beam with point of contraflexure at X-X. 3.7.S.F.and B.M.diagrams for an applied couple or moment In general there are two ways in which the couple or moment can be applied:(a)with horizontal loads and(b)with vertical loads,and the method of solution is different for each. Type (a):couple or moment applied with horizontal loads Consider the beam AB shown in Fig.3.12 to which a moment F.d is applied by means of horizontal loads at a point C,distance a from A. S.F.diagram M-Fd B.M diagram Fd Fig3.12.50 Mechanics of Materials §3.7 dM dx But = Q or i.e. the B.M. change between any two points is the area of the S.F. diagram between these points. This often provides a very quick method of obtaining the B.M. diagram once the S.F. diagram has been drawn. (e) With the chosen sign convention, when the B.M. is positive the beam is sagging and when it is negative the beam is hogging. Thus when the curvature of the beam changes from sagging to hogging, as at x-x in Fig. 3.11, or vice versa, the B.M. changes sign, i.e. becomes instantaneously zero. This is termed a point of inflexion or contra flexure. Thus a point of contra flexure occurs where the B.M. is zero. x x Fig. 3.11. Beam with point of contraflexure at X -X . 3.7. S.F. and B.M. diagrams for an applied couple or moment In general there are two ways in which the couple or moment can be applied: (a) with horizontal loads and (b) with vertical loads, and the method of solution is different for each. Type (a): couple or moment applied with horizontal loads Consider the beam AB shown in Fig. 3.12 to which a moment F.d is applied by means of horizontal loads at a point C, distance a from A. Fig. 3.12