正在加载图片...
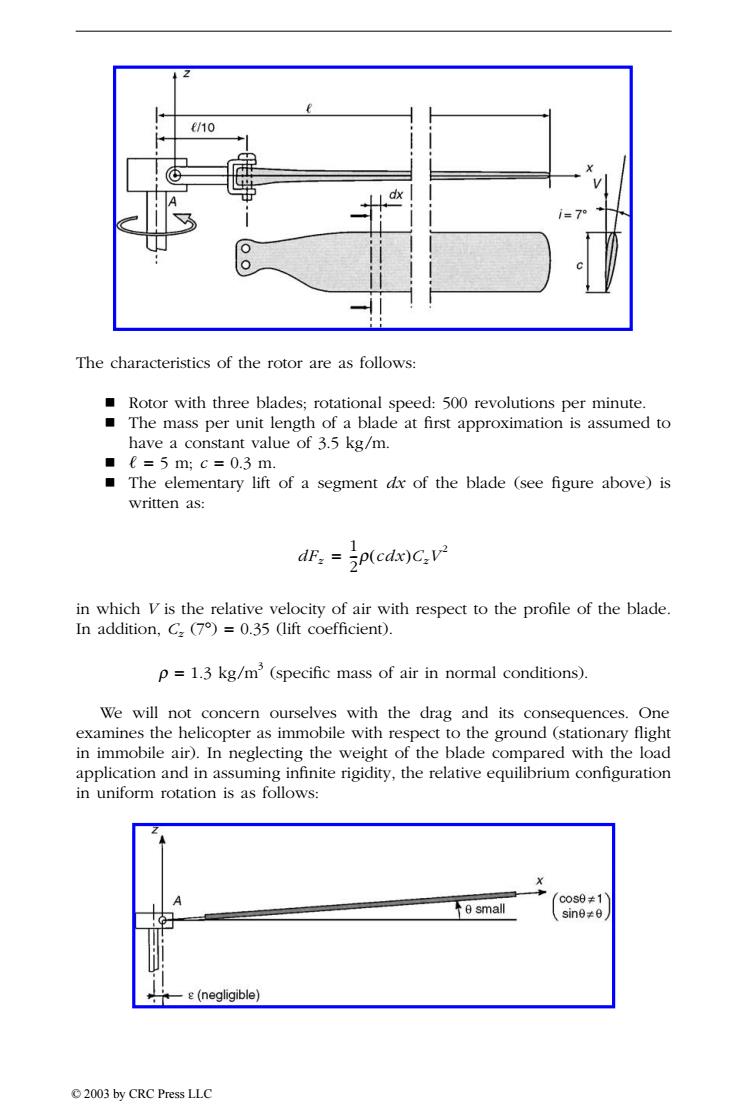
€/10 The characteristics of the rotor are as follows: Rotor with three blades;rotational speed:500 revolutions per minute. The mass per unit length of a blade at first approximation is assumed to have a constant value of 3.5 kg/m. ■e=5m;c=0.3m. The elementary lift of a segment dx of the blade (see figure above)is written as: dF:=p(cdx)C:v2 in which V is the relative velocity of air with respect to the profile of the blade. In addition,C()=0.35 (lift coefficient). p=1.3 kg/m'(specific mass of air in normal conditions). We will not concern ourselves with the drag and its consequences.One examines the helicopter as immobile with respect to the ground(stationary flight in immobile air).In neglecting the weight of the blade compared with the load application and in assuming infinite rigidity,the relative equilibrium configuration in uniform rotation is as follows: c0s0≠1 e small sin8≠e s(negligible) 2003 by CRC Press LLCThe characteristics of the rotor are as follows: Rotor with three blades; rotational speed: 500 revolutions per minute. The mass per unit length of a blade at first approximation is assumed to have a constant value of 3.5 kg/m. = 5 m; c = 0.3 m. The elementary lift of a segment dx of the blade (see figure above) is written as: in which V is the relative velocity of air with respect to the profile of the blade. In addition, Cz (7∞) = 0.35 (lift coefficient). r = 1.3 kg/m3 (specific mass of air in normal conditions). We will not concern ourselves with the drag and its consequences. One examines the helicopter as immobile with respect to the ground (stationary flight in immobile air). In neglecting the weight of the blade compared with the load application and in assuming infinite rigidity, the relative equilibrium configuration in uniform rotation is as follows: dFz 1 2 --r( ) cdx CzV2 = TX846_Frame_C18a Page 348 Monday, November 18, 2002 12:40 PM © 2003 by CRC Press LLC