正在加载图片...
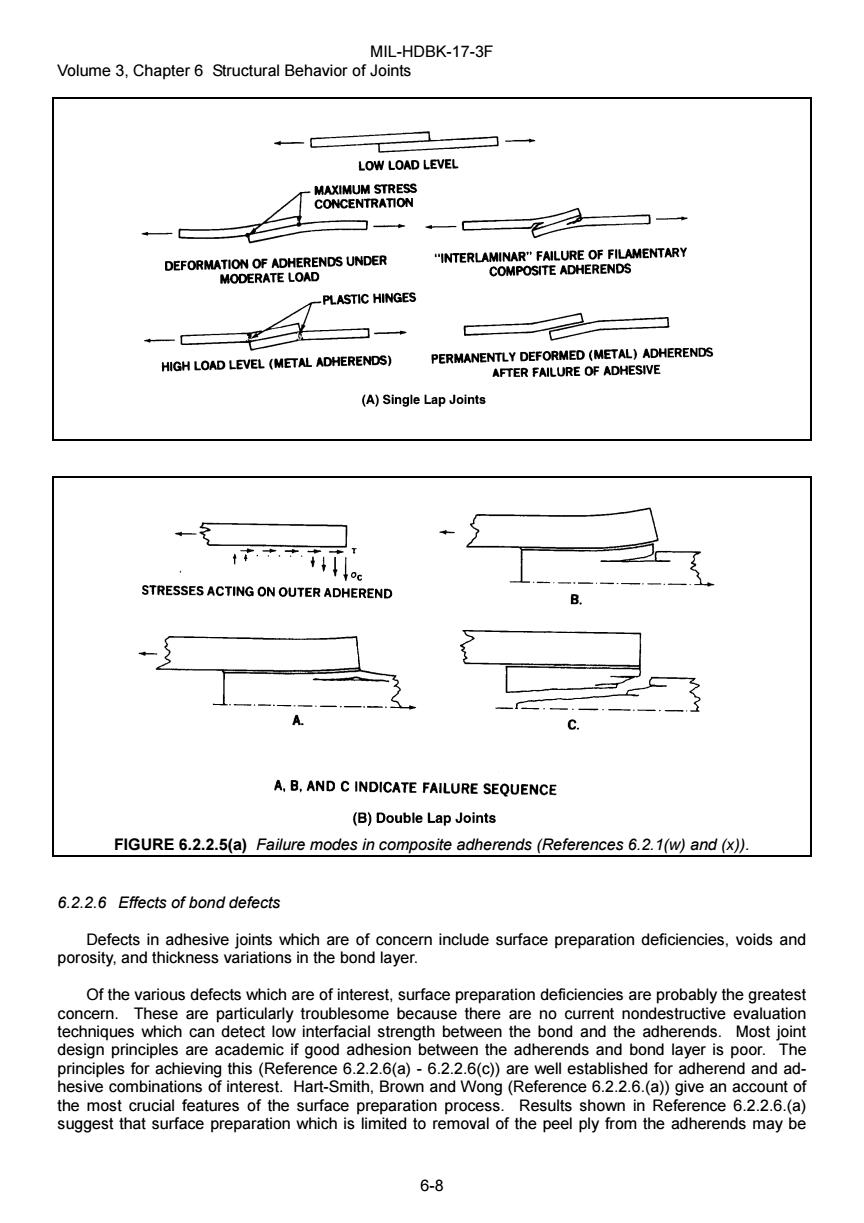
MIL-HDBK-17-3F Volume 3,Chapter 6 Structural Behavior of Joints LOW LOAD LEVEL MAXIMUM STRESS CONCENTRATION 门+ DEFORMATION OF ADHERENDS UNDER "INTERLAMINAR"FAILURE OF FILAMENTARY MODERATE LOAD COMPOSITE ADHERENDS -PLASTIC HINGES HIGH LOAD LEVEL (METAL ADHERENDS) PERMANENTLY DEFORMED (METAL)ADHERENDS AFTER FAILURE OF ADHESIVE (A)Single Lap Joints STRESSES ACTING ON OUTER ADHEREND A,B.AND C INDICATE FAILURE SEQUENCE (B)Double Lap Joints FIGURE 6.2.2.5(a)Failure modes in composite adherends(References 6.2.1(w)and(x)). 6.2.2.6 Effects of bond defects Defects in adhesive joints which are of concern include surface preparation deficiencies,voids and porosity,and thickness variations in the bond layer. Of the various defects which are of interest,surface preparation deficiencies are probably the greatest concern.These are particularly troublesome because there are no current nondestructive evaluation techniques which can detect low interfacial strength between the bond and the adherends.Most joint design principles are academic if good adhesion between the adherends and bond layer is poor.The principles for achieving this (Reference 6.2.2.6(a)-6.2.2.6(c))are well established for adherend and ad- hesive combinations of interest.Hart-Smith,Brown and Wong(Reference 6.2.2.6.(a))give an account of the most crucial features of the surface preparation process.Results shown in Reference 6.2.2.6.(a) suggest that surface preparation which is limited to removal of the peel ply from the adherends may be 6-8MIL-HDBK-17-3F Volume 3, Chapter 6 Structural Behavior of Joints 6-8 FIGURE 6.2.2.5(a) Failure modes in composite adherends (References 6.2.1(w) and (x)). 6.2.2.6 Effects of bond defects Defects in adhesive joints which are of concern include surface preparation deficiencies, voids and porosity, and thickness variations in the bond layer. Of the various defects which are of interest, surface preparation deficiencies are probably the greatest concern. These are particularly troublesome because there are no current nondestructive evaluation techniques which can detect low interfacial strength between the bond and the adherends. Most joint design principles are academic if good adhesion between the adherends and bond layer is poor. The principles for achieving this (Reference 6.2.2.6(a) - 6.2.2.6(c)) are well established for adherend and adhesive combinations of interest. Hart-Smith, Brown and Wong (Reference 6.2.2.6.(a)) give an account of the most crucial features of the surface preparation process. Results shown in Reference 6.2.2.6.(a) suggest that surface preparation which is limited to removal of the peel ply from the adherends may be