正在加载图片...
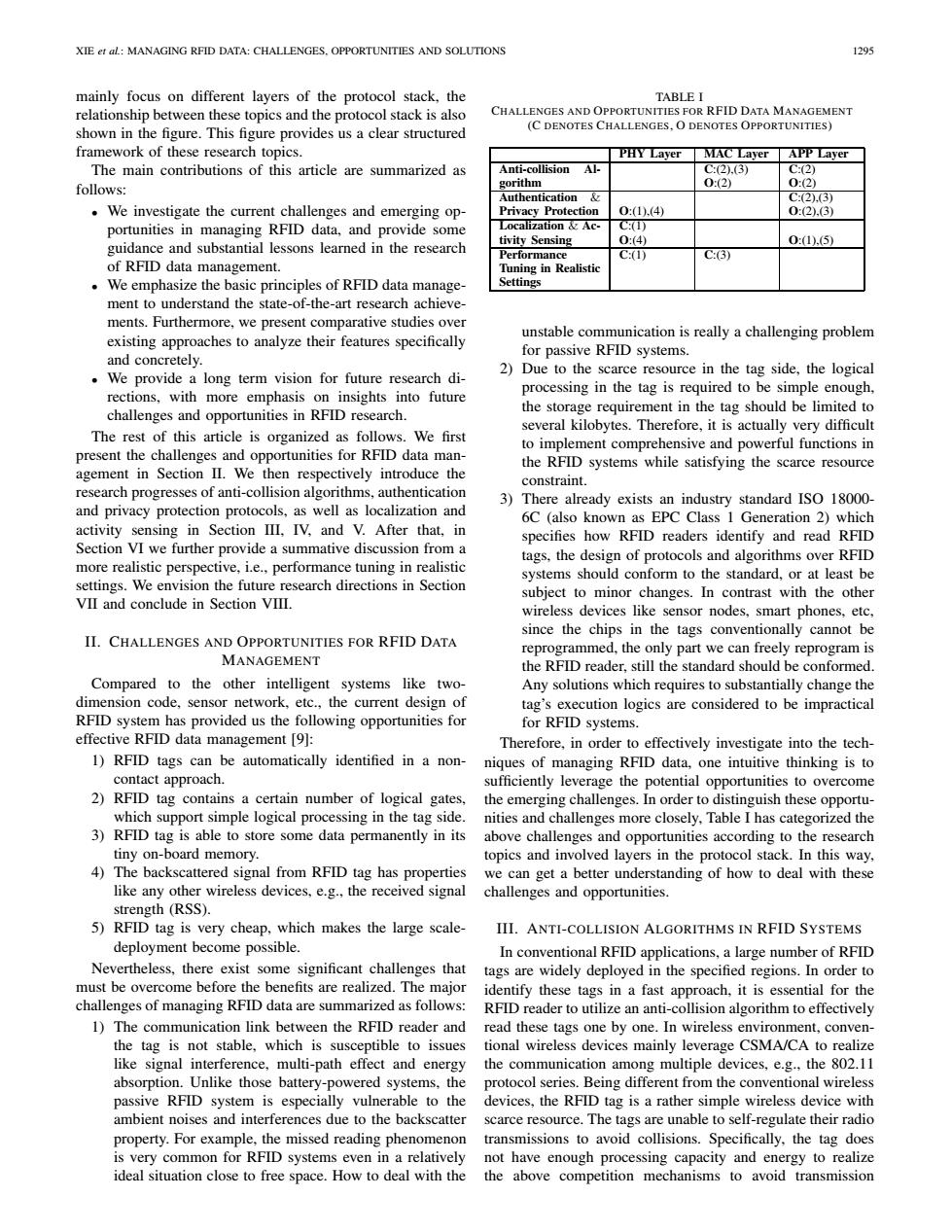
XIE er al:MANAGING RFID DATA:CHALLENGES.OPPORTUNITIES AND SOLUTIONS 1295 mainly focus on different layers of the protocol stack,the TABLE I relationship between these topics and the protocol stack is also CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR RFID DATA MANAGEMENT shown in the figure.This figure provides us a clear structured (C DENOTES CHALLENGES,O DENOTES OPPORTUNITIES) framework of these research topics. PHY Layer MAC Layer APP Layer The main contributions of this article are summarized as Anti-collision Al- C(2).(3) C(2) follows: gorithm 0:(2) 0:(2) Authentication C:2).3) We investigate the current challenges and emerging op- Privacy Protection 0:(1).(4) 0:2).(3) portunities in managing RFID data,and provide some Localization Ac- C(1) guidance and substantial lessons learned in the research tivity Sensing 0:(4) 0:(1),5 Performance C:(1) C(3) of RFID data management. Tuning in Realistic We emphasize the basic principles of RFID data manage- Settings ment to understand the state-of-the-art research achieve- ments.Furthermore,we present comparative studies over unstable communication is really a challenging problem existing approaches to analyze their features specifically for passive RFID systems. and concretely. 2) Due to the scarce resource in the tag side,the logical We provide a long term vision for future research di- processing in the tag is required to be simple enough, rections,with more emphasis on insights into future challenges and opportunities in RFID research. the storage requirement in the tag should be limited to several kilobytes.Therefore,it is actually very difficult The rest of this article is organized as follows.We first to implement comprehensive and powerful functions in present the challenges and opportunities for RFID data man- agement in Section II.We then respectively introduce the the RFID systems while satisfying the scarce resource constraint. research progresses of anti-collision algorithms,authentication 3)There already exists an industry standard ISO 18000- and privacy protection protocols,as well as localization and 6C (also known as EPC Class 1 Generation 2)which activity sensing in Section III,IV,and V.After that,in specifies how RFID readers identify and read RFID Section VI we further provide a summative discussion from a tags,the design of protocols and algorithms over RFID more realistic perspective,i.e.,performance tuning in realistic systems should conform to the standard,or at least be settings.We envision the future research directions in Section subject to minor changes.In contrast with the other VⅡand conclude in Section VⅢ wireless devices like sensor nodes,smart phones,etc, since the chips in the tags conventionally cannot be II.CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR RFID DATA reprogrammed,the only part we can freely reprogram is MANAGEMENT the RFID reader,still the standard should be conformed. Compared to the other intelligent systems like two- Any solutions which requires to substantially change the dimension code,sensor network,etc.,the current design of tag's execution logics are considered to be impractical RFID system has provided us the following opportunities for for RFID systems. effective RFID data management [9]: Therefore,in order to effectively investigate into the tech- 1)RFID tags can be automatically identified in a non- niques of managing RFID data,one intuitive thinking is to contact approach. sufficiently leverage the potential opportunities to overcome 2)RFID tag contains a certain number of logical gates, the emerging challenges.In order to distinguish these opportu- which support simple logical processing in the tag side. nities and challenges more closely,Table I has categorized the 3)RFID tag is able to store some data permanently in its above challenges and opportunities according to the research tiny on-board memory. topics and involved layers in the protocol stack.In this way, 4)The backscattered signal from RFID tag has properties we can get a better understanding of how to deal with these like any other wireless devices,e.g..the received signal challenges and opportunities. strength (RSS). 5)RFID tag is very cheap,which makes the large scale- III.ANTI-COLLISION ALGORITHMS IN RFID SYSTEMS deployment become possible. In conventional RFID applications,a large number of RFID Nevertheless,there exist some significant challenges that tags are widely deployed in the specified regions.In order to must be overcome before the benefits are realized.The major identify these tags in a fast approach,it is essential for the challenges of managing RFID data are summarized as follows: RFID reader to utilize an anti-collision algorithm to effectively 1)The communication link between the RFID reader and read these tags one by one.In wireless environment,conven- the tag is not stable,which is susceptible to issues tional wireless devices mainly leverage CSMA/CA to realize like signal interference,multi-path effect and energy the communication among multiple devices,e.g..the 802.11 absorption.Unlike those battery-powered systems,the protocol series.Being different from the conventional wireless passive RFID system is especially vulnerable to the devices,the RFID tag is a rather simple wireless device with ambient noises and interferences due to the backscatter scarce resource.The tags are unable to self-regulate their radio property.For example,the missed reading phenomenon transmissions to avoid collisions.Specifically,the tag does is very common for RFID systems even in a relatively not have enough processing capacity and energy to realize ideal situation close to free space.How to deal with the the above competition mechanisms to avoid transmissionXIE et al.: MANAGING RFID DATA: CHALLENGES, OPPORTUNITIES AND SOLUTIONS 1295 mainly focus on different layers of the protocol stack, the relationship between these topics and the protocol stack is also shown in the figure. This figure provides us a clear structured framework of these research topics. The main contributions of this article are summarized as follows: • We investigate the current challenges and emerging opportunities in managing RFID data, and provide some guidance and substantial lessons learned in the research of RFID data management. • We emphasize the basic principles of RFID data management to understand the state-of-the-art research achievements. Furthermore, we present comparative studies over existing approaches to analyze their features specifically and concretely. • We provide a long term vision for future research directions, with more emphasis on insights into future challenges and opportunities in RFID research. The rest of this article is organized as follows. We first present the challenges and opportunities for RFID data management in Section II. We then respectively introduce the research progresses of anti-collision algorithms, authentication and privacy protection protocols, as well as localization and activity sensing in Section III, IV, and V. After that, in Section VI we further provide a summative discussion from a more realistic perspective, i.e., performance tuning in realistic settings. We envision the future research directions in Section VII and conclude in Section VIII. II. CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR RFID DATA MANAGEMENT Compared to the other intelligent systems like twodimension code, sensor network, etc., the current design of RFID system has provided us the following opportunities for effective RFID data management [9]: 1) RFID tags can be automatically identified in a noncontact approach. 2) RFID tag contains a certain number of logical gates, which support simple logical processing in the tag side. 3) RFID tag is able to store some data permanently in its tiny on-board memory. 4) The backscattered signal from RFID tag has properties like any other wireless devices, e.g., the received signal strength (RSS). 5) RFID tag is very cheap, which makes the large scaledeployment become possible. Nevertheless, there exist some significant challenges that must be overcome before the benefits are realized. The major challenges of managing RFID data are summarized as follows: 1) The communication link between the RFID reader and the tag is not stable, which is susceptible to issues like signal interference, multi-path effect and energy absorption. Unlike those battery-powered systems, the passive RFID system is especially vulnerable to the ambient noises and interferences due to the backscatter property. For example, the missed reading phenomenon is very common for RFID systems even in a relatively ideal situation close to free space. How to deal with the TABLE I CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR RFID DATA MANAGEMENT (C DENOTES CHALLENGES, O DENOTES OPPORTUNITIES) PHY Layer MAC Layer APP Layer Anti-collision Algorithm C:(2),(3) O:(2) C:(2) O:(2) Authentication & Privacy Protection O:(1),(4) C:(2),(3) O:(2),(3) Localization & Activity Sensing C:(1) O:(4) O:(1),(5) Performance Tuning in Realistic Settings C:(1) C:(3) unstable communication is really a challenging problem for passive RFID systems. 2) Due to the scarce resource in the tag side, the logical processing in the tag is required to be simple enough, the storage requirement in the tag should be limited to several kilobytes. Therefore, it is actually very difficult to implement comprehensive and powerful functions in the RFID systems while satisfying the scarce resource constraint. 3) There already exists an industry standard ISO 18000- 6C (also known as EPC Class 1 Generation 2) which specifies how RFID readers identify and read RFID tags, the design of protocols and algorithms over RFID systems should conform to the standard, or at least be subject to minor changes. In contrast with the other wireless devices like sensor nodes, smart phones, etc, since the chips in the tags conventionally cannot be reprogrammed, the only part we can freely reprogram is the RFID reader, still the standard should be conformed. Any solutions which requires to substantially change the tag’s execution logics are considered to be impractical for RFID systems. Therefore, in order to effectively investigate into the techniques of managing RFID data, one intuitive thinking is to sufficiently leverage the potential opportunities to overcome the emerging challenges. In order to distinguish these opportunities and challenges more closely, Table I has categorized the above challenges and opportunities according to the research topics and involved layers in the protocol stack. In this way, we can get a better understanding of how to deal with these challenges and opportunities. III. ANTI-COLLISION ALGORITHMS IN RFID SYSTEMS In conventional RFID applications, a large number of RFID tags are widely deployed in the specified regions. In order to identify these tags in a fast approach, it is essential for the RFID reader to utilize an anti-collision algorithm to effectively read these tags one by one. In wireless environment, conventional wireless devices mainly leverage CSMA/CA to realize the communication among multiple devices, e.g., the 802.11 protocol series. Being different from the conventional wireless devices, the RFID tag is a rather simple wireless device with scarce resource. The tags are unable to self-regulate their radio transmissions to avoid collisions. Specifically, the tag does not have enough processing capacity and energy to realize the above competition mechanisms to avoid transmission