正在加载图片...
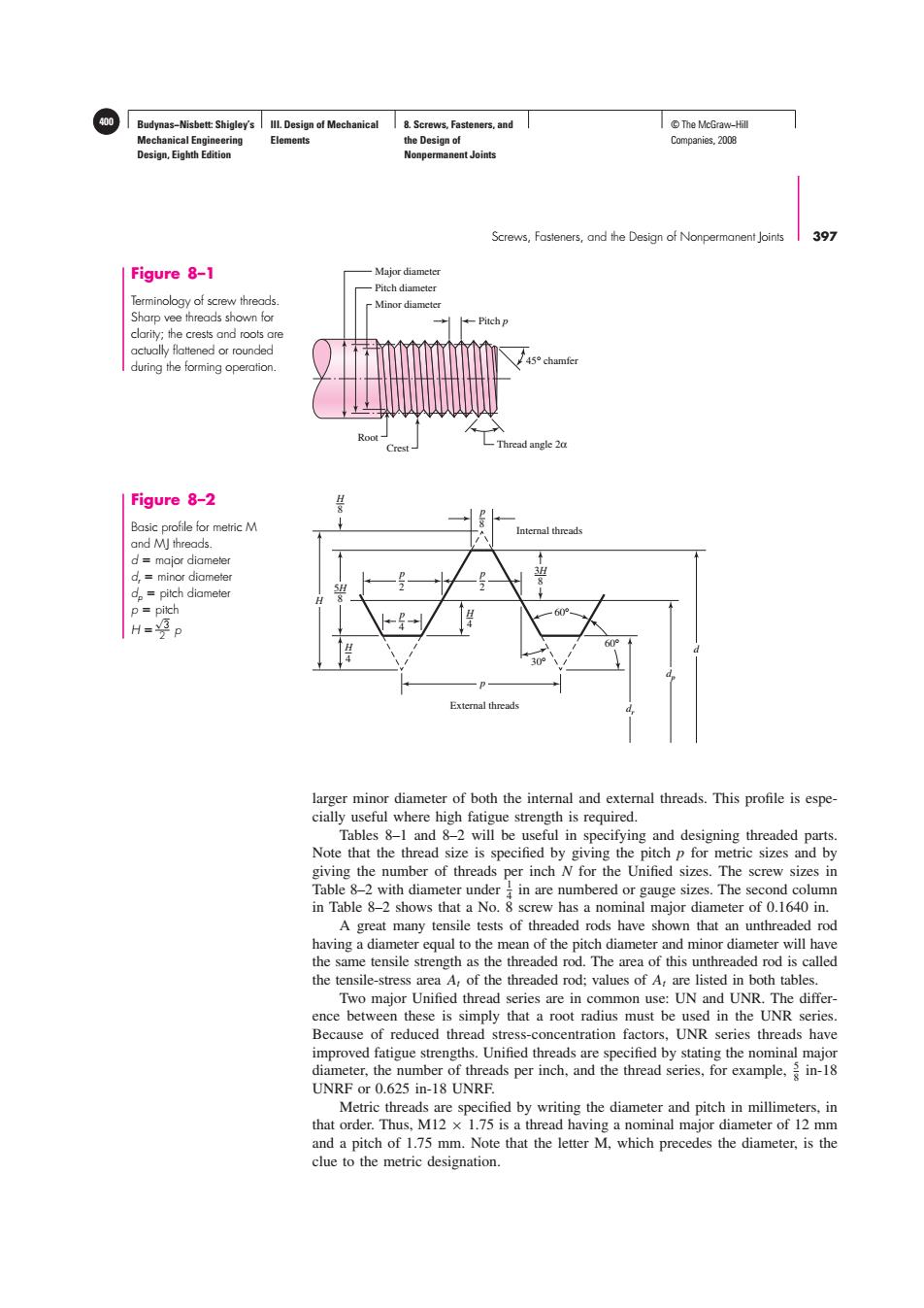
400 Budynas-Nisbett:Shigley's Ill.Design of Mechanical 8.Screws,Fasteners,and ©The McGraw-Hil Mechanical Engineering Elements the Design of Companies,2008 Design,Eighth Edition Nonpermanent Joints Screws,Fasteners,and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints 397 Figure 8-1 Major diameter Pitch diameter Terminology of screw threads. -Minor diameter Sharp vee threads shown for -Pitchp clarity;the crests and roots are actually flattened or rounded during the forming operation t4s°chamfer (res Thread angle 20 Figure 8-2 Basic profile for metric M Internal threads and MJ threads. d=major diameter d,minor diameter d。=pitch diameter p=pitch 60 H=p 60 30 External threads larger minor diameter of both the internal and external threads.This profile is espe cially useful where high fatigue strength is required. Tables 8-1 and 8-2 will be useful in specifying and designing threaded parts. Note that the thread size is specified by giving the pitch p for metric sizes and by giving the number of threads per inch N for the Unified sizes.The screw sizes in Table 8-2 with diameter under in are numbered or gauge sizes.The second column in Table 8-2 shows that a No.8 screw has a nominal major diameter of 0.1640 in. A great many tensile tests of threaded rods have shown that an unthreaded rod having a diameter equal to the mean of the pitch diameter and minor diameter will have the same tensile strength as the threaded rod.The area of this unthreaded rod is called the tensile-stress area A,of the threaded rod;values of A,are listed in both tables. Two major Unified thread series are in common use:UN and UNR.The differ- ence between these is simply that a root radius must be used in the UNR series Because of reduced thread stress-concentration factors,UNR series threads have improved fatigue strengths.Unified threads are specified by stating the nominal major diameter,the number of threads per inch,and the thread series,for example,in-18 UNRF or 0.625 in-18 UNRF. Metric threads are specified by writing the diameter and pitch in millimeters,in that order.Thus,M12 x 1.75 is a thread having a nominal major diameter of 12 mm and a pitch of 1.75 mm.Note that the letter M,which precedes the diameter,is the clue to the metric designation.Budynas−Nisbett: Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition III. Design of Mechanical Elements 8. Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints 400 © The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2008 Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints 397 Major diameter Pitch diameter Minor diameter Pitch p 45° chamfer Thread angle 2α Root Crest Figure 8–1 Terminology of screw threads. Sharp vee threads shown for clarity; the crests and roots are actually flattened or rounded during the forming operation. Internal threads External threads H 4 H 4 5H 8 3H 8 H 8 H p 4 p 2 p p 2 p 8 30° 60° 60° dr dp d Figure 8–2 Basic profile for metric M and MJ threads. d major diameter dr minor diameter dp pitch diameter p pitch H √ 3 2 p larger minor diameter of both the internal and external threads. This profile is especially useful where high fatigue strength is required. Tables 8–1 and 8–2 will be useful in specifying and designing threaded parts. Note that the thread size is specified by giving the pitch p for metric sizes and by giving the number of threads per inch N for the Unified sizes. The screw sizes in Table 8–2 with diameter under 1 4 in are numbered or gauge sizes. The second column in Table 8–2 shows that a No. 8 screw has a nominal major diameter of 0.1640 in. A great many tensile tests of threaded rods have shown that an unthreaded rod having a diameter equal to the mean of the pitch diameter and minor diameter will have the same tensile strength as the threaded rod. The area of this unthreaded rod is called the tensile-stress area At of the threaded rod; values of At are listed in both tables. Two major Unified thread series are in common use: UN and UNR. The difference between these is simply that a root radius must be used in the UNR series. Because of reduced thread stress-concentration factors, UNR series threads have improved fatigue strengths. Unified threads are specified by stating the nominal major diameter, the number of threads per inch, and the thread series, for example, 5 8 in-18 UNRF or 0.625 in-18 UNRF. Metric threads are specified by writing the diameter and pitch in millimeters, in that order. Thus, M12 × 1.75 is a thread having a nominal major diameter of 12 mm and a pitch of 1.75 mm. Note that the letter M, which precedes the diameter, is the clue to the metric designation.�����