正在加载图片...
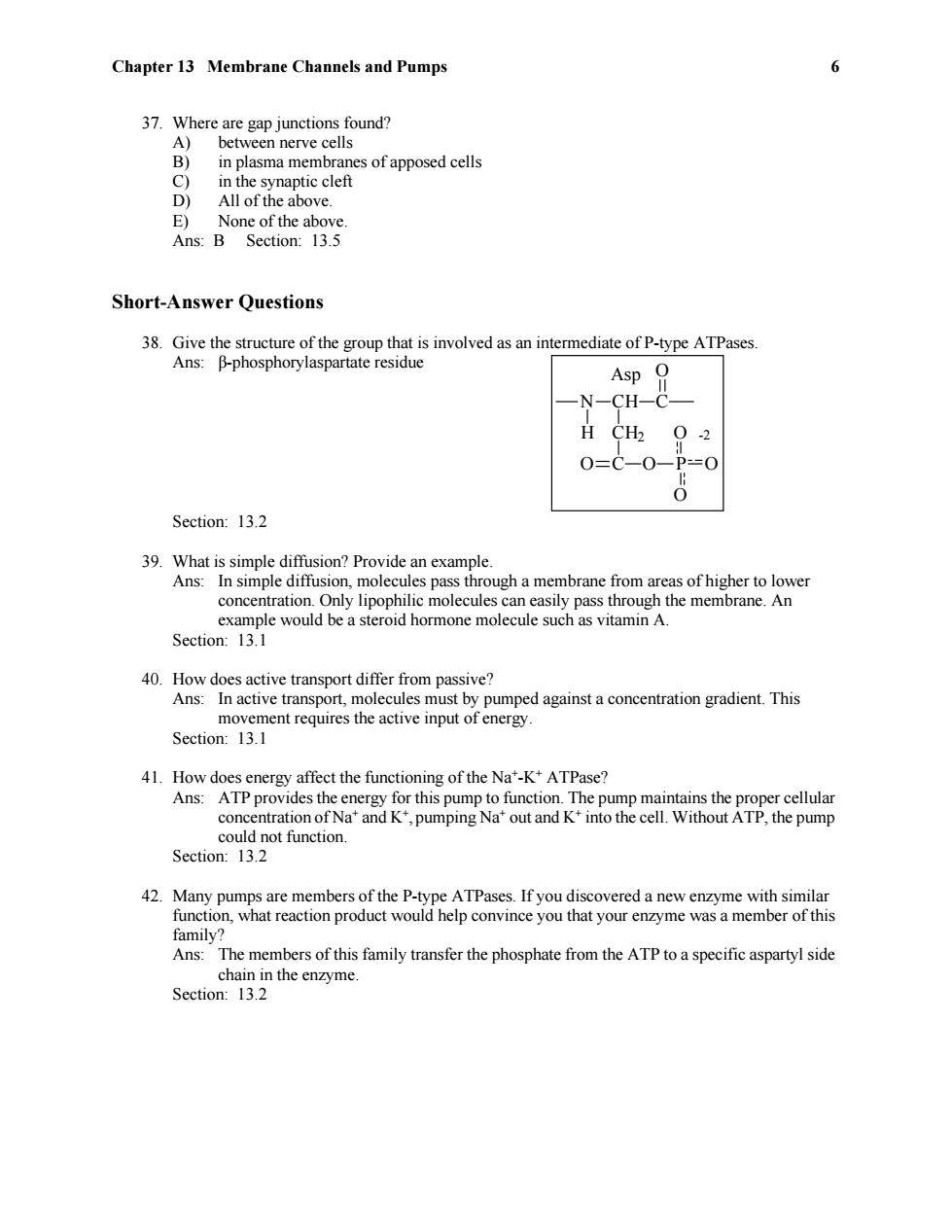
Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 6 37.Where are gap junctions found? A) between nerve cells B) in plasma membranes of apposed cells C) in the synaptic cleft D All of the above. E)None of the above Ans:B Section:13.5 Short-Answer Questions 38.Give the structure of the group that is involved as an intermediate of P-type ATPases. Ans:B-phosphorylaspartate residue Asp 0 -N-CH-C- H CH 02 0=C-0-P=0 Section:13.2 39.What is simple diffusion?Provide an example. Ans:In simple diffusion,molecules pass through a membrane from areas of higher to lower concentration.Only lipophilic molecules can easily pass through the membrane.An example would be a steroid hormone molecule such as vitamin A. Section:13.1 40.How does active transport differ from passive? Ans:In active transport,molecules must by pumped against a concentration gradient.This movement requires the active input of energy. Section:13.1 41.How does energy affect the functioning of the Na'-K*ATPase? Ans:ATP provides the energy for this pump to function.The pump maintains the proper cellular concentration of Na'and K*,pumping Na*out and K+into the cell.Without ATP,the pump could not function. Section:13.2 42.Many pumps are members of the P-type ATPases.If you discovered a new enzyme with similar function,what reaction product would help convince you that your enzyme was a member of this family? Ans:The members of this family transfer the phosphate from the ATP to a specific aspartyl side chain in the enzyme. Section:13.2Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 6 37. Where are gap junctions found? A) between nerve cells B) in plasma membranes of apposed cells C) in the synaptic cleft D) All of the above. E) None of the above. Ans: B Section: 13.5 Short-Answer Questions 38. Give the structure of the group that is involved as an intermediate of P-type ATPases. Ans: β-phosphorylaspartate residue N H CH C O CH2 O C O P O O O -2 Asp Section: 13.2 39. What is simple diffusion? Provide an example. Ans: In simple diffusion, molecules pass through a membrane from areas of higher to lower concentration. Only lipophilic molecules can easily pass through the membrane. An example would be a steroid hormone molecule such as vitamin A. Section: 13.1 40. How does active transport differ from passive? Ans: In active transport, molecules must by pumped against a concentration gradient. This movement requires the active input of energy. Section: 13.1 41. How does energy affect the functioning of the Na + -K+ ATPase? Ans: ATP provides the energy for this pump to function. The pump maintains the proper cellular concentration of Na + and K+ , pumping Na + out and K+ into the cell. Without ATP, the pump could not function. Section: 13.2 42. Many pumps are members of the P-type ATPases. If you discovered a new enzyme with similar function, what reaction product would help convince you that your enzyme was a member of this family? Ans: The members of this family transfer the phosphate from the ATP to a specific aspartyl side chain in the enzyme. Section: 13.2