正在加载图片...
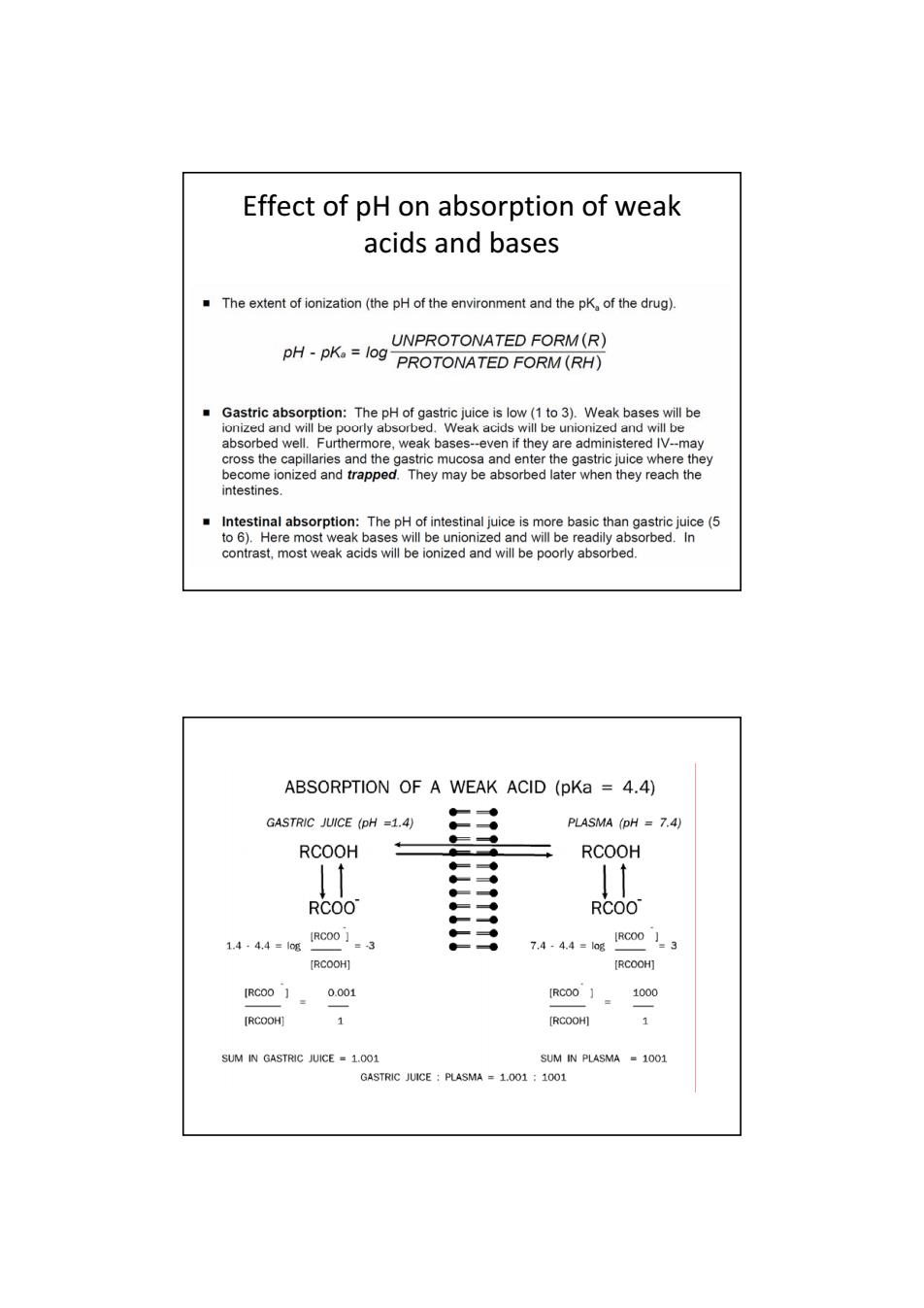
Effect of pH on absorption of weak acids and bases The extent of ionization(the pH of the environment and the pK of the drug). UNPROTONATED FORM(R) pH-pKa log PROTONATED FORM(RH) Gastric absorption:The pH of gastric juice is low (1 to 3).Weak bases will be ionized and will be poorly absorbed.Weak acids will be unionized and will be absorbed well.Furthermore,weak bases--even if they are administered IV--may cross the capillaries and the gastric mucosa and enter the gastric juice where they become ionized and trapped.They may be absorbed later when they reach the intestines. Intestinal absorption:The pH of intestinal juice is more basic than gastric juice(5 to 6).Here most weak bases will be unionized and will be readily absorbed.In contrast,most weak acids will be ionized and will be poorly absorbed. ABSORPTION OF A WEAK ACID (pKa 4.4) 一一● GASTRIC JUICE (pH =1.4) -” PLASMA (pH 7.4) 一● RCOOH RCOOH 一◆ ●一● ●● RCOO ●一● RCOO 1.4.4.4=18 IRC00】 =3 7.4·4.4=1og IRcoo ]3 [RCOOH] [RCOOH] 1RC00】= 0.001 RCO0】 1000 [RCOOH] 1 [RCOOH] 1 SUM IN GASTRIC JUICE 1.001 SUM IN PLASMA 1001 GASTRIC JUICE PLASMA 1.001:1001Effect of pH on absorption of weak acids and bases