正在加载图片...
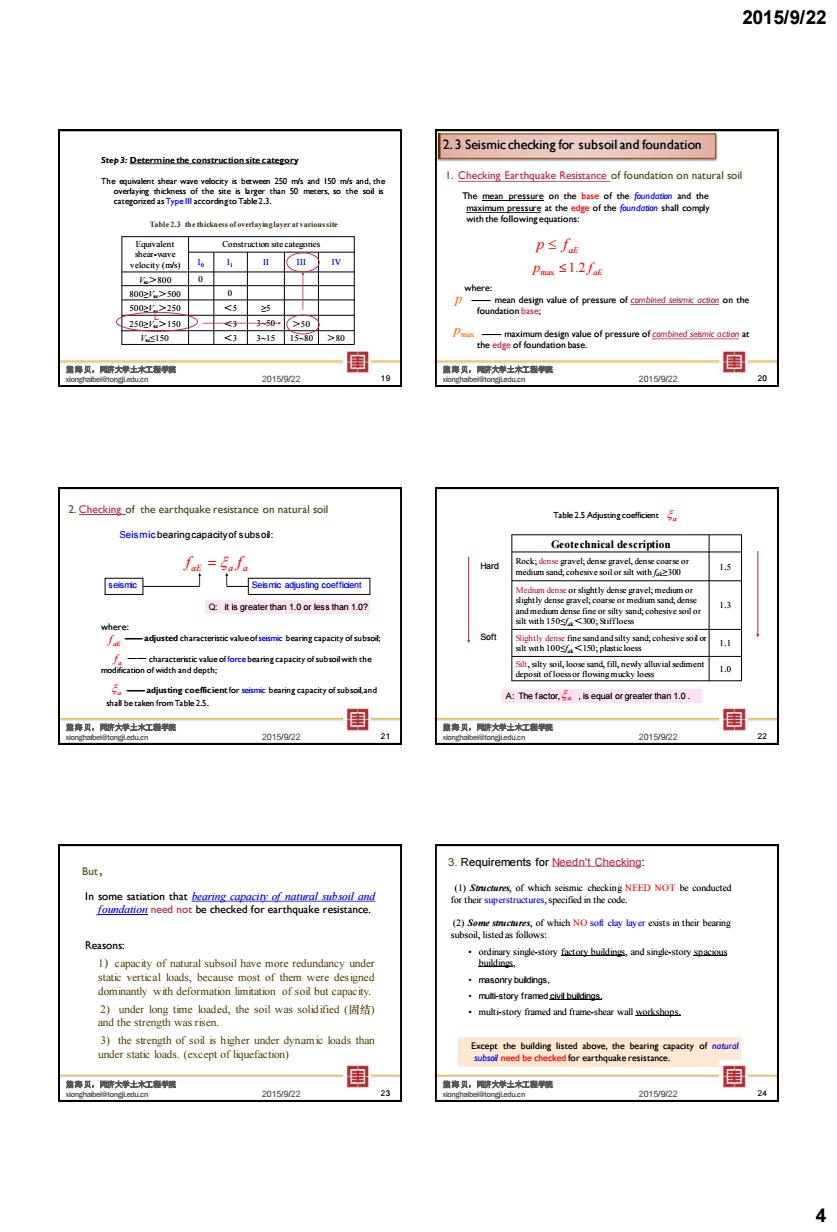
2015/9/22 2 Seismic checking for subsoiland foundation The a 1.1 s12 the 国 一 201502 2.Cheg.ofteearthqpakerosmanceonaturalol emnofub Geotechnical deseription =6f. seismic Q:it is greaterthan 1.0 or less man 1.0? te ton 1.0. 201502 国 2015022 But. 3.Requirements for: sod is 精九腰大神士杠啊 3015022 4 2015/9/22 4 Step 3: Determine the construction site category The equivalent shear wave velocity is between 250 m/s and 150 m/s and, the overlaying thickness of the site is larger than 50 meters, so the soil is categorized as Type III accordingto Table 2.3. Table 2.3 the thickness of overlaying layer at various site Equivalent shear-wave velocity (m/s) Construction site categories I0 I1 II III IV Vse>800 0 800≥Vse>500 0 500≥Vse>250 <5 ≥5 250≥Vse>150 <3 3~50 >50 Vse≤150 <3 3~15 15~80 >80 L 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 19 The mean pressure on the base of the foundation and the maximum pressure at the edge of the foundation shall comply with the following equations: aE p f aE p 1.2 f max where: —— mean design value of pressure of combined seismic action on the foundation base; —— maximum design value of pressure of combined seismic action at the edge of foundation base. p pmax 1. Checking Earthquake Resistance of foundation on natural soil 2. 3 Seismic checking for subsoil and foundation 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 20 aE a a f f where: —— adjusted characteristic value of seismic bearing capacity of subsoil; —— characteristic value of force bearing capacity of subsoil with the modification of width and depth; a f —— adjusting coefficient for seismic bearing capacity of subsoil, and shall be taken from Table 2.5. a seismic Seismic adjusting coefficient Q: it is greater than 1.0 or less than 1.0? 2. Checking of the earthquake resistance on natural soil Seismic bearingcapacityof subsoil: aE f 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 21 Geotechnical description Rock; dense gravel; dense gravel, dense coarse or medium sand; cohesive soil or silt with fak≥300 1.5 Medium dense or slightly dense gravel; medium or slightly dense gravel; coarse or medium sand; dense and medium dense fine or silty sand; cohesive soil or silt with 150≤fak<300; Stiff loess 1.3 Slightly dense fine sand and silty sand; cohesive soil or silt with 100≤fak<150; plastic loess 1.1 Silt, silty soil, loose sand, fill, newly alluvial sediment deposit of loess or flowing mucky loess 1.0 Table 2.5 Adjusting coefficient Hard Soft A: The factor, , is equal or greater than 1.0 . a a 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 22 But, In some satiation that bearing capacity of natural subsoil and foundation need not be checked for earthquake resistance. Reasons: 1)capacity of natural subsoil have more redundancy under static vertical loads, because most of them were designed dominantly with deformation limitation of soil but capacity. 2) under long time loaded, the soil was solidified (固结) and the strength was risen. 3) the strength of soil is higher under dynamic loads than under static loads. (except of liquefaction) 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 23 (1) Structures, of which seismic checking NEED NOT be conducted for their superstructures,specified in the code. (2) Some structures, of which NO soft clay layer exists in their bearing subsoil, listed as follows: • ordinary single-story factory buildings, and single-story spacious buildings, • masonry buildings, • multi-story framed civil buildings, • multi-story framed and frame-shear wall workshops. 3. Requirements for Needn't Checking: Except the building listed above, the bearing capacity of natural subsoil need be checked for earthquake resistance. 2015/9/22 熊海贝,同济大学土木工程学院 xionghaibei@tongji.edu.cn 24