正在加载图片...
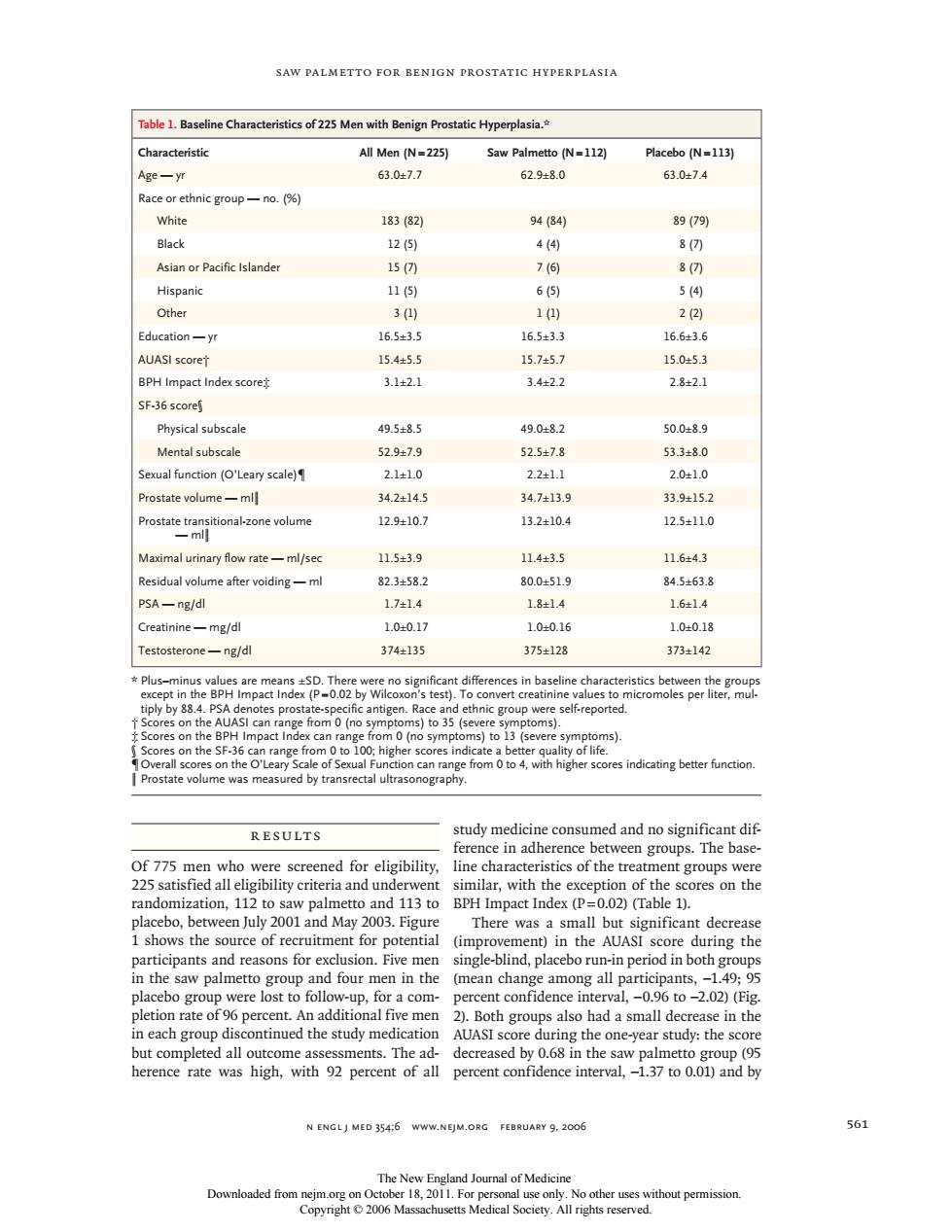
SAW PALMETTO FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA acteristics of 225 Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.* All Men (N=225) Saw Palmetto (N-112) Age-yr 63.047.7 62.9±8.0 63.0±7.4 Race or ethnic group-no.(% White 18382) 94(34 89(79 Black 12(5) 4(4④ 8 Asian or Pacific lslande 15 7间 :0 Hispanic 115) 6( Other 3(1) 1(0) 22) Education-yr 16.5±3.5 16.5±3.3 16.6±3.6 AUASI scoret 154+55 15.7±5.7 150+53 BPH Impact Index score 3.1421 3422 2.821 SF-36score Physical subscale 49.5±8.5 49.0±8.2 50.0±8. Mental subscale 529±7.9 52.5±7.8 53.3+8.0 Sexual function (O'Leary scale) 21+10 22411 20+10 Prostate volume 34.24145 34713.9 339+15 12.9410. 1324104 1251.0 Maximal urinary flow rate-ml/sec 115+39 114+35 116+43 fter voiding- 823+58 80.0=51.9 845638 SA-ng/dl 181 161 Creatinine-mg/dl 1.00.1 1.0±016 1.0±0.18 Testosterone一ng/dl 374±135 375±128 373±142 ethnic grou ca act Ind to 13 fs ores on the Sh on can r cores indicating better function. RESULTS study medicine consumed and no significant dif erence in adherence between groups.The base 775me ned for eligibility, line randomization.112 to saw palmetto and 113 to BPH Impact Index (P=0.02)(Table 1). placebo,between July 2001and May 2003.Figure There was a small but significant decrease shows the source of recruitment for potential (impro men )in the AUASI score during the d reasons for n period in un for a com- ercent confidence interval -096 to -2 02)(Fig 2).Both groups also had a small decrease in the n each group dis AUASI score dur ng t e on-yer study:the s out comp 1.37 to 0.o1)and by N ENGLJ MED 354:6 WWW.NEJM.ORG FEBRUARY 9.2006 561 Downloaded fromn use only.N saw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasia n engl j med 354;6 www.nejm.org february 9, 2006 561 Results Of 775 men who were screened for eligibility, 225 satisfied all eligibility criteria and underwent randomization, 112 to saw palmetto and 113 to placebo, between July 2001 and May 2003. Figure 1 shows the source of recruitment for potential participants and reasons for exclusion. Five men in the saw palmetto group and four men in the placebo group were lost to follow-up, for a completion rate of 96 percent. An additional five men in each group discontinued the study medication but completed all outcome assessments. The adherence rate was high, with 92 percent of all study medicine consumed and no significant difference in adherence between groups. The baseline characteristics of the treatment groups were similar, with the exception of the scores on the BPH Impact Index (P = 0.02) (Table 1). There was a small but significant decrease (improvement) in the AUASI score during the single-blind, placebo run-in period in both groups (mean change among all participants, −1.49; 95 percent confidence interval, −0.96 to −2.02) (Fig. 2). Both groups also had a small decrease in the AUASI score during the one-year study: the score decreased by 0.68 in the saw palmetto group (95 percent confidence interval, −1.37 to 0.01) and by Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of 225 Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.* Characteristic All Men (N = 225) Saw Palmetto (N = 112) Placebo (N = 113) Age — yr 63.0±7.7 62.9±8.0 63.0±7.4 Race or ethnic group — no. (%) White 183 (82) 94 (84) 89 (79) Black 12 (5) 4 (4) 8 (7) Asian or Pacific Islander 15 (7) 7 (6) 8 (7) Hispanic 11 (5) 6 (5) 5 (4) Other 3 (1) 1 (1) 2 (2) Education — yr 16.5±3.5 16.5±3.3 16.6±3.6 AUASI score† 15.4±5.5 15.7±5.7 15.0±5.3 BPH Impact Index score‡ 3.1±2.1 3.4±2.2 2.8±2.1 SF-36 score§ Physical subscale 49.5±8.5 49.0±8.2 50.0±8.9 Mental subscale 52.9±7.9 52.5±7.8 53.3±8.0 Sexual function (O’Leary scale)¶ 2.1±1.0 2.2±1.1 2.0±1.0 Prostate volume — ml∥ 34.2±14.5 34.7±13.9 33.9±15.2 Prostate transitional-zone volume — ml∥ 12.9±10.7 13.2±10.4 12.5±11.0 Maximal urinary flow rate — ml/sec 11.5±3.9 11.4±3.5 11.6±4.3 Residual volume after voiding — ml 82.3±58.2 80.0±51.9 84.5±63.8 PSA — ng/dl 1.7±1.4 1.8±1.4 1.6±1.4 Creatinine — mg/dl 1.0±0.17 1.0±0.16 1.0±0.18 Testosterone — ng/dl 374±135 375±128 373±142 * Plus–minus values are means ±SD. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the groups except in the BPH Impact Index (P = 0.02 by Wilcoxon’s test). To convert creatinine values to micromoles per liter, multiply by 88.4. PSA denotes prostate-specific antigen. Race and ethnic group were self-reported. † Scores on the AUASI can range from 0 (no symptoms) to 35 (severe symptoms). ‡ Scores on the BPH Impact Index can range from 0 (no symptoms) to 13 (severe symptoms). § Scores on the SF-36 can range from 0 to 100; higher scores indicate a better quality of life. ¶ Overall scores on the O’Leary Scale of Sexual Function can range from 0 to 4, with higher scores indicating better function. ∥ Prostate volume was measured by transrectal ultrasonography. The New England Journal of Medicine Downloaded from nejm.org on October 18, 2011. For personal use only. No other uses without permission. Copyright © 2006 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved