正在加载图片...
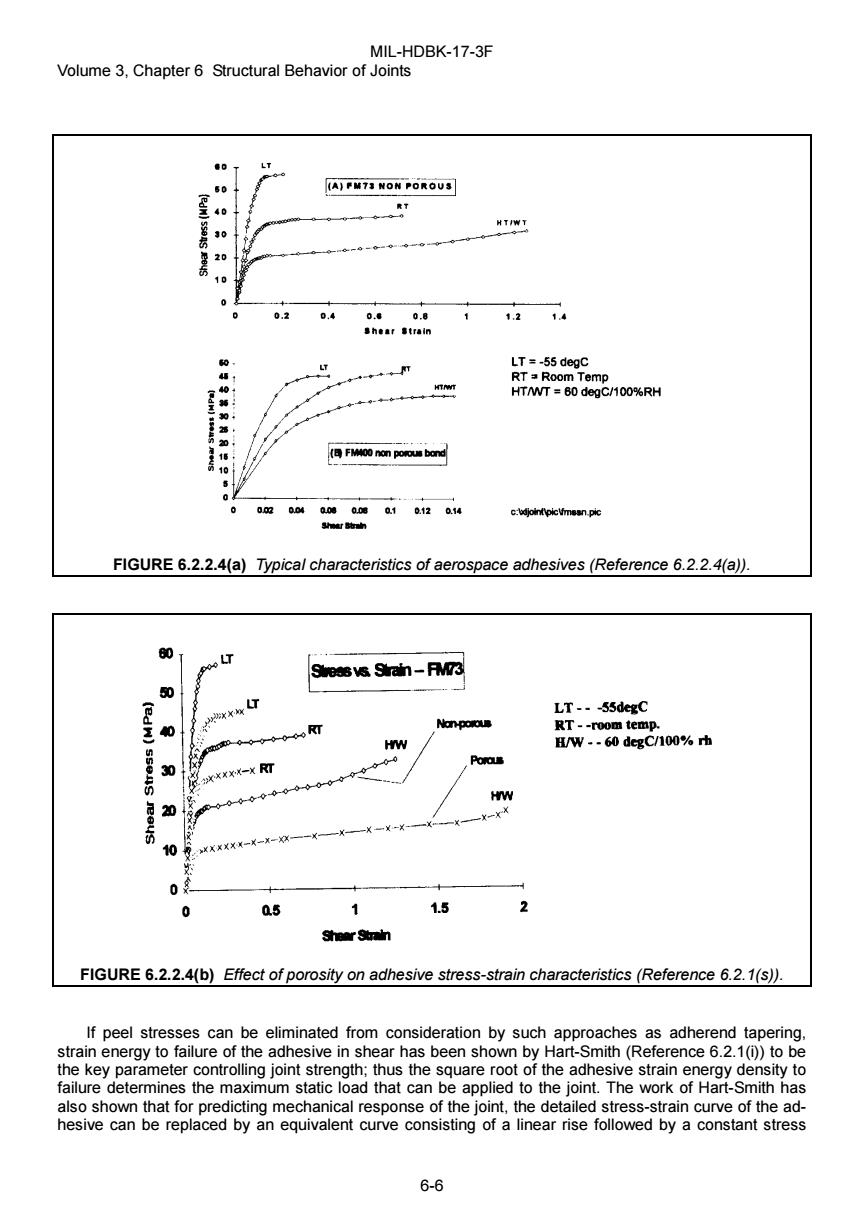
MIL-HDBK-17-3F Volume 3,Chapter 6 Structural Behavior of Joints (A)FM73 NON POROUS (edM)sseas eeys 20 0.2 0.4 0.e0.8 1.2 1.4 Shear事train LT LT =-55 degc s RT=Room Temp T HT/WT 60 degC/100%RH ) 36 FM00 non porous bond 10 002004 0080.08Q10.120.34 c:bdjointpicVimean-pic 陆的 FIGURE 6.2.2.4(a)Typical characteristics of aerospace adhesives(Reference 6.2.2.4(a)). 0 Stessvs Sirain-FM73 50 (edw) LT---55degC Nan-porus RT--room temp. HW H/W --60 degC/100%rh 西 Porous HW 20 -09 10 0 a.5 1.5 Sheer Strain FIGURE 6.2.2.4(b)Effect of porosity on adhesive stress-strain characteristics(Reference 6.2.1(s)). If peel stresses can be eliminated from consideration by such approaches as adherend tapering. strain energy to failure of the adhesive in shear has been shown by Hart-Smith(Reference 6.2.1(i))to be the key parameter controlling joint strength;thus the square root of the adhesive strain energy density to failure determines the maximum static load that can be applied to the joint.The work of Hart-Smith has also shown that for predicting mechanical response of the joint,the detailed stress-strain curve of the ad- hesive can be replaced by an equivalent curve consisting of a linear rise followed by a constant stress 6-6MIL-HDBK-17-3F Volume 3, Chapter 6 Structural Behavior of Joints 6-6 FIGURE 6.2.2.4(a) Typical characteristics of aerospace adhesives (Reference 6.2.2.4(a)). FIGURE 6.2.2.4(b) Effect of porosity on adhesive stress-strain characteristics (Reference 6.2.1(s)). If peel stresses can be eliminated from consideration by such approaches as adherend tapering, strain energy to failure of the adhesive in shear has been shown by Hart-Smith (Reference 6.2.1(i)) to be the key parameter controlling joint strength; thus the square root of the adhesive strain energy density to failure determines the maximum static load that can be applied to the joint. The work of Hart-Smith has also shown that for predicting mechanical response of the joint, the detailed stress-strain curve of the adhesive can be replaced by an equivalent curve consisting of a linear rise followed by a constant stress