正在加载图片...
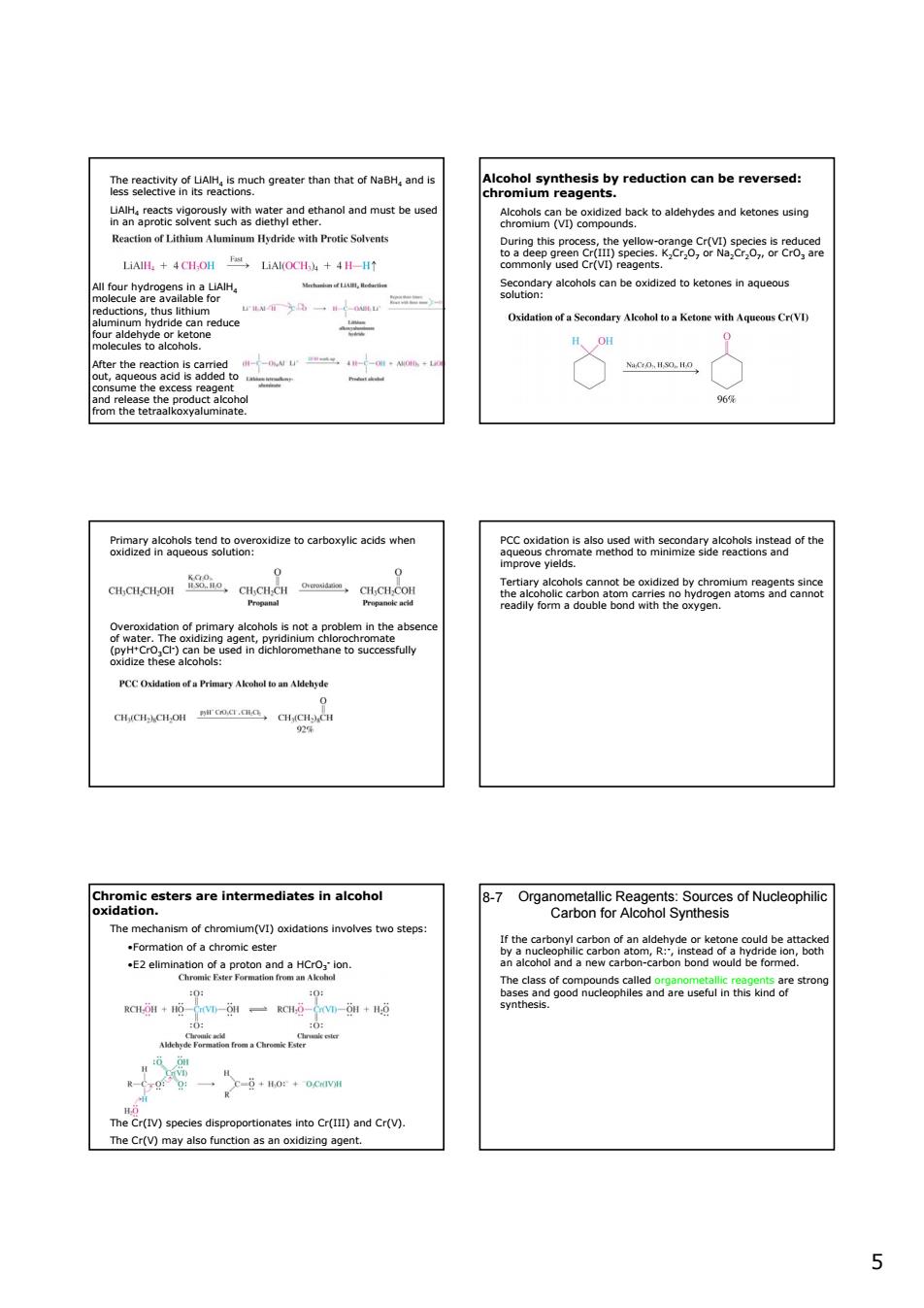
dcbereverd &oosnRe.8gedekoaehydsandketonsusn iIl。+4H,OH feoerbtgaibn2t ne the ie2taeoergonaomrocdaetoartoyccswh 5c2eaoc3aesnoh Ovo 空 B7ogaeamon6Reatgamasowuceoph natomctaprmoenandaHc0:lon w-OH+ mer()d nto Cr()and Cr(V). me Cr(V)may. 5 5 The reactivity of LiAlH4 is much greater than that of NaBH4 and is less selective in its reactions. LiAlH4 reacts vigorously with water and ethanol and must be used in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether. All four hydrogens in a LiAlH4 molecule are available for reductions, thus lithium aluminum hydride can reduce four aldehyde or ketone molecules to alcohols. After the reaction is carried out, aqueous acid is added to consume the excess reagent and release the product alcohol from the tetraalkoxyaluminate. Alcohol synthesis by reduction can be reversed: chromium reagents. Alcohols can be oxidized back to aldehydes and ketones using chromium (VI) compounds. During this process, the yellow-orange Cr(VI) species is reduced to a deep green Cr(III) species. K2Cr2O7 or Na2Cr2O7, or CrO3 are commonly used Cr(VI) reagents. Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones in aqueous solution: Primary alcohols tend to overoxidize to carboxylic acids when oxidized in aqueous solution: Overoxidation of primary alcohols is not a problem in the absence of water. The oxidizing agent, pyridinium chlorochromate (pyH+CrO3Cl- ) can be used in dichloromethane to successfully oxidize these alcohols: PCC oxidation is also used with secondary alcohols instead of the aqueous chromate method to minimize side reactions and improve yields. Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized by chromium reagents since the alcoholic carbon atom carries no hydrogen atoms and cannot readily form a double bond with the oxygen. Chromic esters are intermediates in alcohol oxidation. The mechanism of chromium(VI) oxidations involves two steps: •Formation of a chromic ester •E2 elimination of a proton and a HCrO3 - ion. The Cr(IV) species disproportionates into Cr(III) and Cr(V). The Cr(V) may also function as an oxidizing agent. Organometallic Reagents: Sources of Nucleophilic Carbon for Alcohol Synthesis 8-7 If the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone could be attacked by a nucleophilic carbon atom, R:- , instead of a hydride ion, both an alcohol and a new carbon-carbon bond would be formed. The class of compounds called organometallic reagents are strong bases and good nucleophiles and are useful in this kind of synthesis