正在加载图片...
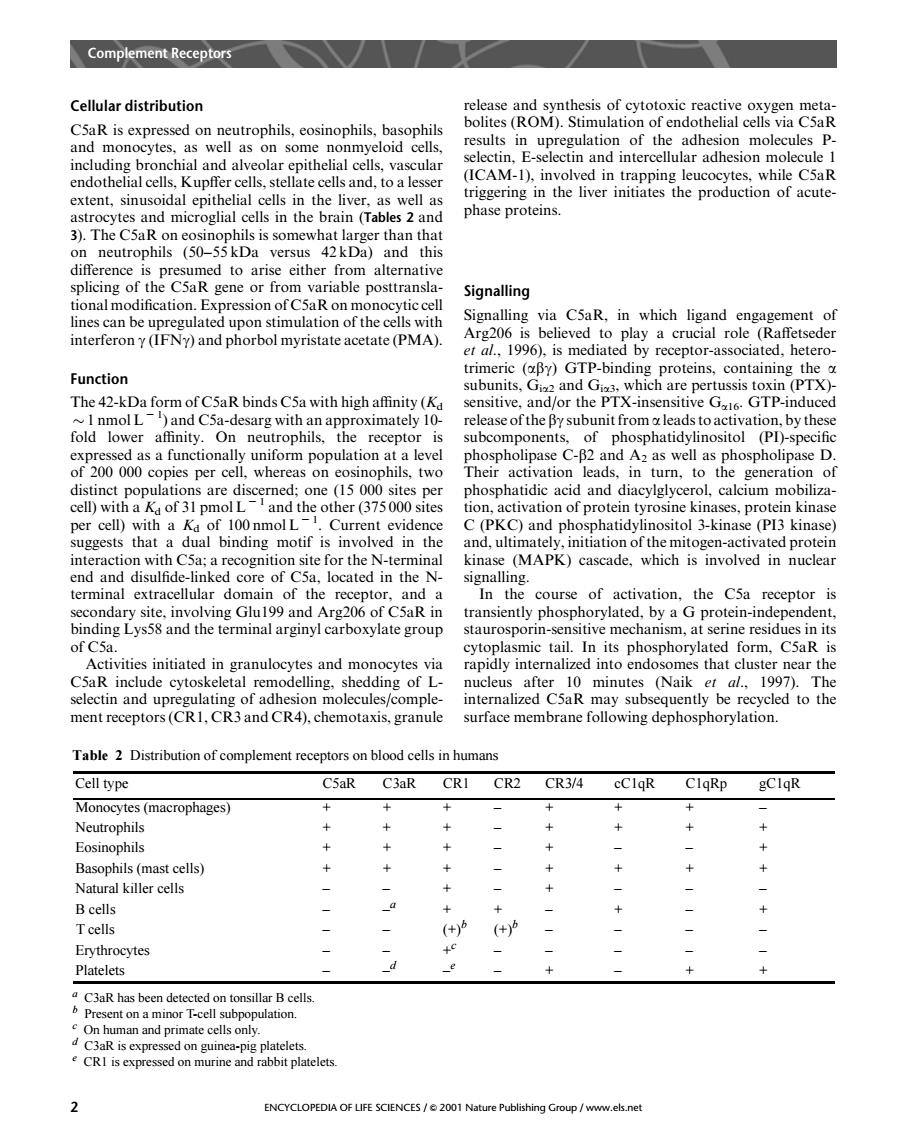
Complemeneepor Cellular distribution elease and synthesis of cytotoxic reactive oxygen meta bolites(ROM).Stimulation of endothelial cells via C5aR ola son adhesion molecules ar adhes endothelial cells.Kupffer cells.stellate cells and.to a lesser (ICAM-1 in d in sion hile C5aR inin the liver initiates the production of acute 3).The C extent,sinusoidal epithelial cells in the liver,as well as cells in the (Ta phase proteins. hils (50-55a difference is presumed to arise either from alternative splicing of the C5aR gene or from variable posttransla- Signalling tate a etate (PMA】 vdto play a cruci Function trimeric (By)GTP-binding proteins containing the subunits,Gi and G.which are pertussis toxin(PTX) nd/or the I X-inse fold nmol I esarg with an approximate sed as a functionally uniform population at a level h ospholipase C-B2 and A2 as well as phospholipase D. of200 000 copies per cell, whereas on eosinophils.two Their activation leads,in turn,to the generation of are phosphatidic acid and l.calcium mop va tol 3-kin .ki suggests that a dual binding motif is involved in the and.ultimately.initation of the mitogen activated protein interaction with C5a;a recognition site for the N-terminal kinase (MAPK)cascade,which is involved in nuclear core of c located in the cours the C5a recepto 1.100a d h binding Lys58 and the terminal arginyl carboxylate group staurosporin-sensitive mechanism.at serine residues in its of C5a cytoplasmic tail.In its phosphorylated form.C5aR is ies initiate in granulocytes and mon ocytes via rapidly internalized into endo es that clust selectin cyt nd y f adhesion cled to the ment receptor s(CrI Cr3and cra)chemotaxis granule surface membrane following dephosphorylation. Table 2 Distribution of complement receptors on blood cells in humans Cell type C5aR C3aR CRI CR2 CR3/4 cClqR ClqRp gCIgR sinophil ophils (mast cells Natural killer cells B cells Tcells (+ (+泸 Platelets nt on am aR is expr rine and rabbit plateletsCellular distribution C5aR is expressed on neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils and monocytes, as well as on some nonmyeloid cells, including bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, stellate cells and, to a lesser extent, sinusoidal epithelial cells in the liver, as well as astrocytes and microglial cells in the brain (Tables 2 and 3). The C5aR on eosinophils is somewhat larger than that on neutrophils (50–55 kDa versus 42 kDa) and this difference is presumed to arise either from alternative splicing of the C5aR gene or from variable posttranslational modification. Expression of C5aR on monocytic cell lines can be upregulated upon stimulation of the cells with interferon g (IFNg) and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA). Function The 42-kDa form of C5aR binds C5a with high affinity (Kd 1 nmol L 2 1 ) and C5a-desarg with an approximately 10- fold lower affinity. On neutrophils, the receptor is expressed as a functionally uniform population at a level of 200 000 copies per cell, whereas on eosinophils, two distinct populations are discerned; one (15 000 sites per cell) with a Kd of 31 pmol L 2 1 and the other (375 000 sites per cell) with a Kd of 100 nmol L 2 1 . Current evidence suggests that a dual binding motif is involved in the interaction with C5a; a recognition site for the N-terminal end and disulfide-linked core of C5a, located in the Nterminal extracellular domain of the receptor, and a secondary site, involving Glu199 and Arg206 of C5aR in binding Lys58 and the terminal arginyl carboxylate group of C5a. Activities initiated in granulocytes and monocytes via C5aR include cytoskeletal remodelling, shedding of Lselectin and upregulating of adhesion molecules/complement receptors (CR1, CR3 and CR4), chemotaxis, granule release and synthesis of cytotoxic reactive oxygen metabolites (ROM). Stimulation of endothelial cells via C5aR results in upregulation of the adhesion molecules Pselectin, E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), involved in trapping leucocytes, while C5aR triggering in the liver initiates the production of acutephase proteins. Signalling Signalling via C5aR, in which ligand engagement of Arg206 is believed to play a crucial role (Raffetseder et al., 1996), is mediated by receptor-associated, heterotrimeric (abg) GTP-binding proteins, containing the a subunits, Gia2 and Gia3, which are pertussis toxin (PTX)- sensitive, and/or the PTX-insensitive Ga16. GTP-induced release of the bg subunit from a leads to activation, by these subcomponents, of phosphatidylinositol (PI)-specific phospholipase C-b2 and A2 as well as phospholipase D. Their activation leads, in turn, to the generation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol, calcium mobilization, activation of protein tyrosine kinases, protein kinase C(PKC) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 kinase) and, ultimately, initiation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, which is involved in nuclear signalling. In the course of activation, the C5a receptor is transiently phosphorylated, by a G protein-independent, staurosporin-sensitive mechanism, at serine residues in its cytoplasmic tail. In its phosphorylated form, C5aR is rapidly internalized into endosomes that cluster near the nucleus after 10 minutes (Naik et al., 1997). The internalized C5aR may subsequently be recycled to the surface membrane following dephosphorylation. Table 2 Distribution of complement receptors on blood cells in humans a C3aR has been detected on tonsillar B cells. b Present on a minor T-cell subpopulation. c On human and primate cells only. d C3aR is expressed on guinea-pig platelets. e CR1 is expressed on murine and rabbit platelets. Cell type C5aR C3aR CR1 CR2 CR3/4 cC1qR C1qRp gC1qR Monocytes (macrophages) + + + – ++ + – Neutrophils + + + – + + + + Eosinophils + + + – + – – + Basophils (mast cells) + + + – ++ + + Natural killer cells – – + – + –– – B cells – –a + + – + – + T cells – – (+)b (+)b –– – – Erythrocytes – – +c –– – – – Platelets – –d –e – + – + + Complement Receptors 2 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net