正在加载图片...
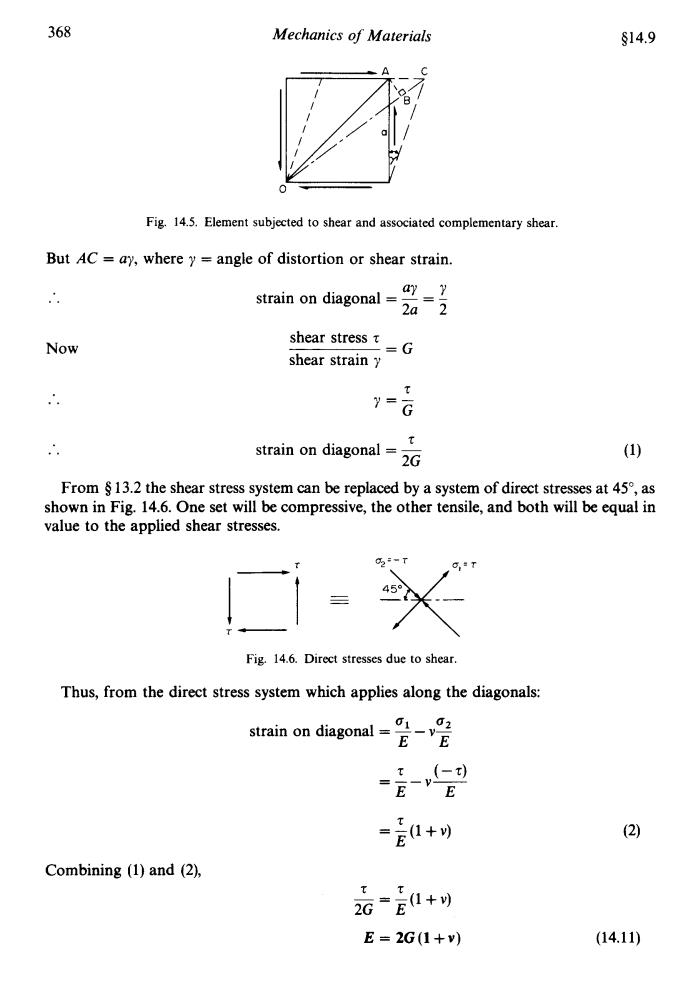
368 Mechanics of Materials §14.9 Fig.14.5.Element subjected to shear and associated complementary shear. But AC ay,where y=angle of distortion or shear strain. strain on diagonal =} 2a2 Now shear stress=G shear strain y y= G strain on diagonalt 2G (10 From $13.2 the shear stress system can be replaced by a system of direct stresses at 45,as shown in Fig.14.6.One set will be compressive,the other tensile,and both will be equal in value to the applied shear stresses. 45° Fig.14.6.Direct stresses due to shear. Thus,from the direct stress system which applies along the diagonals: strain on diagonal= -V- =E1+ T (2) Combining (1)and (2), 2G-E1+) tt E=2G(1+V) (14.11)368 Mechanics of Materials $14.9 Fig. 14.5. Element subjected to shear and associated complementary shear. But AC = ay, where y = angle of distortion or shear strain. .. Now .. .. From Q aY Y strain on diagonal = - = - 2a 2 shear stress z shear strain y =G z y=- G t strain on diagonal = - 2G 3.2 the shear stress system can be replaced by a system of direct stresses at 5", as shown in Fig. 14.6. One set will be compressive, the other tensile, and both will be equal in value to the applied shear stresses. u2=-r /_I ~ - 4x=T _- r- Fig. 14.6. Direct stresses due to shear Thus, from the direct stress system which applies along the diagonals: 01 02 strain on diagonal = -- v- EE (-4 =-- V- EE T = -(1 +v) E Combining (1) and (2), tz -=-(1+v) 2G E E = 2G(l+v) (14.11)