正在加载图片...
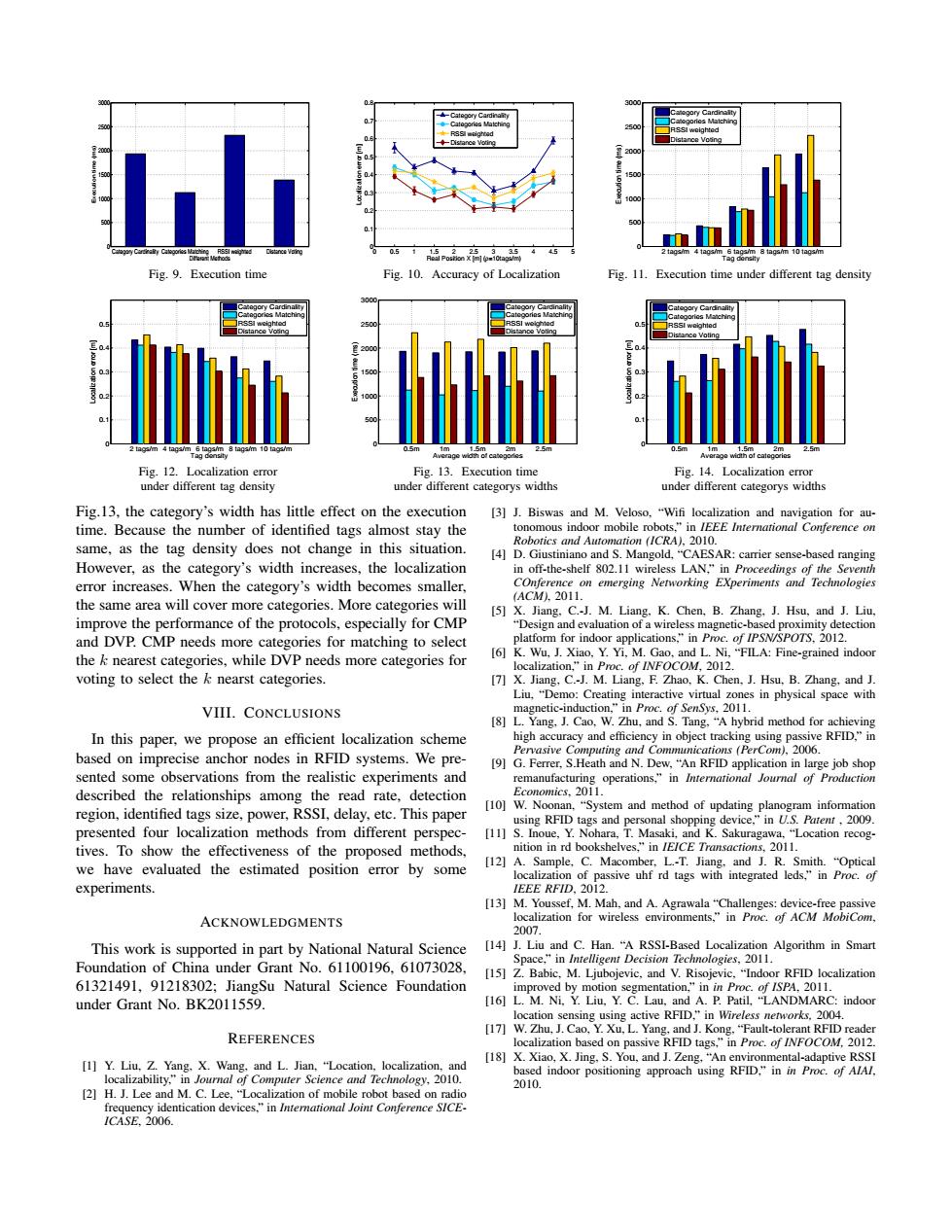
Distance Vosna 8 tags/ Fig.9.Execution time Fig.10.Accuracy of Localization Fig.11.Execution time under different tag density Fig.12.Localization error Fig.13.Execution time Fig.14.Localization error under different tag density under different categorys widths under different categorys widths Fig.13,the category's width has little effect on the execution [3]J.Biswas and M.Veloso,"Wifi localization and navigation for au- time.Because the number of identified tags almost stay the tonomous indoor mobile robots,"in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).2010. same,as the tag density does not change in this situation. [4]D.Giustiniano and S.Mangold,"CAESAR:carrier sense-based ranging However,as the category's width increases,the localization in off-the-shelf 802.11 wireless LAN,"in Proceedings of the Seventh error increases.When the category's width becomes smaller, COnference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies ACM).2011. the same area will cover more categories.More categories will [5]X.Jiang.C.-J.M.Liang,K.Chen,B.Zhang,J.Hsu,and J.Liu. improve the performance of the protocols,especially for CMP "Design and evaluation of a wireless magnetic-based proximity detection and DVP.CMP needs more categories for matching to select platform for indoor applications."in Proc.of IPSN/SPOTS,2012. the k nearest categories,while DVP needs more categories for [6]K.Wu.J.Xiao.Y.Yi,M.Gao,and L.Ni,"FILA:Fine-grained indoor localization,"in Proc.of INFOCOM,2012. voting to select the k nearst categories. [7]X.Jiang.C.J.M.Liang.F.Zhao,K.Chen,J.Hsu,B.Zhang,and J. Liu,"Demo:Creating interactive virtual zones in physical space with VIII.CONCLUSIONS magnetic-induction,"in Proc.of SenSys,2011. [8]L.Yang,J.Cao,W.Zhu,and S.Tang,"A hybrid method for achieving In this paper,we propose an efficient localization scheme high accuracy and efficiency in object tracking using passive RFID,"in based on imprecise anchor nodes in RFID systems.We pre- Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom),2006. [9]G.Ferrer,S.Heath and N.Dew,"An RFID application in large job shop sented some observations from the realistic experiments and remanufacturing operations."in International Journal of Production described the relationships among the read rate,detection Economics,2011. region,identified tags size,power,RSSI,delay,etc.This paper (10]W.Noonan,"System and method of updating planogram information using RFID tags and personal shopping device,"in U.S.Patent,2009. presented four localization methods from different perspec- [11]S.Inoue,Y.Nohara,T.Masaki,and K.Sakuragawa,"Location recog- tives.To show the effectiveness of the proposed methods, nition in rd bookshelves,"in IEICE Transactions,2011. we have evaluated the estimated position error by some [12]A.Sample,C.Macomber,L.-T.Jiang.and J.R.Smith."Optical localization of passive uhf rd tags with integrated leds,"in Proc.of experiments. IEEE RFID,2012. [13]M.Youssef,M.Mah,and A.Agrawala "Challenges:device-free passive ACKNOWLEDGMENTS localization for wireless environments,"in Proc.of ACM MobiCom, 2007. This work is supported in part by National Natural Science [14]J.Liu and C.Han."A RSSI-Based Localization Algorithm in Smart Foundation of China under Grant No.61100196,61073028, Space,"in Intelligent Decision Technologies,2011. [15]Z.Babic,M.Ljubojevic,and V.Risojevic,"Indoor RFID localization 61321491,91218302;JiangSu Natural Science Foundation improved by motion segmentation,"inin Proc.of /SPA.2011. under Grant No.BK2011559 [16]L.M.Ni.Y.Liu,Y.C.Lau,and A.P.Patil,"LANDMARC:indoor location sensing using active RFID,"in Wireless networks.2004. REFERENCES [17]W.Zhu,J.Cao,Y.Xu.L.Yang.and J.Kong."Fault-tolerant RFID reader localization based on passive RFID tags,"in Proc.of INFOCOM,2012. [18]X.Xiao,X.Jing,S.You,and J.Zeng,"An environmental-adaptive RSSI [1]Y.Liu,Z.Yang.X.Wang.and L.Jian,"Location,localization,and localizability,"in Journal of Computer Science and Technology,2010. based indoor positioning approach using RFID."in in Proc.of AlAl. 2010. [2]H.J.Lee and M.C.Lee,"Localization of mobile robot based on radio frequency identication devices"in Intemational Joint Conference SICE- ICASE.2006.Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 Different Methods Execution time (ms) Fig. 9. Execution time 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 Real Position X [m] (ρ=10tags/m) Localization error [m] Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting Fig. 10. Accuracy of Localization 2 tags/m 4 tags/m 6 tags/m 8 tags/m 10 tags/m 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 Tag density Execution time (ms) Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting Fig. 11. Execution time under different tag density 2 tags/m 4 tags/m 6 tags/m 8 tags/m 10 tags/m 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Tag density Localization error [m] Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting Fig. 12. Localization error under different tag density 0.5m 1m 1.5m 2m 2.5m 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 Average width of categories Execution time (ms) Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting Fig. 13. Execution time under different categorys widths 0.5m 1m 1.5m 2m 2.5m 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Average width of categories Localization error [m] Category Cardinality Categories Matching RSSI weighted Distance Voting Fig. 14. Localization error under different categorys widths Fig.13, the category’s width has little effect on the execution time. Because the number of identified tags almost stay the same, as the tag density does not change in this situation. However, as the category’s width increases, the localization error increases. When the category’s width becomes smaller, the same area will cover more categories. More categories will improve the performance of the protocols, especially for CMP and DVP. CMP needs more categories for matching to select the k nearest categories, while DVP needs more categories for voting to select the k nearst categories. VIII. CONCLUSIONS In this paper, we propose an efficient localization scheme based on imprecise anchor nodes in RFID systems. We presented some observations from the realistic experiments and described the relationships among the read rate, detection region, identified tags size, power, RSSI, delay, etc. This paper presented four localization methods from different perspectives. To show the effectiveness of the proposed methods, we have evaluated the estimated position error by some experiments. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work is supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61100196, 61073028, 61321491, 91218302; JiangSu Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. BK2011559. REFERENCES [1] Y. Liu, Z. Yang, X. Wang, and L. Jian, “Location, localization, and localizability,” in Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2010. [2] H. J. Lee and M. C. Lee, “Localization of mobile robot based on radio frequency identication devices,” in International Joint Conference SICEICASE, 2006. [3] J. Biswas and M. Veloso, “Wifi localization and navigation for autonomous indoor mobile robots,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2010. [4] D. Giustiniano and S. Mangold, “CAESAR: carrier sense-based ranging in off-the-shelf 802.11 wireless LAN,” in Proceedings of the Seventh COnference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies (ACM), 2011. [5] X. Jiang, C.-J. M. Liang, K. Chen, B. Zhang, J. Hsu, and J. Liu, “Design and evaluation of a wireless magnetic-based proximity detection platform for indoor applications,” in Proc. of IPSN/SPOTS, 2012. [6] K. Wu, J. Xiao, Y. Yi, M. Gao, and L. Ni, “FILA: Fine-grained indoor localization,” in Proc. of INFOCOM, 2012. [7] X. Jiang, C.-J. M. Liang, F. Zhao, K. Chen, J. Hsu, B. Zhang, and J. Liu, “Demo: Creating interactive virtual zones in physical space with magnetic-induction,” in Proc. of SenSys, 2011. [8] L. Yang, J. Cao, W. Zhu, and S. Tang, “A hybrid method for achieving high accuracy and efficiency in object tracking using passive RFID,” in Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), 2006. [9] G. Ferrer, S.Heath and N. Dew, “An RFID application in large job shop remanufacturing operations,” in International Journal of Production Economics, 2011. [10] W. Noonan, “System and method of updating planogram information using RFID tags and personal shopping device,” in U.S. Patent , 2009. [11] S. Inoue, Y. Nohara, T. Masaki, and K. Sakuragawa, “Location recognition in rd bookshelves,” in IEICE Transactions, 2011. [12] A. Sample, C. Macomber, L.-T. Jiang, and J. R. Smith. “Optical localization of passive uhf rd tags with integrated leds,” in Proc. of IEEE RFID, 2012. [13] M. Youssef, M. Mah, and A. Agrawala “Challenges: device-free passive localization for wireless environments,” in Proc. of ACM MobiCom, 2007. [14] J. Liu and C. Han. “A RSSI-Based Localization Algorithm in Smart Space,” in Intelligent Decision Technologies, 2011. [15] Z. Babic, M. Ljubojevic, and V. Risojevic, “Indoor RFID localization improved by motion segmentation,” in in Proc. of ISPA, 2011. [16] L. M. Ni, Y. Liu, Y. C. Lau, and A. P. Patil, “LANDMARC: indoor location sensing using active RFID,” in Wireless networks, 2004. [17] W. Zhu, J. Cao, Y. Xu, L. Yang, and J. Kong, “Fault-tolerant RFID reader localization based on passive RFID tags,” in Proc. of INFOCOM, 2012. [18] X. Xiao, X. Jing, S. You, and J. Zeng, “An environmental-adaptive RSSI based indoor positioning approach using RFID,” in in Proc. of AIAI, 2010