正在加载图片...
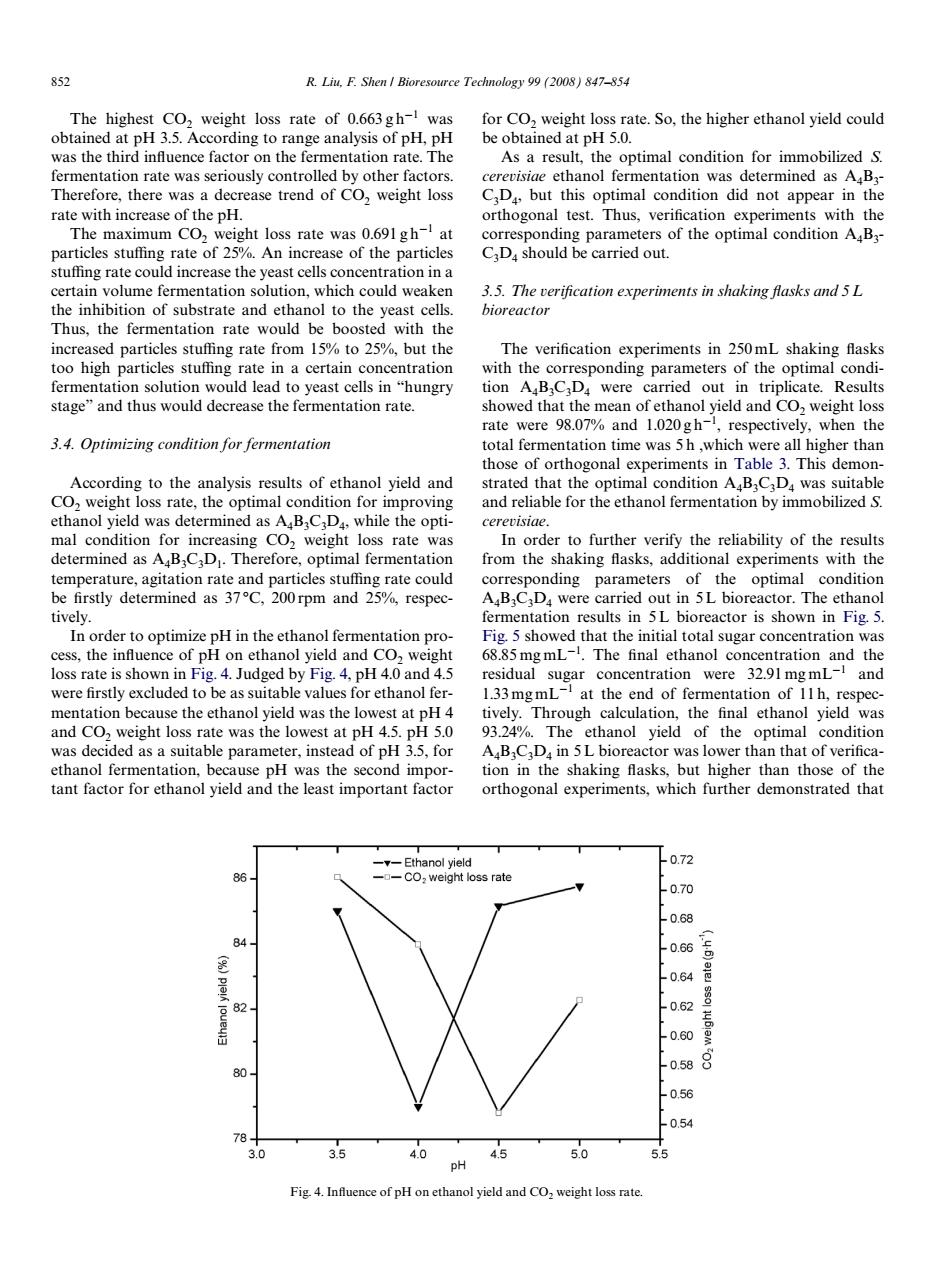
852 R.Liu.F.Shen Bioresource Technology 99 (2008)847-854 The highest CO,weight loss rate of 0.663gh-was for CO,weight loss rate.So,the higher ethanol yield could obtained at pH 3.5.According to range analysis of pH,pH be obtained at pH 5.0. was the third influence factor on the fermentation rate.The As a result,the optimal condition for immobilized S. fermentation rate was seriously controlled by other factors. cerevisiae ethanol fermentation was determined as A4B3- Therefore,there was a decrease trend of CO,weight loss C.Da,but this optimal condition did not appear in the rate with increase of the pH. orthogonal test.Thus,verification experiments with the The maximum CO2 weight loss rate was 0.691gh-at corresponding parameters of the optimal condition A B3- particles stuffing rate of 25%.An increase of the particles C.D.should be carried out. stuffing rate could increase the yeast cells concentration in a certain volume fermentation solution,which could weaken 3.5.The verification experiments in shaking flasks and 5 L the inhibition of substrate and ethanol to the yeast cells. bioreactor Thus,the fermentation rate would be boosted with the increased particles stuffing rate from 15%to 25%,but the The verification experiments in 250mL shaking flasks too high particles stuffing rate in a certain concentration with the corresponding parameters of the optimal condi- fermentation solution would lead to yeast cells in"hungry tion A B3CD4 were carried out in triplicate.Results stage"and thus would decrease the fermentation rate. showed that the mean of ethanol yield and CO,weight loss rate were 98.07%and 1.020gh-,respectively,when the 3.4.Optimizing condition for fermentation total fermentation time was 5h,which were all higher than those of orthogonal experiments in Table 3.This demon- According to the analysis results of ethanol yield and strated that the optimal condition ABC Da was suitable CO2 weight loss rate,the optimal condition for improving and reliable for the ethanol fermentation by immobilized S. ethanol yield was determined as A B3C Da,while the opti- cerevisiae. mal condition for increasing CO2 weight loss rate was In order to further verify the reliability of the results determined as A BC,D.Therefore,optimal fermentation from the shaking flasks,additional experiments with the temperature,agitation rate and particles stuffing rate could corresponding parameters of the optimal condition be firstly determined as 37C,200rpm and 25%,respec- A B C Da were carried out in 5L bioreactor.The ethanol tively. fermentation results in 5L bioreactor is shown in Fig.5. In order to optimize pH in the ethanol fermentation pro- Fig.5 showed that the initial total sugar concentration was cess,the influence of pH on ethanol yield and CO,weight 68.85mgmL-.The final ethanol concentration and the loss rate is shown in Fig.4.Judged by Fig.4,pH 4.0 and 4.5 residual sugar concentration were 32.91 mgmL-and were firstly excluded to be as suitable values for ethanol fer- 1.33mgmL-at the end of fermentation of 11h,respec- mentation because the ethanol yield was the lowest at pH 4 tively.Through calculation,the final ethanol yield was and CO,weight loss rate was the lowest at pH 4.5.pH 5.0 93.24%.The ethanol yield of the optimal condition was decided as a suitable parameter,instead of pH 3.5,for A B3C3D in 5L bioreactor was lower than that of verifica- ethanol fermentation,because pH was the second impor- tion in the shaking flasks,but higher than those of the tant factor for ethanol yield and the least important factor orthogonal experiments,which further demonstrated that -Ethanol yield -0.72 86- -CO weight loss rate 0.70 0.68 84 0.66 0.64 豆 82 0.62 0.60 0.58 80 0.56 .0.54 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 pH Fig.4.Influence of pH on ethanol yield and CO,weight loss rate.852 R. Liu, F. Shen / Bioresource Technology 99 (2008) 847–854 The highest CO2 weight loss rate of 0.663 g h¡1 was obtained at pH 3.5. According to range analysis of pH, pH was the third inXuence factor on the fermentation rate. The fermentation rate was seriously controlled by other factors. Therefore, there was a decrease trend of CO2 weight loss rate with increase of the pH. The maximum CO2 weight loss rate was 0.691 g h¡1 at particles stuYng rate of 25%. An increase of the particles stuYng rate could increase the yeast cells concentration in a certain volume fermentation solution, which could weaken the inhibition of substrate and ethanol to the yeast cells. Thus, the fermentation rate would be boosted with the increased particles stuYng rate from 15% to 25%, but the too high particles stuYng rate in a certain concentration fermentation solution would lead to yeast cells in “hungry stage” and thus would decrease the fermentation rate. 3.4. Optimizing condition for fermentation According to the analysis results of ethanol yield and CO2 weight loss rate, the optimal condition for improving ethanol yield was determined as A4B3C3D4, while the optimal condition for increasing CO2 weight loss rate was determined as A4B3C3D1. Therefore, optimal fermentation temperature, agitation rate and particles stuYng rate could be Wrstly determined as 37 °C, 200 rpm and 25%, respectively. In order to optimize pH in the ethanol fermentation process, the inXuence of pH on ethanol yield and CO2 weight loss rate is shown in Fig. 4. Judged by Fig. 4, pH 4.0 and 4.5 were Wrstly excluded to be as suitable values for ethanol fermentation because the ethanol yield was the lowest at pH 4 and CO2 weight loss rate was the lowest at pH 4.5. pH 5.0 was decided as a suitable parameter, instead of pH 3.5, for ethanol fermentation, because pH was the second important factor for ethanol yield and the least important factor for CO2 weight loss rate. So, the higher ethanol yield could be obtained at pH 5.0. As a result, the optimal condition for immobilized S. cerevisiae ethanol fermentation was determined as A4B3- C3D4, but this optimal condition did not appear in the orthogonal test. Thus, veriWcation experiments with the corresponding parameters of the optimal condition A4B3- C3D4 should be carried out. 3.5. The veriWcation experiments in shaking Xasks and 5 L bioreactor The veriWcation experiments in 250 mL shaking Xasks with the corresponding parameters of the optimal condition A4B3C3D4 were carried out in triplicate. Results showed that the mean of ethanol yield and CO2 weight loss rate were 98.07% and 1.020 g h¡1 , respectively, when the total fermentation time was 5 h ,which were all higher than those of orthogonal experiments in Table 3. This demonstrated that the optimal condition A4B3C3D4 was suitable and reliable for the ethanol fermentation by immobilized S. cerevisiae. In order to further verify the reliability of the results from the shaking Xasks, additional experiments with the corresponding parameters of the optimal condition A4B3C3D4 were carried out in 5 L bioreactor. The ethanol fermentation results in 5 L bioreactor is shown in Fig. 5. Fig. 5 showed that the initial total sugar concentration was 68.85 mg mL¡1 . The Wnal ethanol concentration and the residual sugar concentration were 32.91 mg mL¡1 and 1.33 mg mL¡1 at the end of fermentation of 11 h, respectively. Through calculation, the Wnal ethanol yield was 93.24%. The ethanol yield of the optimal condition A4B3C3D4 in 5 L bioreactor was lower than that of veriWcation in the shaking Xasks, but higher than those of the orthogonal experiments, which further demonstrated that Fig. 4. InXuence of pH on ethanol yield and CO2 weight loss rate