正在加载图片...
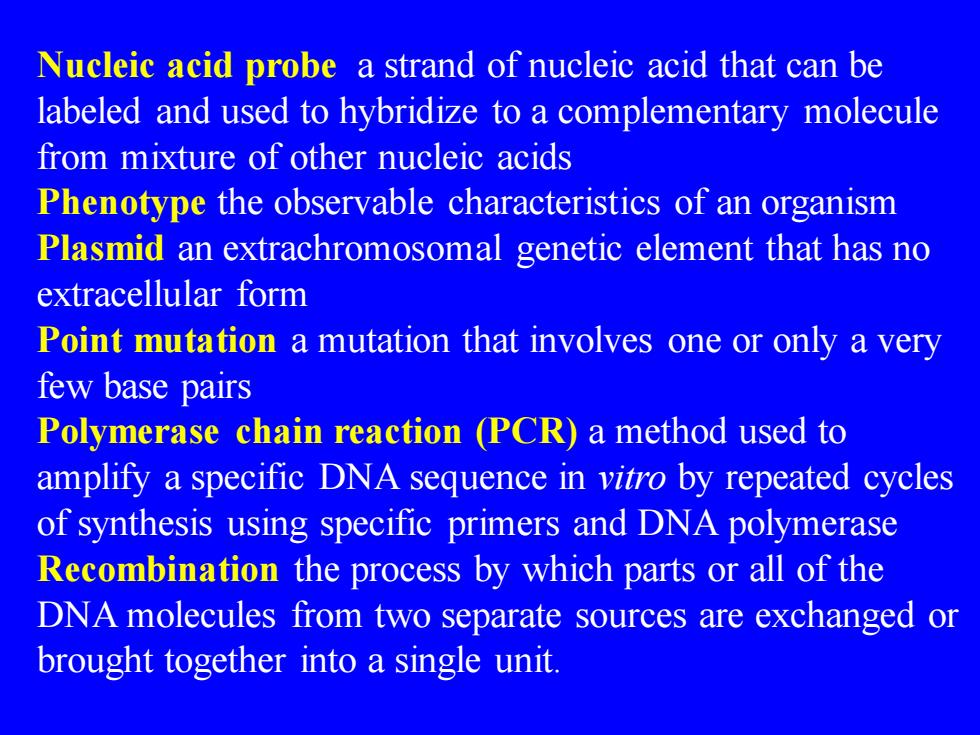
Nucleic acid probe a strand of nucleic acid that can be labeled and used to hybridize to a complementary molecule from mixture of other nucleic acids Phenotype the observable characteristics of an organism Plasmid an extrachromosomal genetic element that has no extracellular form Point mutation a mutation that involves one or only a very few base pairs Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) a method used to amplify a specific DNA sequence in vitro by repeated cycles of synthesis using specific primers and DNA polymerase Recombination the process by which parts or all of the DNA molecules from two separate sources are exchanged or brought together into a single unit.Nucleic acid probe a strand of nucleic acid that can be labeled and used to hybridize to a complementary molecule from mixture of other nucleic acids Phenotype the observable characteristics of an organism Plasmid an extrachromosomal genetic element that has no extracellular form Point mutation a mutation that involves one or only a very few base pairs Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) a method used to amplify a specific DNA sequence in vitro by repeated cycles of synthesis using specific primers and DNA polymerase Recombination the process by which parts or all of the DNA molecules from two separate sources are exchanged or brought together into a single unit