正在加载图片...
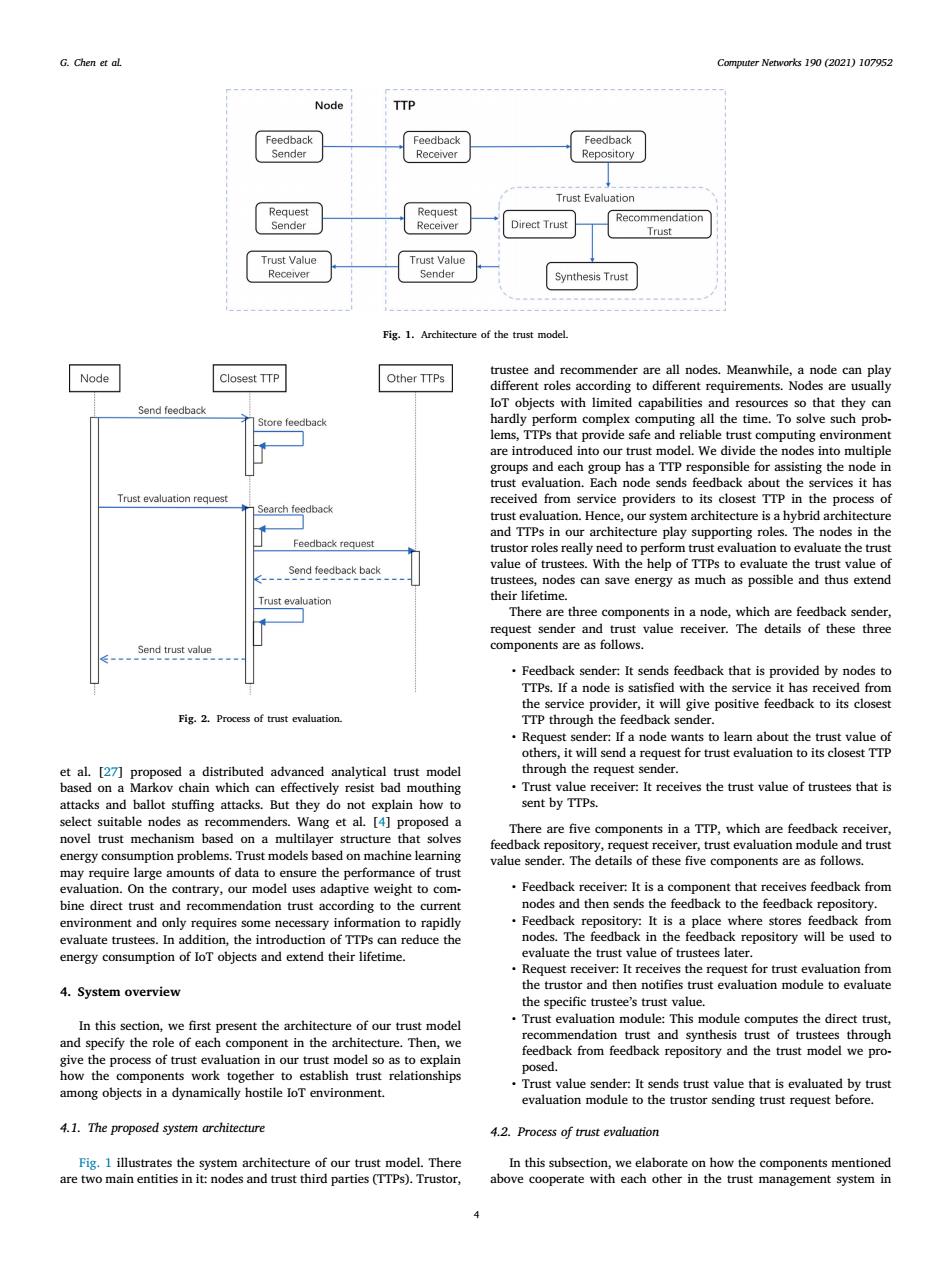
G.Chen et al. Computer Networks 190(2021)107952 Node TTP Feedback Feedback Feedback sender Recerver RKepository Trust Evaluation Request Request Recommendation Sender Receiver Direct Trust Trust Trust Value Trust Value Receiver Sender Synthesis Trust Fig.1.Architecture of the trust model. trustee and recommender are all nodes.Meanwhile,a node can play Node Closest TTP Other TTPs different roles according to different requirements.Nodes are usually Send feedback IoT objects with limited capabilities and resources so that they can Store feedback hardly perform complex computing all the time.To solve such prob- lems,TTPs that provide safe and reliable trust computing environment are introduced into our trust model.We divide the nodes into multiple groups and each group has a TTP responsible for assisting the node in trust evaluation.Each node sends feedback about the services it has Trust evaluation request received from service providers to its closest TTP in the process of Search feedback trust evaluation.Hence,our system architecture is a hybrid architecture and TTPs in our architecture play supporting roles.The nodes in the Feedback request trustor roles really need to perform trust evaluation to evaluate the trust Send feedback back value of trustees.With the help of TTPs to evaluate the trust value of trustees,nodes can save energy as much as possible and thus extend Trust evaluation their lifetime. There are three components in a node,which are feedback sender, request sender and trust value receiver.The details of these three Send trust value components are as follows. Feedback sender:It sends feedback that is provided by nodes to TTPs.If a node is satisfied with the service it has received from the service provider,it will give positive feedback to its closest Fig.2.Process of trust evaluation. TTP through the feedback sender. Request sender:If a node wants to learn about the trust value of others,it will send a request for trust evaluation to its closest TTP et al.[27]proposed a distributed advanced analytical trust model through the request sender. based on a Markov chain which can effectively resist bad mouthing Trust value receiver:It receives the trust value of trustees that is attacks and ballot stuffing attacks.But they do not explain how to sent by TTPs. select suitable nodes as recommenders.Wang et al.[4]proposed a There are five components in a TTP,which are feedback receiver, novel trust mechanism based on a multilayer structure that solves energy consumption problems.Trust models based on machine learning feedback repository,request receiver,trust evaluation module and trust value sender.The details of these five components are as follows. may require large amounts of data to ensure the performance of trust evaluation.On the contrary,our model uses adaptive weight to com- Feedback receiver:It is a component that receives feedback from bine direct trust and recommendation trust according to the current nodes and then sends the feedback to the feedback repository. environment and only requires some necessary information to rapidly Feedback repository:It is a place where stores feedback from evaluate trustees.In addition,the introduction of TTPs can reduce the nodes.The feedback in the feedback repository will be used to energy consumption of IoT objects and extend their lifetime. evaluate the trust value of trustees later. Request receiver:It receives the request for trust evaluation from 4.System overview the trustor and then notifies trust evaluation module to evaluate the specific trustee's trust value In this section,we first present the architecture of our trust model Trust evaluation module:This module computes the direct trust, and specify the role of each component in the architecture.Then,we recommendation trust and synthesis trust of trustees through give the process of trust evaluation in our trust model so as to explain feedback from feedback repository and the trust model we pro- how the components work together to establish trust relationships posed. .Trust value sender:It sends trust value that is evaluated by trust among objects in a dynamically hostile IoT environment. evaluation module to the trustor sending trust request before. 4.1.The proposed system architecture 4.2.Process of trust evaluation Fig.1 illustrates the system architecture of our trust model.There In this subsection,we elaborate on how the components mentioned are two main entities in it:nodes and trust third parties (TTPs).Trustor, above cooperate with each other in the trust management system inComputer Networks 190 (2021) 107952 4 G. Chen et al. Fig. 1. Architecture of the trust model. Fig. 2. Process of trust evaluation. et al. [27] proposed a distributed advanced analytical trust model based on a Markov chain which can effectively resist bad mouthing attacks and ballot stuffing attacks. But they do not explain how to select suitable nodes as recommenders. Wang et al. [4] proposed a novel trust mechanism based on a multilayer structure that solves energy consumption problems. Trust models based on machine learning may require large amounts of data to ensure the performance of trust evaluation. On the contrary, our model uses adaptive weight to combine direct trust and recommendation trust according to the current environment and only requires some necessary information to rapidly evaluate trustees. In addition, the introduction of TTPs can reduce the energy consumption of IoT objects and extend their lifetime. 4. System overview In this section, we first present the architecture of our trust model and specify the role of each component in the architecture. Then, we give the process of trust evaluation in our trust model so as to explain how the components work together to establish trust relationships among objects in a dynamically hostile IoT environment. 4.1. The proposed system architecture Fig. 1 illustrates the system architecture of our trust model. There are two main entities in it: nodes and trust third parties (TTPs). Trustor, trustee and recommender are all nodes. Meanwhile, a node can play different roles according to different requirements. Nodes are usually IoT objects with limited capabilities and resources so that they can hardly perform complex computing all the time. To solve such problems, TTPs that provide safe and reliable trust computing environment are introduced into our trust model. We divide the nodes into multiple groups and each group has a TTP responsible for assisting the node in trust evaluation. Each node sends feedback about the services it has received from service providers to its closest TTP in the process of trust evaluation. Hence, our system architecture is a hybrid architecture and TTPs in our architecture play supporting roles. The nodes in the trustor roles really need to perform trust evaluation to evaluate the trust value of trustees. With the help of TTPs to evaluate the trust value of trustees, nodes can save energy as much as possible and thus extend their lifetime. There are three components in a node, which are feedback sender, request sender and trust value receiver. The details of these three components are as follows. • Feedback sender: It sends feedback that is provided by nodes to TTPs. If a node is satisfied with the service it has received from the service provider, it will give positive feedback to its closest TTP through the feedback sender. • Request sender: If a node wants to learn about the trust value of others, it will send a request for trust evaluation to its closest TTP through the request sender. • Trust value receiver: It receives the trust value of trustees that is sent by TTPs. There are five components in a TTP, which are feedback receiver, feedback repository, request receiver, trust evaluation module and trust value sender. The details of these five components are as follows. • Feedback receiver: It is a component that receives feedback from nodes and then sends the feedback to the feedback repository. • Feedback repository: It is a place where stores feedback from nodes. The feedback in the feedback repository will be used to evaluate the trust value of trustees later. • Request receiver: It receives the request for trust evaluation from the trustor and then notifies trust evaluation module to evaluate the specific trustee’s trust value. • Trust evaluation module: This module computes the direct trust, recommendation trust and synthesis trust of trustees through feedback from feedback repository and the trust model we proposed. • Trust value sender: It sends trust value that is evaluated by trust evaluation module to the trustor sending trust request before. 4.2. Process of trust evaluation In this subsection, we elaborate on how the components mentioned above cooperate with each other in the trust management system in