正在加载图片...
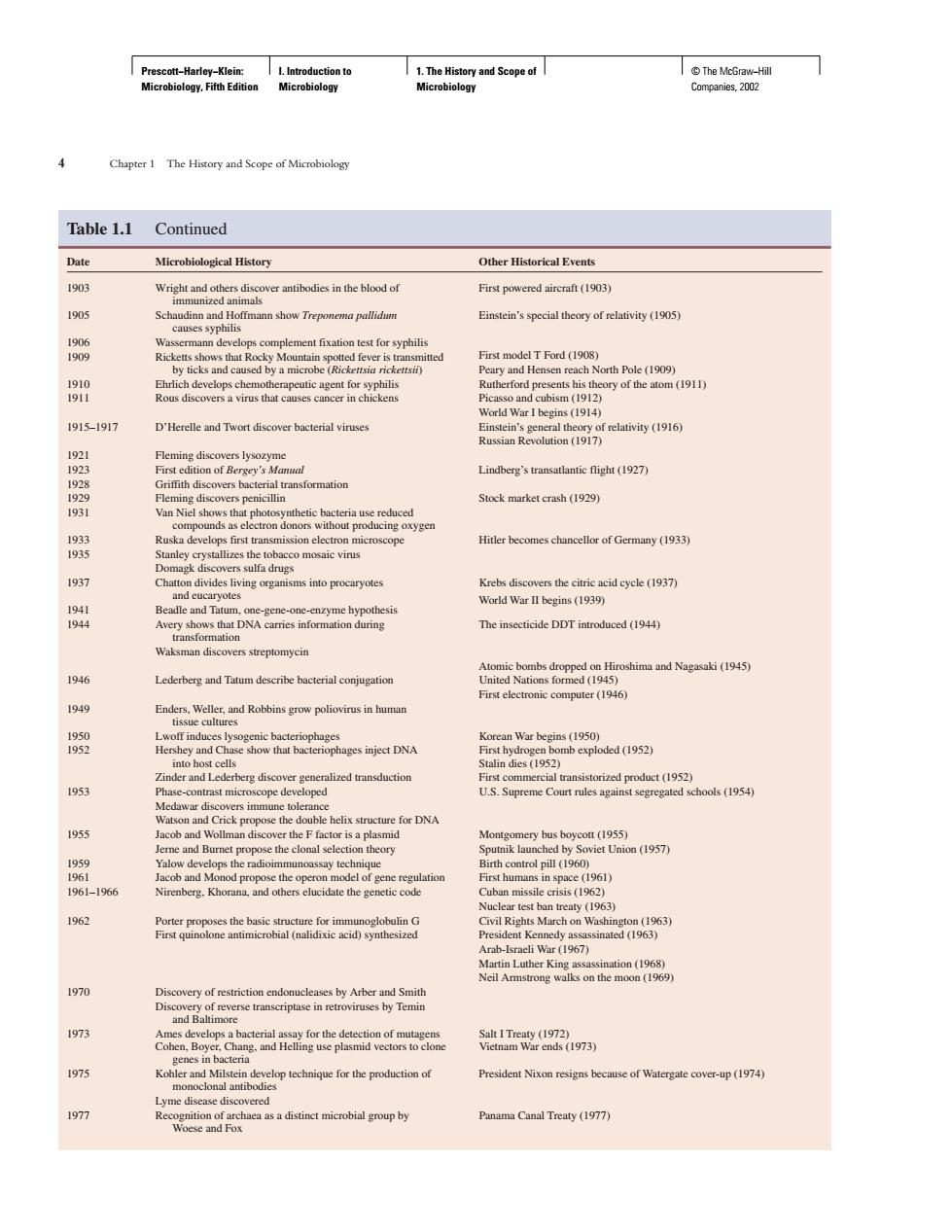
eiea Table 1.1 Continued Date Microbiological History Other Historical Events 1905 Scha nn show Treponema pallidum Einstein's special theory of relativity (1905) ticks and ca fotTFmda90g 1915-1917 D'Herellead bacterial virse Lindberg's flight (197) 8 ellor of Gemmany (1933) 1937 18 duced (194) 1946 Lederberg and Tatum describe bacterial conjugation 1949 n War begin DNA oded (1952 1953 hools(1954 re for DNA 195 (9) 1962 Arab-l 1970 1973 Ty973 197s ergale cover-up(1 1977 Canal Treaty (197) Prescott−Harley−Klein: Microbiology, Fifth Edition I. Introduction to Microbiology 1. The History and Scope of Microbiology © The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2002 4 Chapter 1The History and Scope of Microbiology Table 1.1 Continued Date Microbiological History Other Historical Events 1903 Wright and others discover antibodies in the blood of First powered aircraft (1903) immunized animals 1905 Schaudinn and Hoffmann show Treponema pallidum Einstein’s special theory of relativity (1905) causes syphilis 1906 Wassermann develops complement fixation test for syphilis 1909 Ricketts shows that Rocky Mountain spotted fever is transmitted First model T Ford (1908) by ticks and caused by a microbe (Rickettsia rickettsii) Peary and Hensen reach North Pole (1909) 1910 Ehrlich develops chemotherapeutic agent for syphilis Rutherford presents his theory of the atom (1911) 1911 Rous discovers a virus that causes cancer in chickens Picasso and cubism (1912) World War I begins (1914) 1915–1917 D’Herelle and Twort discover bacterial viruses Einstein’s general theory of relativity (1916) Russian Revolution (1917) 1921 Fleming discovers lysozyme 1923 First edition of Bergey’s Manual Lindberg’s transatlantic flight (1927) 1928 Griffith discovers bacterial transformation 1929 Fleming discovers penicillin Stock market crash (1929) 1931 Van Niel shows that photosynthetic bacteria use reduced compounds as electron donors without producing oxygen 1933 Ruska develops first transmission electron microscope Hitler becomes chancellor of Germany (1933) 1935 Stanley crystallizes the tobacco mosaic virus Domagk discovers sulfa drugs 1937 Chatton divides living organisms into procaryotes Krebs discovers the citric acid cycle (1937) and eucaryotes World War II begins (1939) 1941 Beadle and Tatum, one-gene-one-enzyme hypothesis 1944 Avery shows that DNA carries information during The insecticide DDT introduced (1944) transformation Waksman discovers streptomycin Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki (1945) 1946 Lederberg and Tatum describe bacterial conjugation United Nations formed (1945) First electronic computer (1946) 1949 Enders, Weller, and Robbins grow poliovirus in human tissue cultures 1950 Lwoff induces lysogenic bacteriophages Korean War begins (1950) 1952 Hershey and Chase show that bacteriophages inject DNA First hydrogen bomb exploded (1952) into host cells Stalin dies (1952) Zinder and Lederberg discover generalized transduction First commercial transistorized product (1952) 1953 Phase-contrast microscope developed U.S. Supreme Court rules against segregated schools (1954) Medawar discovers immune tolerance Watson and Crick propose the double helix structure for DNA 1955 Jacob and Wollman discover the F factor is a plasmid Montgomery bus boycott (1955) Jerne and Burnet propose the clonal selection theory Sputnik launched by Soviet Union (1957) 1959 Yalow develops the radioimmunoassay technique Birth control pill (1960) 1961 Jacob and Monod propose the operon model of gene regulation First humans in space (1961) 1961–1966 Nirenberg, Khorana, and others elucidate the genetic code Cuban missile crisis (1962) Nuclear test ban treaty (1963) 1962 Porter proposes the basic structure for immunoglobulin G Civil Rights March on Washington (1963) First quinolone antimicrobial (nalidixic acid) synthesized President Kennedy assassinated (1963) Arab-Israeli War (1967) Martin Luther King assassination (1968) Neil Armstrong walks on the moon (1969) 1970 Discovery of restriction endonucleases by Arber and Smith Discovery of reverse transcriptase in retroviruses by Temin and Baltimore 1973 Ames develops a bacterial assay for the detection of mutagens Salt I Treaty (1972) Cohen, Boyer, Chang, and Helling use plasmid vectors to clone Vietnam War ends (1973) genes in bacteria 1975 Kohler and Milstein develop technique for the production of President Nixon resigns because of Watergate cover-up (1974) monoclonal antibodies Lyme disease discovered 1977 Recognition of archaea as a distinct microbial group by Panama Canal Treaty (1977) Woese and Fox