正在加载图片...
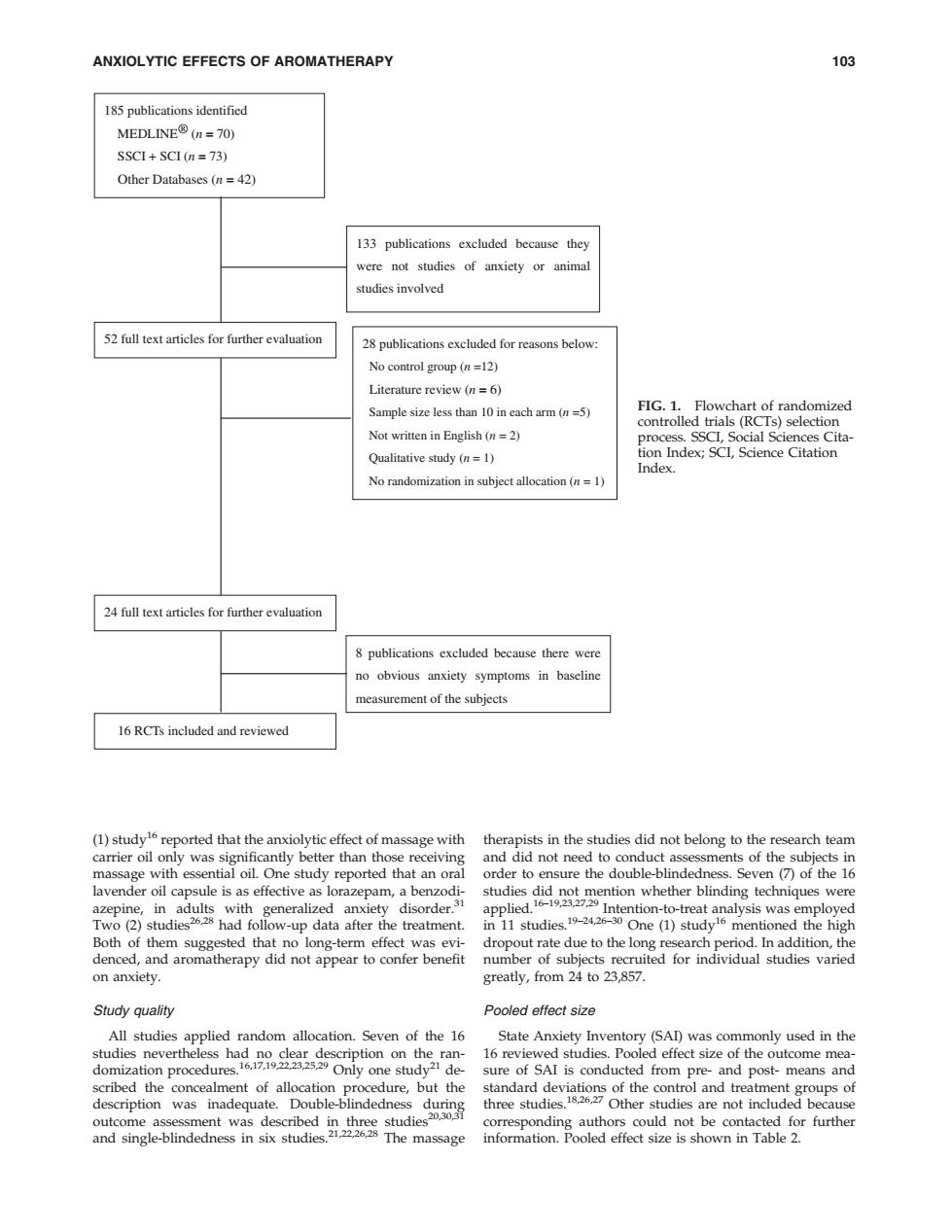
ANXIOLYTIC EFFECTS OF AROMATHERAPY 103 185 publications identified MEDLINE®(I=7O) SSCI+SCI(n=73) Other Databases (n =42) 133 publications excluded because they were not studies of anxiety or animal studies involved 52 full text articles for further evaluation 28 publications excluded for reasons below: No control group(n=12) Literature review (n 6) Sample size less than 10 in each arm (n =5) FIG.1.Flowchart of randomized controlled trials (RCTs)selection Not written in English (n=2) process.SSCI,Social Sciences Cita- Qualitative study (n=1) tion Index;SCI,Science Citation Index. No randomization in subject allocation (n=1) 24 full text articles for further evaluation 8 publications excluded because there were no obvious anxiety symptoms in baseline measurement of the subjects 16 RCTs included and reviewed (1)study16reported that the anxiolytic effect of massage with therapists in the studies did not belong to the research team carrier oil only was significantly better than those receiving and did not need to conduct assessments of the subjects in massage with essential oil.One study reported that an oral order to ensure the double-blindedness.Seven(7)of the 16 lavender oil capsule is as effective as lorazepam,a benzodi- studies did not mention whether blinding techniques were azepine,in adults with generalized anxiety disorder.31 applied Intention-to-treat analysis was employed Two (2)studies had follow-up data after the treatment.in 11 studies.4 One (1)study mentioned the high Both of them suggested that no long-term effect was evi- dropout rate due to the long research period.In addition,the denced,and aromatherapy did not appear to confer benefit number of subjects recruited for individual studies varied on anxiety. greatly,from 24 to 23,857. Study quality Pooled effect size All studies applied random allocation.Seven of the 16 State Anxiety Inventory (SAl)was commonly used in the studies nevertheless had no clear description on the ran- 16 reviewed studies.Pooled effect size of the outcome mea- domization procedures.Only one study de sure of SAI is conducted from pre-and post-means and scribed the concealment of allocation procedure,but the standard deviations of the control and treatment groups of description was inadequate.Double-blindedness during three studies.18,26,27 Other studies are not included because outcome assessment was described in three studies corresponding authors could not be contacted for further and single-blindedness in six studies.21,222628 The massage information.Pooled effect size is shown in Table 2.(1) study16 reported that the anxiolytic effect of massage with carrier oil only was significantly better than those receiving massage with essential oil. One study reported that an oral lavender oil capsule is as effective as lorazepam, a benzodiazepine, in adults with generalized anxiety disorder.31 Two (2) studies26,28 had follow-up data after the treatment. Both of them suggested that no long-term effect was evidenced, and aromatherapy did not appear to confer benefit on anxiety. Study quality All studies applied random allocation. Seven of the 16 studies nevertheless had no clear description on the randomization procedures.16,17,19,22,23,25,29 Only one study21 described the concealment of allocation procedure, but the description was inadequate. Double-blindedness during outcome assessment was described in three studies20,30,31 and single-blindedness in six studies.21,22,26,28 The massage therapists in the studies did not belong to the research team and did not need to conduct assessments of the subjects in order to ensure the double-blindedness. Seven (7) of the 16 studies did not mention whether blinding techniques were applied.16–19,23,27,29 Intention-to-treat analysis was employed in 11 studies.19–24,26–30 One (1) study16 mentioned the high dropout rate due to the long research period. In addition, the number of subjects recruited for individual studies varied greatly, from 24 to 23,857. Pooled effect size State Anxiety Inventory (SAI) was commonly used in the 16 reviewed studies. Pooled effect size of the outcome measure of SAI is conducted from pre- and post- means and standard deviations of the control and treatment groups of three studies.18,26,27 Other studies are not included because corresponding authors could not be contacted for further information. Pooled effect size is shown in Table 2. 185 publications identified MEDLINE® (n = 70) SSCI + SCI (n = 73) Other Databases (n = 42) 133 publications excluded because they were not studies of anxiety or animal studies involved 52 full text articles for further evaluation 16 RCTs included and reviewed 8 publications excluded because there were no obvious anxiety symptoms in baseline measurement of the subjects 24 full text articles for further evaluation 28 publications excluded for reasons below: No control group (n =12) Literature review (n = 6) Sample size less than 10 in each arm (n =5) Not written in English (n = 2) Qualitative study (n = 1) No randomization in subject allocation (n = 1) FIG. 1. Flowchart of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) selection process. SSCI, Social Sciences Citation Index; SCI, Science Citation Index. ANXIOLYTIC EFFECTS OF AROMATHERAPY 103