正在加载图片...
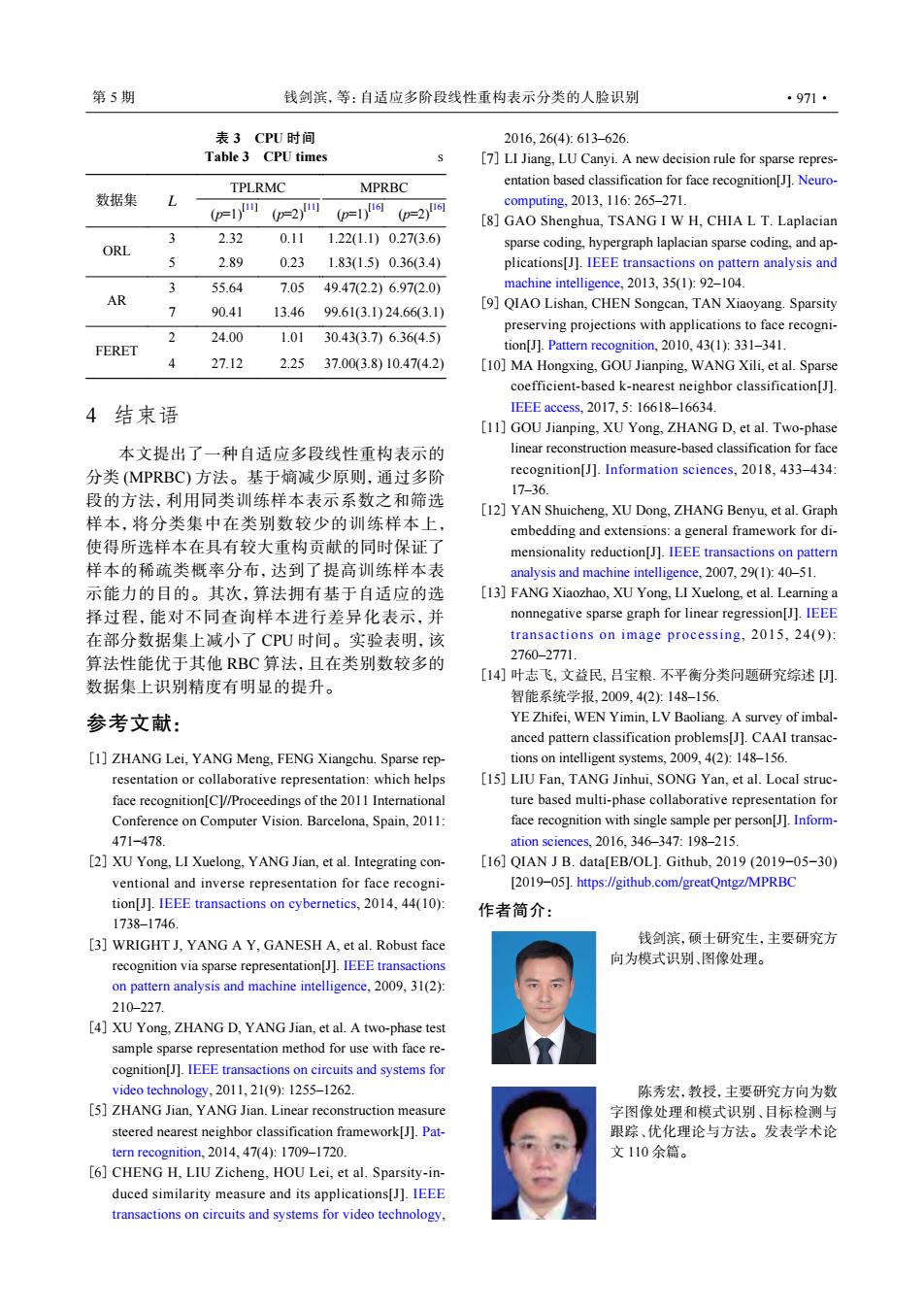
第5期 钱剑滨,等:自适应多阶段线性重构表示分类的人脸识别 ·971· 表3CPU时间 2016,26(4):613-626 Table 3 CPU times [7]LI Jiang,LU Canyi.A new decision rule for sparse repres- TPLRMC MPRBC entation based classification for face recognition[J].Neuro- 数据集 L (=1)m 0p=2m=p=2 computing,2013,116:265-271 [8]GAO Shenghua,TSANG I W H,CHIA L T.Laplacian 3 2.32 0.11 1.22(1.1)0.27(3.6) ORL sparse coding,hypergraph laplacian sparse coding,and ap- 2.89 0.23 1.83(1.5)0.36(3.4) plications[J].IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and 3 55.64 7.05 49.47(2.2)6.97(2.0) machine intelligence,2013,35(1):92-104 AR > 90.41 13.4699.61(3.1)24.66(3.1) [9]QIAO Lishan,CHEN Songcan,TAN Xiaoyang.Sparsity preserving projections with applications to face recogni- 2 24.00 1.01 30.43(3.7)6.36(4.5) FERET tion[J].Pattern recognition,2010,43(1):331-341 1 27.12 2.25 37.00(3.8)10.47(4.2) [10]MA Hongxing,GOU Jianping,WANG Xili,et al.Sparse coefficient-based k-nearest neighbor classification[J]. 4结束语 IEEE access,.2017,5:16618-16634 [11]GOU Jianping,XU Yong,ZHANG D,et al.Two-phase 本文提出了一种自适应多段线性重构表示的 linear reconstruction measure-based classification for face 分类MPRBC)方法。基于熵减少原则,通过多阶 recognition[J].Information sciences,2018,433-434: 17-36. 段的方法,利用同类训练样本表示系数之和筛选 [12]YAN Shuicheng,XU Dong,ZHANG Benyu,et al.Graph 样本,将分类集中在类别数较少的训练样本上, embedding and extensions:a general framework for di- 使得所选样本在具有较大重构贡献的同时保证了 mensionality reduction[J].IEEE transactions on pattern 样本的稀疏类概率分布,达到了提高训练样本表 analysis and machine intelligence,2007,29(1):40-51. 示能力的目的。其次,算法拥有基于自适应的选 [13]FANG Xiaozhao,XU Yong,LI Xuelong,et al.Learning a 择过程,能对不同查询样本进行差异化表示,并 nonnegative sparse graph for linear regression[J].IEEE 在部分数据集上减小了CPU时间。实验表明,该 transactions on image processing,2015,24(9): 算法性能优于其他RBC算法,且在类别数较多的 2760-2771. [14]叶志飞,文益民,吕宝粮.不平衡分类问题研究综述 数据集上识别精度有明显的提升。 智能系统学报,2009,4(2):148-156. 参考文献: YE Zhifei,WEN Yimin,LV Baoliang.A survey of imbal- anced pattern classification problems[J].CAAI transac- [1]ZHANG Lei,YANG Meng,FENG Xiangchu.Sparse rep- tions on intelligent systems,2009,4(2):148-156. resentation or collaborative representation:which helps [15]LIU Fan,TANG Jinhui,SONG Yan,et al.Local struc- face recognition[Cl//Proceedings of the 2011 International ture based multi-phase collaborative representation for Conference on Computer Vision.Barcelona,Spain,2011: face recognition with single sample per person[J].Inform- 471-478 ation sciences.2016,346-347:198-215. [2]XU Yong,LI Xuelong,YANG Jian,et al.Integrating con- [16]QIAN J B.data[EB/OL].Github,2019(2019-05-30) ventional and inverse representation for face recogni- [2019-05].https://github.com/greatQntgz/MPRBC tion[J].IEEE transactions on cybernetics,2014,44(10): 作者简介: 1738-1746 [3]WRIGHT J,YANG A Y,GANESH A,et al.Robust face 钱剑滨,硕士研究生,主要研究方 recognition via sparse representation[J].IEEE transactions 向为模式识别、图像处理。 on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,2009,31(2): 210-227 [4]XU Yong,ZHANG D,YANG Jian,et al.A two-phase test sample sparse representation method for use with face re- cognition[J].IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology,2011,21(9):1255-1262. 陈秀宏,教授,主要研究方向为数 [5]ZHANG Jian,YANG Jian.Linear reconstruction measure 字图像处理和模式识别、目标检测与 steered nearest neighbor classification framework[J].Pat- 跟踪、优化理论与方法。发表学术论 tern recognition,2014,47(4):1709-1720. 文110余篇。 [6]CHENG H,LIU Zicheng,HOU Lei,et al.Sparsity-in- duced similarity measure and its applications[J].IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology,表 3 CPU 时间 Table 3 CPU times s 数据集 L TPLRMC MPRBC (p=1)[11] (p=2)[11] (p=1)[16] (p=2)[16] ORL 3 2.32 0.11 1.22(1.1) 0.27(3.6) 5 2.89 0.23 1.83(1.5) 0.36(3.4) AR 3 55.64 7.05 49.47(2.2) 6.97(2.0) 7 90.41 13.46 99.61(3.1) 24.66(3.1) FERET 2 24.00 1.01 30.43(3.7) 6.36(4.5) 4 27.12 2.25 37.00(3.8) 10.47(4.2) 4 结束语 本文提出了一种自适应多段线性重构表示的 分类 (MPRBC) 方法。基于熵减少原则,通过多阶 段的方法,利用同类训练样本表示系数之和筛选 样本,将分类集中在类别数较少的训练样本上, 使得所选样本在具有较大重构贡献的同时保证了 样本的稀疏类概率分布,达到了提高训练样本表 示能力的目的。其次,算法拥有基于自适应的选 择过程,能对不同查询样本进行差异化表示,并 在部分数据集上减小了 CPU 时间。实验表明,该 算法性能优于其他 RBC 算法,且在类别数较多的 数据集上识别精度有明显的提升。 参考文献: ZHANG Lei, YANG Meng, FENG Xiangchu. Sparse representation or collaborative representation: which helps face recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 471−478. [1] XU Yong, LI Xuelong, YANG Jian, et al. Integrating conventional and inverse representation for face recognition[J]. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2014, 44(10): 1738–1746. [2] WRIGHT J, YANG A Y, GANESH A, et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2009, 31(2): 210–227. [3] XU Yong, ZHANG D, YANG Jian, et al. A two-phase test sample sparse representation method for use with face recognition[J]. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, 2011, 21(9): 1255–1262. [4] ZHANG Jian, YANG Jian. Linear reconstruction measure steered nearest neighbor classification framework[J]. Pattern recognition, 2014, 47(4): 1709–1720. [5] CHENG H, LIU Zicheng, HOU Lei, et al. Sparsity-induced similarity measure and its applications[J]. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, [6] 2016, 26(4): 613–626. LI Jiang, LU Canyi. A new decision rule for sparse representation based classification for face recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2013, 116: 265–271. [7] GAO Shenghua, TSANG I W H, CHIA L T. Laplacian sparse coding, hypergraph laplacian sparse coding, and applications[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 92–104. [8] QIAO Lishan, CHEN Songcan, TAN Xiaoyang. Sparsity preserving projections with applications to face recognition[J]. Pattern recognition, 2010, 43(1): 331–341. [9] MA Hongxing, GOU Jianping, WANG Xili, et al. Sparse coefficient-based k-nearest neighbor classification[J]. IEEE access, 2017, 5: 16618–16634. [10] GOU Jianping, XU Yong, ZHANG D, et al. Two-phase linear reconstruction measure-based classification for face recognition[J]. Information sciences, 2018, 433–434: 17–36. [11] YAN Shuicheng, XU Dong, ZHANG Benyu, et al. Graph embedding and extensions: a general framework for dimensionality reduction[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2007, 29(1): 40–51. [12] FANG Xiaozhao, XU Yong, LI Xuelong, et al. Learning a nonnegative sparse graph for linear regression[J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2015, 24(9): 2760–2771. [13] 叶志飞, 文益民, 吕宝粮. 不平衡分类问题研究综述 [J]. 智能系统学报, 2009, 4(2): 148–156. YE Zhifei, WEN Yimin, LV Baoliang. A survey of imbalanced pattern classification problems[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2009, 4(2): 148–156. [14] LIU Fan, TANG Jinhui, SONG Yan, et al. Local structure based multi-phase collaborative representation for face recognition with single sample per person[J]. Information sciences, 2016, 346–347: 198–215. [15] QIAN J B. data[EB/OL]. Github, 2019 (2019−05−30) [2019−05]. https://github.com/greatQntgz/MPRBC [16] 作者简介: 钱剑滨,硕士研究生,主要研究方 向为模式识别、图像处理。 陈秀宏,教授,主要研究方向为数 字图像处理和模式识别、目标检测与 跟踪、优化理论与方法。发表学术论 文 110 余篇。 第 5 期 钱剑滨,等:自适应多阶段线性重构表示分类的人脸识别 ·971·