正在加载图片...
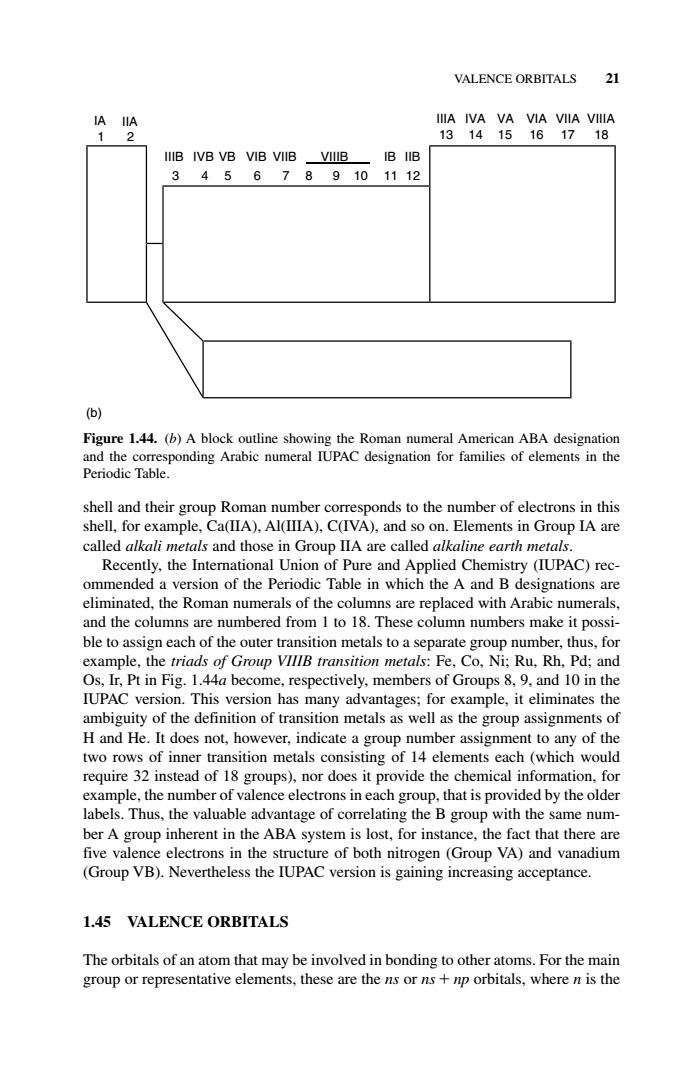
VALENCE ORBITALS 21 IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB-VIIIB IB IIB 3456789101112 ) Figure 1.44.(b)A block outline showing the Roman numeral American ABA designation nPC gai forof e Elements in Group IA are Saes ad those in Group IA are salled Recently,the Interational Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)rec- ommended a version of the Periodic Table in which the A and B designations are eliminated,the Roman numerals of the columns are replaced with Arabic numerals, and the columns are numbered from I to 18.These column numbers make it possi- ble tos ach of the outer transition metak ooo le.the triads of respectively,members of Groups version has many advantages;for example,itin inates the ambiguity of the definition of transition metals as well as the group assignments of H and He.It does not,however,indicate a group number assignment to any of the two rows of inner transition metals consisting of 14 elements each (which would require 32 instead of 18 groups),nor does it provide the chemical information,for example,the number of valence electrons in each group.that is provided by the older labels.Thus,the valuable advantage of correlating the B group with the same num- ber A group inherent in the ABA for insta ce,the e fact that there five val Group VB).Neventheles the TUincrein aan 1.45 VALENCE ORBITALS The orbitals of an atom that may be involved in bonding to other atoms.For the main group or representative elem nts these are the e ns or ns+np orbitals,where n is theVALENCE ORBITALS 21 shell and their group Roman number corresponds to the number of electrons in this shell, for example, Ca(IIA), Al(IIIA), C(IVA), and so on. Elements in Group IA are called alkali metals and those in Group IIA are called alkaline earth metals. Recently, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommended a version of the Periodic Table in which the A and B designations are eliminated, the Roman numerals of the columns are replaced with Arabic numerals, and the columns are numbered from 1 to 18. These column numbers make it possible to assign each of the outer transition metals to a separate group number, thus, for example, the triads of Group VIIIB transition metals: Fe, Co, Ni; Ru, Rh, Pd; and Os, Ir, Pt in Fig. 1.44a become, respectively, members of Groups 8, 9, and 10 in the IUPAC version. This version has many advantages; for example, it eliminates the ambiguity of the definition of transition metals as well as the group assignments of H and He. It does not, however, indicate a group number assignment to any of the two rows of inner transition metals consisting of 14 elements each (which would require 32 instead of 18 groups), nor does it provide the chemical information, for example, the number of valence electrons in each group, that is provided by the older labels. Thus, the valuable advantage of correlating the B group with the same number A group inherent in the ABA system is lost, for instance, the fact that there are five valence electrons in the structure of both nitrogen (Group VA) and vanadium (Group VB). Nevertheless the IUPAC version is gaining increasing acceptance. 1.45 VALENCE ORBITALS The orbitals of an atom that may be involved in bonding to other atoms. For the main group or representative elements, these are the ns or ns np orbitals, where n is the 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 IIA (b) IA IIIB IIIA IVB IVA VB VA VIB VIA VIIB VIIA VIIIB VIIIA IB IIB Figure 1.44. (b) A block outline showing the Roman numeral American ABA designation and the corresponding Arabic numeral IUPAC designation for families of elements in the Periodic Table. c01.qxd 5/17/2005 5:12 PM Page 21