正在加载图片...
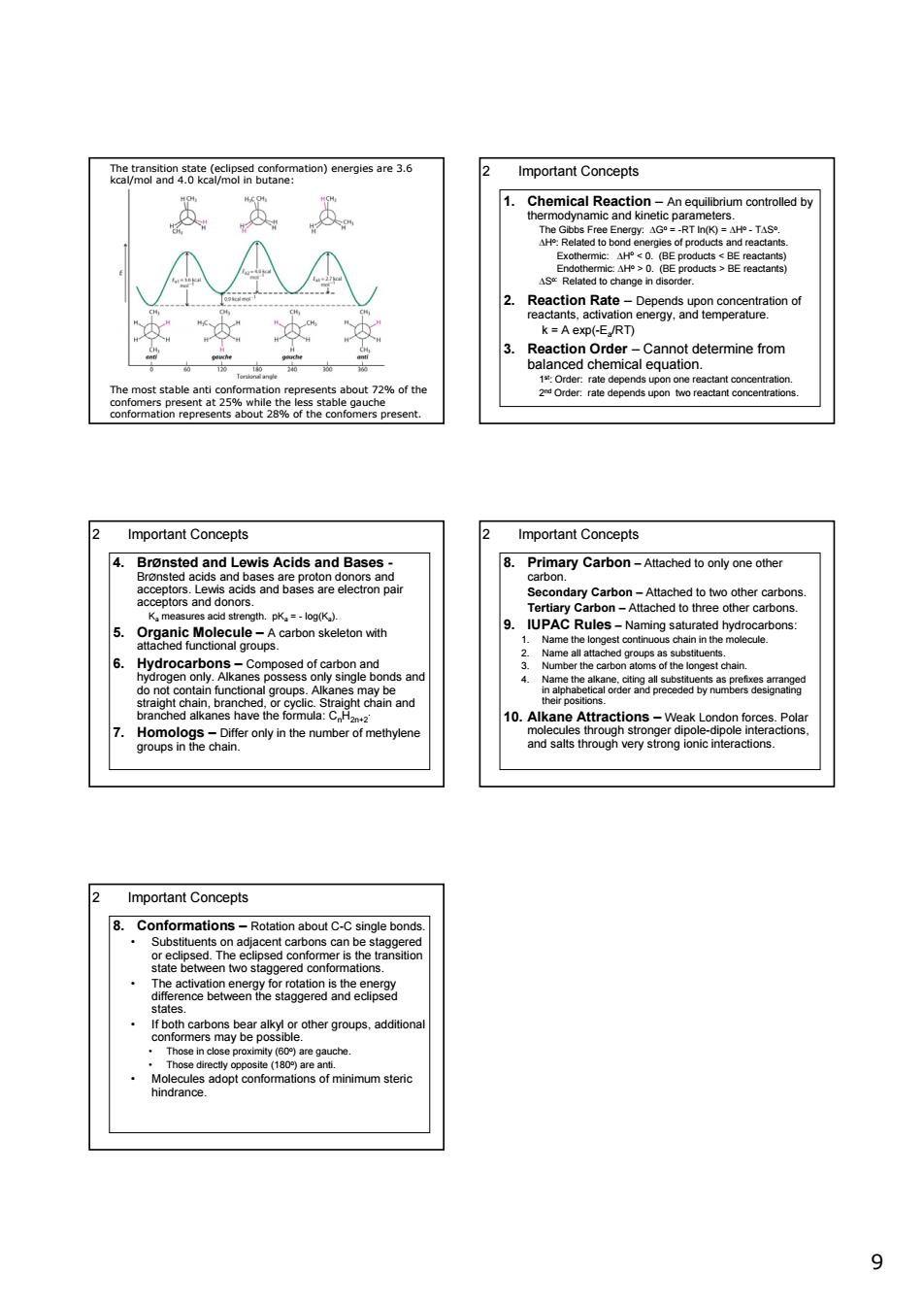
ymen4g5ematoa)enegesae36 2 Important Concepts 下SamicalReastoneictaatsmcomtoeay AAA 2. Ractnaeoabeotgaoegeno 2 Important Concepts Important Concepts wis Acids and Pmaycabon-Aaeetonyoneoe dan Carhon d to two other c TUPAC Rules- d to thre nds an ctions- 2 Important Concepts .Co C-C wo st 9 9 The transition state (eclipsed conformation) energies are 3.6 kcal/mol and 4.0 kcal/mol in butane: The most stable anti conformation represents about 72% of the confomers present at 25% while the less stable gauche conformation represents about 28% of the confomers present. 2 Important Concepts 1. Chemical Reaction – An equilibrium controlled by thermodynamic and kinetic parameters. The Gibbs Free Energy: ΔGo = -RT ln(K) = ΔHo - TΔSo. ΔHo: Related to bond energies of products and reactants. Exothermic: ΔHo < 0. (BE products < BE reactants) Endothermic: ΔHo > 0. (BE products > BE reactants) ΔSo: Related to change in disorder. 2. Reaction Rate – Depends upon concentration of reactants, activation energy, and temperature. k = A exp(-Ea/RT) 3. Reaction Order – Cannot determine from balanced chemical equation. 1st: Order: rate depends upon one reactant concentration. 2nd Order: rate depends upon two reactant concentrations. 2 Important Concepts 4. BrØnsted and Lewis Acids and Bases - BrØnsted acids and bases are proton donors and acceptors. Lewis acids and bases are electron pair acceptors and donors. Ka measures acid strength. pKa = - log(Ka). 5. Organic Molecule – A carbon skeleton with attached functional groups. 6. Hydrocarbons – Composed of carbon and hydrogen only. Alkanes possess only single bonds and do not contain functional groups. Alkanes may be straight chain, branched, or cyclic. Straight chain and branched alkanes have the formula: CnH2n+2. 7. Homologs – Differ only in the number of methylene groups in the chain. 2 Important Concepts 8. Primary Carbon – Attached to only one other carbon. Secondary Carbon – Attached to two other carbons. Tertiary Carbon – Attached to three other carbons. 9. IUPAC Rules – Naming saturated hydrocarbons: 1. Name the longest continuous chain in the molecule. 2. Name all attached groups as substituents. 3. Number the carbon atoms of the longest chain. 4. Name the alkane, citing all substituents as prefixes arranged in alphabetical order and preceded by numbers designating their positions. 10. Alkane Attractions – Weak London forces. Polar molecules through stronger dipole-dipole interactions, and salts through very strong ionic interactions. 2 Important Concepts 8. Conformations – Rotation about C-C single bonds. • Substituents on adjacent carbons can be staggered or eclipsed. The eclipsed conformer is the transition state between two staggered conformations. • The activation energy for rotation is the energy difference between the staggered and eclipsed states. • If both carbons bear alkyl or other groups, additional conformers may be possible. • Those in close proximity (60o) are gauche. • Those directly opposite (180o) are anti. • Molecules adopt conformations of minimum steric hindrance